Moulage
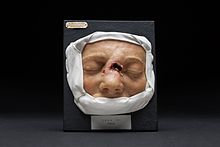
Moulages are colored, three-dimensional and life-size impressions of body parts for the natural reproduction of human diseases. The word comes from the French mouler ('form', 'molding') or moule ('casting form') and, via old French modle, from the Latin modulus and is related to the German model .
Up until the 1950s, pathological findings were plastic-reproduced in medicine , especially in dermatology and venereology , for teaching purposes and for disease documentation. The first moulages were made in the middle of the 19th century. Since the first International Congress on Skin and Venereal Diseases in 1889 in the Musée des Moulages at the Hôpital St. Louis in Paris, moulages have been regarded as the ideal teaching aids in dermatological university teaching.
For this purpose, impressions, for example made of plaster of paris, and later also made of silicone, were taken and filled with a wax or wax-resin mixture. The raw models were then removed from the impression mold after hardening and painted directly on the patient. In this way, moulages or pictures of them have been preserved to this day, which are almost identical to an original finding.
Moulages were not only used as an aid in the lecture. They were templates for high-quality, yet inexpensive color prints (citochromy technique) in atlases and textbooks, but also in scientific publications. Moulages of sexually transmitted diseases were shown in public to educate and deter.
After the three-dimensional life-size wax objects were almost forgotten by color photography in the second half of the 20th century, they have been rediscovered in recent years. Today they are valued as valuable medical-historical documents, some of which show diseases that hardly exist or no longer exist in this form today (e.g. late forms of syphilis , skin tuberculosis , smallpox ). Well-preserved collections have regained importance in teaching and are used by medical students to prepare for the state examination. In the dermatological clinic of the University Hospital Zurich, the introductory course in the special subject of skin and venereal diseases has been taking place in the Moulage Museum for several years.
Important moulage collections
There were or are important moulage collections especially in (alphabetical list):
| place | Institute | Compilation | Number and type of moulages | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens | Andreas Syngros Hospital | from 1912 (under Georgios Fotinos ) | 1660: Skin and sexually transmitted diseases | modeled on the Paris Hôpital Saint-Louis |
| Berlin | Berlin Medical History Museum of the Charité | from approx. 1900? | 257 (including eye moulages by Berlin mouleur Fritz Kolbow from the Greeff collection) | z. T. (since 2007) exhibited in the permanent exhibition "On the trail of life" |
| Wroclaw | Dermatological University Clinic in Wroclaw | from 1890 (under Neisser) | once 2700, today 313 (especially tuberculosis ), as well as eight specimens from Castan's Panoptikum | inspired by the Parisian moulages by Jules Baretta; As an important German-speaking skin center, gave the impetus for many other German-speaking collections; Today there are more “Breslau” moulages (by Alfons Kröner) in Kiel than in Breslau |
| Dresden | Dresden-Friedrichstadt Hospital (and German Hygiene Museum ): "Friedrichstädter Moulagensammlung" | from 1903 (under Johannes Werther ) | once 368, today 60 | relatively bad state of preservation; 18 are now in the collection of the Hygiene Museum, and some better-preserved exhibits are on display there |
| Dresden | German Hygiene Museum | approx. 2000 | Most of them can be viewed on the Internet (www.dhmd.de/neu) | |
| gain | Erlangen Dermatology Clinic at the University of Erlangen | 1923–1945 (under Leo Hauck ) | 136 | The moulage collection in Erlangen was built up by Leonhard Hauck , who in 1906 became senior physician in the new department for skin diseases at the Erlangen Medical Clinic. |
| Freiburg in Breisgau | University Clinic and Museum ("Uniseum") of the University of Freiburg : "Freiburg Moulagensammlung" | 1899 (under Eduard Jacobi , later Georg Alexander Rost and Alfred Stühmer ) - 1957 | once 1200, today 822 (especially venereal diseases such as syphilis) | Jacobi was a volunteer in Breslau under Neissen (see Kiel) for two years before he became the first director in Freiburg in 1899; later published "Atlases of Skin Diseases" (editions from 1903 to 1942, also in translations) with moulages, especially by Alfons Kröner, known as a textbook Today around 100 moulages in the clinic's seminar room, 32 in the Uniseum, the rest in the basement of the lecture hall |
| Goettingen | Originally Göttingen Dermatology Clinic, since 1993 Department of Ethics and History of Medicine at the University of Göttingen | Skin diseases, with a focus on sexually transmitted diseases | first publicly exhibited in autumn 2007 in the Göttingen Municipal Museum | |
| Hamburg | Medical history museum at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf | The collection is essentially composed of two parts. On the one hand it consists of moulages, which originally belonged to the AK St. Georg in Hamburg and which go back to a collection of the dermatologist Oscar Lassar . On the other hand, it is formed by the moulage collection of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf itself, which the dermatologist Paul Mulzer (1880–1947) created. | There are 598 moulages of different production times and origins. | One of the moulages belonging to the collection showing tuberculids is shown on the website of the Medical History Museum . |
| Kiel | University Dermatology Clinic Kiel | from 1906 (under Viktor Klingmüller) | 455 (skin diseases, especially venereal diseases) | Klingmüller, who trained in Breslau, brought the basis of the collection with him as early as 1906; thanks to his continued collecting activity, today 354 moulages originating from Wroclaw |
| Madrid | San Juan de Dios Hospital | from 1870 (until before 1966) | approx. 850 (mainly skin diseases) | color catalog from 2006 |
| Mannheim | Panoptikum Mannheim | around 1890 | approx. 80-90 | partly from the workshop of Louis and Gustav Castan, special are the 4 full-body moulages which, among other things, depict pregnant women and caesarean sections. |
| Paris | Hôpital St. Louis | from 1865 (Moulageur Pierre Jules Francois Baretta, 1834–1923) - 1950s | Today over 4000 (the world's largest and most important collection, including up to 2000 by Baretta; skin diseases, surgery and gynecology) | Paris was an important impetus for many European collections and the technique of moulage production; Collection exhibited in the meeting room of the hospital since 1885 |
| Rostock | Rostock Dermatology Clinic | from 1902 | until 1942 approx. 3000, of which 122 have been preserved. 34 moulages were made in Rostock, the rest in the Dresden Hygiene Museum. | In 1902 the University Dermatology Clinic was founded in Rostock and the newly established chair for dermatology was occupied by Maximilian Wolters . Wolters laid the foundation stone for the Rostock moulage collection, which was almost completely destroyed in 1942. |
| Temple ( Texas ) | Scott & White Memorial Hospital | 1934–1955 (under Ken and Margeret Philips) | once over 3000, today 1200-1300 (mainly pathological-surgical) | issued in the Department of Anatomical Pathology; Viewing after registration |
| Tübingen | University Dermatology Clinic Tübingen and Museum of the University of Tübingen MUT | the "wax body" collection is made up of two parts: moulages been since the 19th century center of the Department of Dermatology, since the early 20th century by the.. Tropenklinik Paul Lechler Hospital of for Medical Mission (Difäm) German Institute acquired | a total of almost 300 moulages, two thirds from dermatological and one third from tropical medicine stocks | extremely rare tropical diseases with disease stages that are currently extinct; extensive dermatological fund ; Collection is Practice Seminar Exhibition inventoried by the Museum of the University of Tuebingen MUT in the winter semester 2015/16 and scientifically developed, from June 2016 Exhibition "illness as an art (form): plaster casts of medicine" in the Museum Schloss height Tübingen |
| Vienna | Federal Pathological-Anatomical Museum of the Natural History Museum Vienna in the Narrenturm | Objects by Carl Henning, among others | ||
| Zurich | Moulage Museum | from 1918 (under Bruno Bloch) - 1948 | 1800 were produced and have been preserved (including human and animal experiments, e.g. consequences of X-ray therapy); today 1200 skin diseases and 600 surgical ones | consists almost entirely of locally made moulages; generally in very good condition; 600 exhibited in the museum |
Web links
- Archive for medical wax pictures
- Moulage Museum of the University of Zurich
- Moulage collection of the University Dermatology Clinic Kiel
- Berlin Medical History Museum Berlin
- Atlas of skin diseases (E. Jacobi, 5th edition 1913) with photos of moulages
- Supplies from overseas , explanations about the moulage collection of the University Clinic Hamburg-Eppendorf at Monumente Online
- University collections in Germany with moulages (database of university museums and collections in Germany)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wachsmoulage from the collection "wax body" of the Museum of the University of Tuebingen MUT Eberhard Karls University Tübingen
- ↑ Benedikt Ignatzek: From the history of dermatology. In: Würzburg medical history reports. Volume 23, 2004, pp. 524-527; here: p. 526.
- ↑ Thomas Schnalke : Moulagen. In: Werner E. Gerabek , Bernhard D. Haage, Gundolf Keil , Wolfgang Wegner (eds.): Enzyklopädie Medizingeschichte. De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2005, ISBN 3-11-015714-4 , p. 1012 f.
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Andreas Sygros Hospital in Athens ( Memento of the original from April 28, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Berlin Medical History Museum of the Charité ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ a b c d Moulage collection: Moulages by Alfons Kröner on the website of the Kiel University Dermatology Clinic
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Friedrichstadt hospital in Dresden ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ The moulage collection of the German Hygiene Museum in Dresden ( Memento of the original from April 28, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ The moulage collection of the University Dermatology Clinic Erlangen ( Memento of the original from November 26, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010), Hornstein, Otto P .: Chronicle of the dermatological university clinic Erlangen. A "provisional" celebrates its 70th anniversary , Erlangen, 1993
- ↑ The moulage collection of the University Dermatology Clinic Freiburg ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Ethics and History of Medicine department of the University of Göttingen ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Museum Olavide in Madrid / Spain ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ Heise, Helmut; Bad, K .; Zimmermann, R .: The Rostock Moulagen Collection, in: Der Hautarzt , Volume 53 (2002), pp. 347–351
- ↑ The moulage collection of the Scott & White Memorial Hospital in Temple / USA, Texas ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. on the pages of the archive for medical wax images (moulages) of the Charité (accessed November 21, 2010)
- ↑ Strölin, Anke: wax body. Moulagensammlung , in: Seidl, Ernst (ed.): Collections. Museum of the University of Tübingen MUT , p. 63, 4th expanded and supplemented edition (2015)
- ↑ Felix Czeike (Ed.): Henning, Karl. In: Historisches Lexikon Wien . Volume 3, Kremayr & Scheriau, Vienna 1994, ISBN 3-218-00545-0 , p. 143 ( digitized version ).
- ↑ UZH - Moulage Museum - Moulages. In: moulagen.uzh.ch. Retrieved April 8, 2014 .