Chalcone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Chalcone, ( E ) -isomer | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chalcone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 12 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
pale yellow prisms |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 208.26 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.07 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
346.5 ° C (mixture) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
14 m Pa (25 ° C) (mixture) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Chalcone is an aromatic unsaturated ketone that forms the basic substance of many important biologically active compounds, the so-called chalcones . The substance exists in two different isomers , which differ in their configuration with regard to the double bond.
Manufacturing
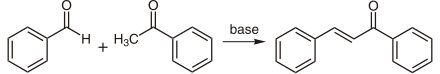
Chalcone can be made from benzaldehyde , acetophenone, and a base such as sodium hydroxide by aldol condensation .
use
Chalcone is used in perfumery . Derivatives with hydroxyl groups and halogens in the benzene nuclei have a bacteriostatic effect . Dihydro-chalcone derivatives of naringin and neohesperidin have a sweetener character (see Neohesperidin-dihydrochalcone ). Dihydrochalcones occur as ingredients in plants.
Derivatives
Chalcone can be substituted in several positions. For example, isoliquiritigenin , a natural product , is hydroxylated at positions 2 ', 4' and 4 . The xanthohumol found in hops ( Humulus lupulus ) is a multiply substituted chalcone. The hydroxylated chalcones also include robtein , butein and pedicin .
Locants at chalconies
Xanthohumol is a bitter substance from hops
See also
- Anthocyanins: properties
- Anthocyanins: biosynthesis
- Flavonoids: biosynthesis
- Mosses: Ingredients
- Phlorizin
- Cinnamic acid: biosynthesis
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on chalcone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on (E) -Chalcones in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Chalcones in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ a b Datasheet 1,3-Diphenyl-2-propenone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ US Army Armament Research & Development Command , Chemical Systems Laboratory, NIOSH Exchange Chemicals. Vol. NX # 04476
- ^ National Academy of Sciences , National Research Council, Chemical-Biological Coordination Center, Review. Vol. 5, p. 28, 1953.
- ↑ José A. González, Ana Estévez-Braun: Effect of (E) -Chalcone on Potato-Cyst Nematodes (Globodera pallida and G. rostochiensis). In: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry . 46, 1998, p. 1163, doi : 10.1021 / jf9706686 .
- ^ Wissenschaft-Online-Lexika: Entry on Chalcon in the Lexikon der Chemie , accessed August 26, 2008.