Detarieae
| Detarieae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
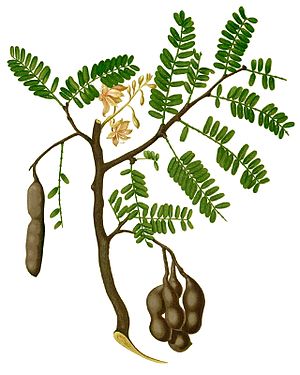
Tamarind tree ( Tamarindus indica ), illustration |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Detarieae | ||||||||||||
| DC. |
Detarieae is a tribe in the subfamily of the carob family (Caesalpinioideae) within the legume family (Fabaceae). Some types provide high quality commercial timbers .
description









Appearance and leaves
There are woody plants and thrive as unreinforced trees or shrubs , rare subshrubs .
The alternate and spiral or two-line arranged leaves are pinnate in pairs; in 22 genera they are reduced to a pair of pinnate leaves. The stalks of the leaflets are often twisted (in 24 genera). The underside of the leaf has an epidermis that is almost always (in 69 genera) colored by safranin , the hairs ( trichomes ) are often enlarged (in 25 genera) at their base and embedded, and epidermal crystals are not uncommon (in 17 genera). Almost always (57/61 genera) conspicuous phloem transfer cells are present, sometimes with mesophyll fibers and / or scleraids (12 genera). The leaflets are often dotted with glands. If stipules are present then they are intrapetiolar.
Inflorescences and flowers
The flowers stand together in inflorescences . There are almost always covers ; they are relatively small, overlapping like roof tiles and sloping early to large and conspicuous. The hermaphroditic flowers are more or less zygomorphic and usually four (in 75 genera) or rarely five-fold with a double flower envelope . The four or rarely five sepals overlap like roof tiles; sometimes they are greatly reduced. The petals stand together to form a somewhat to strongly zygomorphic crown; petals are often reduced or absent. There are two to many stamens present. There is only one carpel .
Fruits and seeds
There are legumes formed. The seeds do not contain endosperm ; Strength is almost always there.
Sets of chromosomes
The base chromosome number is usually n = 12 (21/27).
ecology
The species of this tribe go symbioses with ektotrophischen mycorrhizae - fungi one. Some species have leaves that attract ants .
As a co-evolution of plants and animals have specially adapted in form and color flowers that bees attract.
ingredients
Characteristic ingredients are tannins and terpenoids . Some types also produce resin.
Systematics and distribution
The Tribus Detarieae was set up in 1825 by Augustin-Pyrame de Candolle . Synonyms for Detarieae DC. are: Cynometreae Benth. , Phyllocarpeae Britton & Rose , Amherstieae Benth. , Subfamily Brachystegioideae Hutch. , Macrolobiea Breteler .
About 58% of the genera occur in Africa including Madagascar , about 20% are distributed in the Neotropic and 12% in tropical Asia . Only the genera Copaifera , Crudia and Cynometra are pantropically distributed, but they are all probably not monophyletic . Afzelia , Guibourtia , Hymenaea , Intsia and Sindora are represented in at least two of these regions.
The Tribus Detarieae includes 82 to 84 genera with 736 to 772 species:
- Afzelia Sm .: The 12 to 14 species are common in tropical Asia and Africa.
-
Amherstia Wall. : It contains only one type:
- Tohab tree ( Amherstia nobilis Wall. ): It occurs only in southern Myanmar .
- Anthonotha P.Beauv. : The approximately 17 species are in Africa, almost all only in the Guineo-Congolese region.
- Aphanocalyx olive. : The approximately 14 species are common in tropical Africa.
-
Augouardia Pellegr. : It contains only one type:
- Augouardia letestui Pellegr. : It is native to Gabon and the Congo.
- Baikiaea Benth. : The five or so species are mainly found in tropical Africa, only one species also occurs in subtropical Africa (in Angola , Botswana , Namibia , Zambia and Zimbabwe ).
-
Barnebydendron J.H. Kirkbr. : It contains only one type:
- Barnebydendron riedelii (Tul.) JHKirkbr. : It occurs in southern Costa Rica , Guatemala and Honduras , in the Brazilian state of Acre and in the Peruvian region of Madre de Dios .
- Berlinia Sol. ex Hook. f. : The approximately 18 species are common in Africa.
- Bikinia Wieringa : The eleven or so species are common in tropical Africa.
-
Brachycylix (Harms) RSCowan : It contains only one species:
- Brachycylix vageleri (Harms) Cowan : It is native to Colombia .
- Brachystegia Benth. : The 30 to 34 species are common in tropical Africa.
-
Brandzeia Baill. : It contains only one type:
- Brandzeia filicifolia Baill. : It is native to Madagascar .
-
Brodriguesia R.S. Cowan : It contains only one species:
- Brodriguesia santosii R.S. Cowan : It occurs only in the Brazilian state of Bahia .
- Brownea Jacq. : The 25 to 31 species occur in northern South America (Colombia, Ecuador and Venezuela ) and on the Caribbean islands.
- Browneopsis Huber : The six or so species are distributed from Panama to Colombia to the Brazilian Amazon basin and Peru .
-
Colophospermum Kirk ex J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Mopane ( Colophospermum mopane (Kirk ex Benth.) Kirk ex J.Léonard , Syn .: Copaiba mopane (Kirk ex Benth.) Kuntze , Copaifera mopane Kirk ex Benth. , Hardwickia mopane (Kirk ex Benth.) Breteler et al. ): It is widespread in southern tropical and southern Africa .
- Copaifera L .: The 25 to 43 species are common in the Neotropics and Africa.
- Crudia Schreb. : The up to 55 species are mainly distributed in tropical Africa.
- Cryptosepalum Benth. : The eleven or so species are common in tropical Africa.
- Cynometra L .: The 80 to 90 species are widespread in the tropics.
- Daniellia Benn. : The ten or so species are common in tropical and subtropical Africa.
- Detarium Juss. : The three or so species are common in tropical Africa.
- Dicymbe Spruce ex Benth. & Hook. f. : The approximately 13 species are common in the Neotropic.
- Didelotia Baill. : The twelve or so species are common in Africa.
-
Ecuadendron D.A. Neill : It contains only one species:
- Ecuadendron acosta-solisianum D.A.Neill : This endangered species (endangered according to IUCN ) thrives at altitudes between 300 and 400 meters in Ecuador. In the year 2000, fewer than 100 copies were counted at the only three known locations.
- Elizabetha R.H. Schomb. ex Benth. : The eleven or so species are common in the New World .
-
Endertia Steenis & de Wit : It contains only one species:
- Endertia spectabilis Steenis & de Wit : It occurs in Java and Kalimantan .
- Englerodendron Harms : The roughly two species are common in tropical Africa.
-
Eperua Aubl. : The approximately 14 species are common in the Neotropic .
- Eperua falcata Aubl. : Occurs in northern Brazil, in the Guyanas and up to Venezuela and Colombia as well as in Trinidad.
- Eurypetalum Harms : The three or so species are common in Africa.
-
Gilbertiodendron J.Léonard : The approximately 27 species are common in Africa. Including:
- Gilbertiodendron dewevrei (De Wild.) J. Léonard
-
Gilletiodendron Vermoesen : The five or so species are common in Africa. Including:
- Gilletiodendron mildbraedii (Harms) Vermoesen
-
Gabonius Wieringa & Mackinder : It was set up in 2013 and contains only one species:
- Gabonius ngouniensis (Pellegr.) Wieringa & Mackinder : It occurs only in western Gabon.
-
Goniorrhachis deaf. : It contains only one type:
- Goniorrhachis marginata Deaf. : It occurs only in the Brazilian state of Bahia.
- Gossweilerodendron Harms : The roughly two species are common in Africa.
- Guibourtia Benn. : The 16 or so species are common in Africa.
-
Hardwickia Roxb. : It contains only one type:
- Hardwickia binata Roxb. : It is native to India.
- Heterostemon desf. : The seven or so species are common in South America.
- Humboldtia Vahl : The approximately seven species occur in southwest India and Sri Lanka (one species).
-
Hylodendron deaf. : It contains only one type:
- Hylodendron gaboon pigeon . : It occurs in tropical Africa in Cameroon , Gabon, Zaire and Nigeria .
- Hymenaea L .: Of the 15 to 16 species, apart from one African species, all other species have a neotropical distribution.
- Hymenostegia (Benth.) Harms : The 16 or so species are common in Africa.
-
Icuria Wieringa : It contains only one species:
- Icuria dunensis Wieringa : It occurs only in northern Mozambique .
- Merbau ( Intsia Thouars ): The three to nine species occur in Southeast Asia , the Pacific and Madagascar.
-
Isoberlinia Craib & Stapf ex Holland : The five or so species are common in tropical Africa, for example:
- Isoberlinia doka Craib & Stapf
- Julbernardia Pellegr. : The eight to eleven species are common in tropical Africa.
- Kingiodendron Harms : The five or so species are common in Asia.
-
Lebruniodendron J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Lebruniodendron leptanthum (Harms) J.Leonard : It occurs in Cameroon and Zaire.
- Leonardoxa Aubrév. : The five or so species are common in tropical Africa.
- Leucostegane Prain : There are about two species on the Malay Peninsula and in Sarawak .
-
Librevillea Hoyle : it contains only one species:
- Librevillea klainei (Harms) Hoyle : It is common in Angola, Cameroon and Gabon.
- Loesenera Harms : The four or so species are common in Africa.
- Lysidice Hance : The only two species occur in southern and southwestern China and in Vietnam.
- Macrolobium Schreb. : The 73 to 80 species are distributed from Panama to western South America.
- Maniltoa Scheff. : The approximately 20 species are common in Southeast Asia.
-
Michelsonia Hauman : It only contains one species (sometimes with a second species):
- Michelsonia microphylla (Troupin) Hauman : It occurs in Africa.
-
Micklethwaitia G.P. Lewis & Schrire : It contains only one species:
- Micklethwaitia carvalhoi (Harms) GPLewis & Schrire : It occurs in Mozambique.
- Microberlinia A. Chev. : The only two species occur in Cameroon, Republic of the Congo and Gabon. They provide the Zebrano -Holz.
- Neoapaloxylon Rauschert : The three or so species occur in Madagascar.
-
Neochevalierodendron J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Neochevalierodendron stephanii (A.Chev.) J.Léonard : It occurs in Gabon.
- Normandiodendron J.Léonard : The roughly two species are common in Africa.
- Oddoniodendron De Wild. : The three or so species are common in tropical Africa.
-
Oxystigma Harms : Only one species is common in Africa.
- Oxystigma mannii Harms : From Central Africa
- Paloue Aubl. : The five or so species are common in the Amazon region.
-
Paloveopsis R.S. Cowan : It contains only one species:
- Paloveopsis emarginata Cowan : It is common in Brazil and Guyana .
-
Paramacrolobium J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Paramacrolobium coeruleum (Taub.) J.Léonard : It occurs in tropical Africa.
-
Pellegriniodendron J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Pellegriniodendron diphyllum (Harms) J.Léonard : It occurs in tropical Africa.
-
Peltogyne bird : The approximately 25 species are distributed in the Amazon region and in tropical Africa. Some species of this genus provide the amaranth wood .
- Peltogyne venosa (Vahl) Benth. : From South America
- Plagiosiphon Harms : The five or so species are common in Africa.
-
Polystemonanthus Harms : It contains only one species:
- Polystemonanthus dinklagei Harms : It occurs in the Ivory Coast and Liberia .
-
Prioria Griseb. : It contains about 14 species:
- Prioria copaifera Griseb. : It occurs in Jamaica , Costa Rica, Nicaragua , Panama and Colombia.
- Prioria oxyphylla (Harms) Breteler : From Central Africa
-
Pseudomacrolobium Hauman : It contains only one species:
- Pseudomacrolobium mengei (De Wild.) Hauman : It occurs in Zaire.
-
Pseudosindora Symington : it contains only one species:
- Pseudosindora palustris Symington : It occurs in Indonesia .
- Saraca L .: The eleven to twenty species are common in tropical Asia.
- Schotia Jacq. : The only four species left are common in southern Africa.
- Scorodophloeus Harms : The two or three species are common in Africa.
- Sindora Miq. : The 18 to 20 species occur mainly in Southeast Asia, but also in Gabon.
-
Sindoropsis J.Léonard : It contains only one species:
- Sindoropsis letestui (Pellegr.) J.Léonard : It occurs in Gabon.
-
Stemonocoleus Harms : It contains only one species:
- Stemonocoleus micranthus Harms : It occurs in tropical Africa.
- Talbotiella Baker f. : The three or so species are common in Africa.
-
Tamarindus L .: It contains only one species:
- Tamarind tree ( Tamarindus indica L. ): It is widespread in Africa and is also found on the Cape Verde Islands , Socotra and Yemen . It is grown in many tropical to subtropical areas.
- Tessmannia Harms : The twelve or so species are common in Africa.
- Tetraberlinia (Harms) Hauman : The seven or so species are common in Africa.
- Zenkerella Taub. : The five or so species are common in Africa.
use
The wood is used by some species: for example, some species of the genus Peltogyne produce the amaranth wood . The fruits are used by a few species ( tamarind tree ( Tamarindus indica )).
Individual evidence
- ^ A b David J. Mabberley: The Plant-book . Cambridge University Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0-521-82071-4 , pp. 1021 ( Detarieae on p. 475 in the Google book search).
- ↑ a b c d e Leslie Watson, Michael J. Dallwitz: The Genera of Leguminosae-Caesalpinioideae and Swartzieae : DELTA data sheet.
- ↑ a b c Detarieae on Tree of Life Web Project . (English)
- ↑ Detarieae at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, accessed April 26, 2015.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet from Legumes of the World at Royal Botanical Gardens Kew. Last accessed on April 26, 2015
- ^ Detarieae in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved April 26, 2015.
- ^ Frans J. Breteler: Revision of the African genus Anthonotha (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae). In: Plant Ecology and Evolution. Volume 143, No. 1, 2010, pp. 70-99, DOI: 10.5091 / plecevo.2010.369 .
- ↑ Philip A. Silverstone Sopkin: A New Species of Browneopsis (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae) from the Cauca Valley, Colombia. In: Novon: A Journal for Botanical Nomenclature. Volume 20, No. 2, 2010, pp. 207-211, doi : 10.3417 / 2008100 .
- ↑ Manuel de la Estrella, Carlos Aedo, Barbara Mackinder, Mauricio Velayos: Taxonomic Revision of Daniellia (Leguminosae: Caesalpinioideae). In: Systematic Botany. Volume 35, No. 2, 2010, pp. 296-324, DOI: 10.1600 / 036364410791638414 , (PDF file; 4.6 MB).
- ↑ Ecuadendron acosta-solisianum in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2011. Posted by: D. Neill, N. Pitman, 2004. Accessed on 19/10/2011.
- ^ Jan J. Wieringa, Barbara A. Mackinder, André SJ van Proosdi: Gabonius gen. Nov. (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae, Detarieae), a distant cousin of Hymenostegia endemic to Gabon. In: Phytotaxa , Volume 142, Issue 1, 2013 pp. 15–24. doi : 10.11646 / phytotaxa.142.1.2
Web links
further reading
- M. Fougère-Danezan, PS Herendeen, S. Maumont, A. Bruneau: Morphological evolution in the variable resin-producing Detarieae (Fabaceae): do morphological characters retain a phylogenetic signal? In: Annals of botany. Volume 105, number 2, February 2010, pp. 311-325, doi : 10.1093 / aob / mcp280 , PMID 19939978 , PMC 2814753 (free full text).