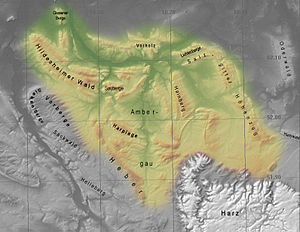
Innerstebergland
The Innerstebergland is over 900 km² in size and up to 358.9 m above sea level. NHN high landscape in the northern part of the German low mountain range and in the eastern part of the Weser-Leine-Bergland in Lower Saxony ( Germany ).
The Innerstebergland is named after the Innerste , a tributary of the Leine .
geography
location
The Innerstebergland extends in the catchment area of the Innerste from Hildesheim and the southwest of Salzgitter to Goslar and Seesen on the northwestern edge of the Harz Mountains . In the northwest the landscape borders on the Calenberger Loessbörde , in the north on the Braunschweig-Hildesheimer Loessbörde and in the east on the Harz rim hollow - all parts of the Loessbörden on the northern edge of the low mountain range threshold. In the southeast the Harz borders, in the south the southwestern Harz foreland and in the southwest the Alfelder Bergland .
In its center and in the south is the Ambergau , a lowland landscape on the Nette , a tributary of the innermost. The valley with the main towns Sibbesse, Bodenburg and Lamspringe, between the Hildesheim Forest in the northeast and the foothills and the Sackwald in the southwest, is called Flenithigau .
In and on the edge of the Innerstebergland there are these clearly delimited mountain ranges , which are mostly made up of layers and partly on the border to neighboring landscapes (viewed in alphabetical order): Giesener Berge , Hainberg , Harplage , Heber , Hildesheimer Wald , Salzgitter-Höhenzug ( with the Lichtenbergen ), Sauberge and Vorholz . These rivers run between these mountain ranges : Innerste , Lamme , Neile and Nette and their tributaries.
Landscape image
The mountain ranges of the Innerstebergland are mostly covered with deciduous forest , especially beech forests . The flowing waters run in slightly hilly, heavily loess-covered lowlands , to which the basin-like Ambergau belongs. The fertile soils are heavily used for arable farming. The landscape also includes the quarries and opencast mines, which are mostly closed and partly filled with water, in which Keuper sandstone has been mined since the Middle Ages .
Ridges and mountains
The Innerstebergland, the highest point of which is the 358.9 m high Griesberg in the Hildesheim Forest, has eight mountain ranges - sorted by height in meters (m) above sea level:
|
|
Flowing waters
The rivers of the Innerstebergland include:
- Alme - in the west, tributary of the Riehe
- Beuster - in the northwest, tributary of the innermost
- Inmost - in the north, northeast and east, tributary of the Leine
- Lamme - in the west, influx of the innermost
- Neile - in the south-eastern center, tributary to the innermost
- Nice - in the center (Ambergau), inflow of the innermost
- Riehe - in the west, tributary of the Lamme
Localities
In the Innerstebergland and on its edge, there are, among others, these villages :
References and comments
- ↑ a b c d mountain height according to unknown / not researched source
- ↑ a b Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ Mountain height according to the topographical overview map of Lower Saxony ( memento of the original from July 7, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (DTK 25), on natur-erleben.niedersachsen.de
Web links
- Gerhard Meier-Hilbert: Geographical structures (of the Hildesheimer Land) (PDF; 1.2 MB)
- Landscape profile 37900 Innerstebergland (with map), from the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN)
Coordinates: 52 ° 1 ′ N , 10 ° 7 ′ E