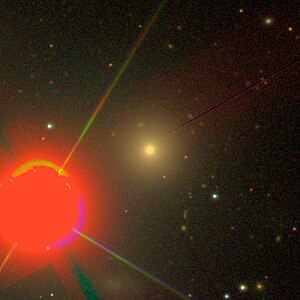
NGC 3636
| Galaxy NGC 3636 |
|
|---|---|
|
|
| SDSS recording | |
| AladinLite | |
| Constellation | cups |
|
Position equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|
| Right ascension | 11 h 20 m 25.0 s |
| declination | -10 ° 16 ′ 54 ″ |
| Appearance | |
| Morphological type | E0 |
| Brightness (visual) | 12.4 mag |
| Brightness (B-band) | 13.4 mag |
| Angular expansion | 1.3 ′ × 1.3 ′ |
| Surface brightness | 13.0 mag / arcmin² |
| Physical data | |
| Affiliation | LGG 235 |
| Redshift | 0.005807 ± 0.000043 |
| Radial velocity | (1741 ± 13) km / s |
|
Stroke distance v rad / H 0 |
(71 ± 5) · 10 6 ly (21.7 ± 1.5) Mpc |
| history | |
| discovery | William Herschel |
| Discovery date | March 4, 1786 |
| Catalog names | |
| NGC 3636 • PGC 34709 • MCG -02-29-019 • GC 2383 • H II 550 • h 862 • | |
NGC 3636 is an elliptical galaxy of Hubble type E0 in the constellation cup of the south celestial equator , an estimated 71 million light-years from the Milky Way 's center. Together with two other galaxies, it forms the NGC 3672 group or LGG 235 .
The object was discovered on March 4, 1786 by the German-British astronomer and musician William Herschel .