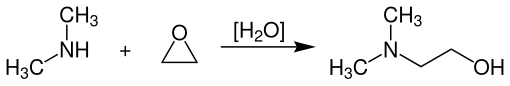N, N -dimethylethanolamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Dimethylaminoethanol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 11 NO | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an ammonia- like odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 89.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.89 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<−40 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
131 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
39.9 hPa (50 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water and ethanol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4300 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
N, N -Dimethylethanolamine (according to IUPAC nomenclature : 2- (dimethylamino) ethan-1-ol , also known as DMEA for short ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of alkylated amino alcohols . It isclosely related to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine via choline (the trimethylethanolammonium cation). The compound is an important intermediate product in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries , which has a wide range of applications.
Occurrence
Dimethylaminoethanol occurs as a metabolic product of the metabolism of choline in many living things. Larger amounts are found in fish ( sardines , salmon , anchovies ).
Extraction and presentation
N , N- dimethylethanolamine is produced industrially by reacting ethylene oxide with dimethylamine at temperatures of 125-160 ° C. and pressures of 15-30 bar in the presence of catalytic amounts of water in liquid-cooled jacketed tubular reactors .
The product is purified and worked up by multi-stage distillation in rectification columns .
Furthermore, can the dimethylaminoethanol, by methylation of monoethanolamine are synthesized.
properties
The flash point is 31 ° C, the ignition temperature 220 ° C.
use
Dimethylaminoethanol is used as an aid to dispersion of pigments in water-based paints use. It is also required as an intermediate or starting material for the production of dyes , emulsifiers , corrosion protection agents , textile auxiliaries, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals .
Dimethylaminoethanol is said to have a large number of positive effects, including nootropic effects , for which, however, there is no clear evidence. In Alzheimer -Patients no consistent results were observed. One author reported increased lucid dreams after using DMAE.
Dimethylaminoethanol as a topical gel is said to reduce the formation of wrinkles.
safety instructions
As a tertiary amine, dimethylaminoethanol is a strong base, which is also the reason for its caustic effect. It is of only low acute toxicity ( LD 50 ( rat , oral ): 2.00 g / kg, LD 50 ( rabbit , dermal ): 1.37 g / kg).
literature
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences : Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE) [108-01-0] and Selected Salts and Esters. Review of Toxicological Literature (Update), November 2002
Trade names
Risatarun (D, except trade, approval was not granted due to a lack of long-term studies)
Pharmaton Vital Geriavit (CH), Vita Gerin (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on DIMETHYL MEA in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 21, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on 2- (dimethylamino) ethanol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 22, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-198.
- ↑ Entry on 2-dimethylaminoethanol in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Patent EP2651861B1 : Process for the production of an N, N-dialkylethanolamine with high color stability. Published on February 25, 2015 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: Frank-Friedrich Pape, Johann-Peter Melder, Alfred Krause, Roland Bou Chedid, Martin Rudloff.
- ↑ M. Fisman, H. Mersky, E. Helmes: Double-blind trial of 2-dimethylaminoethanol in Alzheimer's disease. In: The American journal of psychiatry. Volume 138, Number 7, July 1981, pp. 970-972, PMID 7020434 .
- ↑ CC PFEIFFER, EH JENNEY, W. GALLAGHER, RP SMITH, W. BEVAN, KF KILLAM, EK KILLAM, W. BLACKMORE: Stimulant effect of 2-dimethylaminoethanol; possible precursor of brain acetylcholine. In: Science. Volume 126, Number 3274, September 1957, pp. 610-611, PMID 13467254 .
- ↑ W. Sergio: Use of DMAE (2-dimethylaminoethanol) in the induction of lucid dreams. In: Medical Hypotheses. 26, 1988, pp. 255-257, doi : 10.1016 / 0306-9877 (88) 90129-6 .
- ^ R. Grossman: The role of dimethylaminoethanol in cosmetic dermatology. In: American Journal of Clinical Dermatology . Volume 6, Number 1, 2005, pp. 39-47, PMID 15675889 . (Review).
- ↑ I. Uhoda, N. Faska, C. Robert, G. Cauwenbergh, GE Piérard: . Split face study on the cutaneous tensile effect of 2-dimethylaminoethanol (deanol) gel In: Skin Research and Technology . Volume 8, Number 3, August 2002, pp. 164-167, PMID 12236885 .