Prosopis
| Prosopis | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Prosopis alba , habitus |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Prosopis | ||||||||||||
| L. |
Prosopis is a genus in the subfamily of the mimosa plants (Mimosoideae) within the family of the Leguminosae (Fabaceae). They are plants ( xerophytes ) thatare very well adapted to dry locations. The common German names Süßhülsenbaum or Mesquitebaum (from nahuatl : mizquitl ) are also used.
description
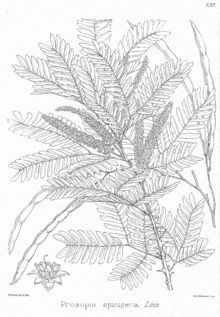



Appearance and leaves
Prosopis species grow as trees or shrubs , rarely semi-shrubs and reach very different heights. You have deep roots. Some Prosopis species have thorns 4 to 75 millimeters long ; some of them are tough enough to pierce the soles of shoes or car tires. The thorns are reshaped branches or stipules.
The stalked leaves are arranged alternately on the branches, are double-pinnate and vary in size and shape depending on the species. There are one or two first-order partial leaves. The number of leaflets varies from a few to many pairs, depending on the species. The leaves of some species have adaptations to drought. Stipules are absent, small, or transformed into thorns.
Inflorescences and flowers
They form lateral, mostly cylindrical racemose or spherical inflorescences .
The small, hermaphrodite flowers are five-fold with a double flower envelope (perianth). The five sepals are fused and the calyx teeth are only short. The five petals are fused to the middle. There are ten free stamens . The ovaries can stand on a stem. There are many ovules in the single carpel . The pollination is done by insects.
Fruits and seeds
The elongated, thick or flattened, straight or sickle-shaped legumes do not open when ripe and have a spongy mesocarp . The seeds are egg-shaped and flattened.
Ingredients and chromosome numbers
The occurrence of 4-hydroxypipecolic acid in leaves and seeds is considered a generic chemotaxonomic characteristic . The number of chromosomes is usually 2n = 28.
ecology
Prosopis species are extremely well adapted to the dry climatic conditions of their habitat. In their homeland they are seen by many farmers as " waste wood " because they compete with the grasses of the steppe for moisture. Destroying the shrubs is difficult, however, because they can reproduce vegetatively from root remains in the ground and are resistant to various herbicides . The plants grow extremely quickly and can also thrive where other plants have no livelihood.






Systematics and distribution
The main distribution of the genus Prosopis is the Neotropis from western North America to Patagonia , it is particularly diverse in Argentina . It can also be found in Africa and the Middle East .
The genus Prosopis was established in 1767 by Carl von Linné in Systema Naturae , 12th edition, 2, pp. 282, 293. The type species is Prosopis spicigera L. , today a synonym for Prosopis cineraria (L.) Druce . The genus Prosopis belongs to the tribe Mimoseae in the subfamily Mimosoideae within the family of Fabaceae . Synonyms for Prosopis L. are Lagonychium M.Bieb. , Sopropis Britton & Rose , Strombocarpa (Benth.) A. Gray .
The genus Prosopis is divided into five sections:
- Algarobia section : it contains about 30 species.
- Section anonychium : It contains only the only African, thornless species Prosopis africana .
- Section Monilicarpa Ruiz Leal ex Burkart : it contains only one species.
- Prosopis section : The only three Asian species have spines similar to the rose species ( Rosa ).
- Strombocarpa Benth Section . : The nine or so species have stipules that have been transformed into thorns and closed, twisted legumes.
There are around 45 species of prosopis :
- Prosopis abbreviata Benth. : The home is Argentina .
- Prosopis affinis Spreng. : It iswidespreadin Argentina, Brazil (only in Rio Grande do Sul ), Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay.
- Prosopis africana (Guill. & Perr.) Taub. : It iswidespreadin tropical Africa and Saudi Arabia .
- Prosopis alba Griseb. : It is native to Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay and Peru. It thrives in the Gran Chaco and is called "Algarrobo Blanco" there.
- Prosopis alpataco Phil .: The original range in Argentina and Chile is not exactly known. It is an invasive plant in some areas.
- Prosopis argentina Burkart : It occurs in the Argentine provinces of Catamarca, La Rioja, Mendoza and San Juan.
- Prosopis articulata S. Watson : The range extends from Arizona to Baja California and Sonora .
- Prosopis burkartii O.Muniz : The homeland is the Chilean Tarapaca.
- Prosopis caldenia Burkart : It occurs in Argentina.
- Prosopis calingastana Burkart : The original home is in the Argentine Andes .
- Prosopis campestris Griseb. : The original home is in the Argentine Córdoba and San Luis.
- Prosopis castellanosii Burkart : The original homeland is in Mendoza and Neuquen, Argentina.
- Prosopis chilensis (Molina) Stuntz : It is native to Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru and is called "Algarrobo Chileno" in Chile. It is a neophyte in many areas of the world.
- Prosopis cineraria (L.) Druce , Syn .: Mimosa cineraria L. , Prosopis spicigera L .: It thrives in India e.g. B. in the Thar desert, in western Pakistan , Afghanistan , Iran and on the Arabia .
- Prosopis denudans Benth. : It occurs in Argentina.
- Prosopis elata (Burkart) Burkart : Home is Argentina and Paraguay.
- Prosopis farcta (Sol. Ex Russell) JFMacbr. : Areas are located in western Pakistan , Afghanistan , Asia Minor , the Arabian Peninsula, Cyprus , the Caucasus and Central Asia .
- Prosopis ferox Griseb. : The home is Argentina and Bolivia.
- Prosopis fiebrigii Harms : Home is Argentina and Paraguay.
- Prosopis flexulosa DC. : The homeland is Argentina, Bolivia and Chile and is called "Algarrobo Amarillo" there.
- Honey mesquite ( Prosopis glandulosa Torr. ): The distribution area extends from the central USA to southern Mexico.
- Prosopis hassleri Harms : The home is Argentina and Paraguay and is called "Algarrobo del Chaco" or "Algarrobo Paraguayo" there.
- Prosopis humilis Hook. : It occurs in Argentina.
- Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC. : The wide distribution area stretches from Mexico to Peru and there it is called "Bayahonda" and also "Algarrobo Colorado".
- Prosopis koelziana Burkart : The home is in Iran, Saudi Arabia and South Yemen .
- Prosopis kuntzei Kuntze : The homeland is Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay.
- Prosopis laevigata (Willd.) MCJohnst. : The wide distribution area extends from Texas to Mexico and from Bolivia to Peru and Argentina.
- Prosopis nigra (Griseb.) Hieron. : The wide distribution area extends from Bolivia via Paraguay and Uruguay to Argentina. It is called "Algarrobo Negro" in South America.
- Prosopis pallida (Willd.) Kunth ( Syn .: Prosopis limensis ): The original homeland is in Bolivia (only Chuquisaca), Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. It is an invasive plant in some areas. It is called in Spanish "Algarrobo", "Huarango" in Peru and "Mesquite" and in Hawaii "Kiawe".
- Prosopis palmeri S. Watson : It is originally endemic to southern Lower California. But today it also occurs in other areas.
- Screw Bean Mesquite ( Prosopis pubescens Benth. , Syn .: Strombocarpa pubescens (Benth.) A.Gray ): It is in western New Mexico, Texas, Arizona, southern California, southern Nevada, southwestern Utah, Baja California, Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Sonora home.
- Prosopis pugionata Burkart : The exact homeland in Argentina is not known.
- Prosopis reptans Benth. : Areas in Texas and the Mexican states of Nuevo Leon, San Luis Potosi, Tamaulipas, as well as Peruvian Huancavelica and Argentina are known.
- Prosopis rojasiana Burkart : The original home is only Chaco in Paraguay. Today it can also be found in other areas.
- Prosopis rubriflora Hassl. : The distribution area is probably Brazil and Paraguay.
- Prosopis ruizlealii Burkart : The original home is only Mendoza and Neuquen in Argentina. Today it can also be found in other areas.
- Prosopis ruscifolia Griseb. : The wide distribution area extends from northeastern Brazil through eastern Bolivia and western Paraguay to Argentina.
- Prosopis sericantha Hook. : It occurs in Argentina.
- Creeping Mesquite ( Prosopis strombulifera (Lam.) Benth. ): Home is Argentina and northern Peru.
- Tamarugo ( Prosopis tamarugo Phil. ): The homeland is northern Chile.
- Prosopis tamaulipana Burkart : It is common in Mexico.
- Prosopis torquata (Lag.) DC. : It occurs in Argentina.
- Velvet mesquite ( Prosopis velutina Wooton ): It occurs in Arizona , New Mexico and the Mexican state of Sonora .
- Prosopis vinalillo stucco. : It occurs in Arizona , New Mexico and the Mexican state of Sonora .
use
The wood is very hard and can be used to make furniture or as firewood. It is popular as a fire base for barbecues , where it gives the meat a special touch.
The beans of the mesquite tree can be dried and made into flour, which is used as a base for jellies and as a spice. The fermented beans also provide the basis for mesquite wine .
literature
- SI Ali: Mimosaceae in the Flora of Pakistan : Prosopis - Online. (Section description)
- AD Burghardt, SM Espert: Phylogeny of Prosopis (Leguminosae) as shown by morphological and biochemical evidence , In: Austral. Syst. Bot. , Volume 20, 2007, pp. 332-339.
Individual evidence
- ^ R. Hegnauer: Chemotaxonomie der Pflanzen , Volume 11a Leguminosae , Birkhäuser 1994. ISBN 3-7643-5165-9 .
- ^ Arturo Burkart: A monograph of the genus Prosopis , In: Journal of the Arnold Arboretum , 57, 1976, pp. 219–249 / pp. 450–525.
- ^ Prosopis at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- ^ A b Prosopis in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ↑ Data sheet at International Legume Database Information Service = ILDIS - LegumeWeb - World Database of Legumes , Version 10.38 from July 20, 2010.
Web links
- Information about the neotropical species. (English)
- Identification aid for selected species. (English; PDF file; 507 kB)
- Common names and habitats in the Global Invasive Species Database . (English)