Tokyo (city)
| Tōkyō-shi (incorporated) 東京 市 |
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Geographical location in Japan | ||
| Region : | Kanto | |
| Prefecture : | Tokyo | |
| Coordinates : | 35 ° 41 ' N , 139 ° 46' E | |
| Basic data | ||
| Incorporated on: | Jul 1, 1943 | |
| Incorporated in: | Tokyo Districts / Tokyo Prefecture | |
| Surface: | ||
| Residents : | 6,778,804 (October 1, 1940) |
|
| Symbols | ||
| Flag / coat of arms: | ||
| town hall | ||
| Address : |
Tōkyō City Hall 2 Yūrakuchō Kōjimachi-ku , Tōkyō -shi Tōkyō |
|
Tokyo ( Japanese 東京 市 , Tōkyō- shi ) was a Japanese city in the old Tokyo Prefecture ( 東京 府 , Tōkyō-fu ). It existed from May 1, 1889 to July 1, 1943, when it merged with the old to the new Tokyo Prefecture ( 東京 都 , Tōkyō-to ). Today's 23 districts (collectively referred to as Tokyo ) correspond to this historic Tokyo.
The term Tokyo city is often used today to refer to these 23 districts collectively. Since these do not share a common mayor or city council, they also do not form a city administratively. The districts are almost independent cities under partial administration by the prefecture.
history


In 1867, the Shogun Tokugawa Yoshinobu resigned and restored the imperial rule. In the following year, the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate , the city of Edo , was renamed the seat of the new government and Tokyo (literally: eastern capital ). Shortly thereafter, the old Tokyo ( -fu ) prefecture was founded. The prefecture originally consisted only of the city, but was quickly enlarged to its present size.
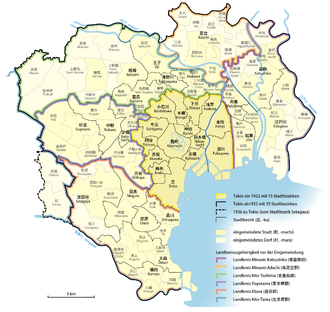
In 1878 the prefecture consisted of 15 Ku (districts) and 6 Gun (districts). These boroughs that arose on the soil of ancient Edo were:
- Kōjimachi (today: Chiyoda )
- Kyōbashi (today: Chūō )
- Kanda (today: Chiyoda)
- Nihonbashi (today: Chūō)
- Fukagawa (today: Kōtō )
- Honjo (today: Sumida )
- Asakusa (today: Taitō )
- Shitaya (today: Taitō)
- Hongō (today: Bunkyō )
- Koishikawa (today: Bunkyō)
- Ushigome (today: Shinjuku )
- Yotsuya (today: Shinjuku)
- Akasaka (today: Minato )
- Azabu (today: Minato)
- Shiba (today: Minato)
With the community reform of 1889, in the communities to Mura (villages), Chō (small towns) or Shi (large cities) were appointed, the appointment to Shi took place . However, the city remained dependent on the prefecture as the prefectural governor was also mayor. From 1898 the mayor was elected independently.
In 1932, 82 communities from five districts were incorporated into the city of Tokyo, the expanded urban area was also known as Dai-Tōkyō ( 大 東京 ), "Greater Tokyo". The area of the city of Tokyo grew from 80.5 to 478.6 km², the population from around 2.1 to 5.4 million (population from 1933). The incorporated area was divided into 20 new city districts:
- Jōtō (today: Kōtō)
- Mukōjima (today: Sumida)
- Arakawa
- Takinokawa (today: day care center )
- Toshima
- Yodobashi (today: Shinjuku )
- Shibuya
- Meguro
- Shinagawa
- Ebara (today: Shinagawa)
- Edogawa
- Katsushika
- Adachi
- Ōji (today: day care center)
- Itabashi (today: Itabashi and Nerima )
- Nakano
- Suginami
- Setagaya
- Ōmori (today: Ōta )
- Kamata (today: Ōta)
In 1936 two more parishes were incorporated and added to the Setagaya district. After that, the urban area corresponded to that of the later 23 districts, apart from minor border corrections and the reclamation of new land.
In 1943 the Tōkyō-tosei was enacted: City of Tokyo and the old Tokyo prefecture to form the new Tokyo ( -to ) prefecture . The boroughs were administered directly by the prefecture and the city of Tokyo ceased to exist.
A prefectural reform took place in 1947, giving Tokyo the same status as other prefectures while maintaining its name (- to instead of the usual -ken ) and special jurisdiction over the Tokyo metropolitan area. The number of districts has been reduced to 22. Each of them received a status comparable to a city.
Nerima was split off from Itabashi in 1947 and became the 23rd district.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Tokubetsu-ku kyōgikai ("Joint Conference of Special Districts", an association of the 23 districts of Tokyo): 特別 区 の 区域 の 沿革 に つ い て (PDF; 532 kB), p. 6