Presidential election in Poland 2005
| ‹ 2000 • |
||
|---|---|---|
| Presidential election in Poland | ||
| October 9, 2005 (first ballot) | ||
| October 23, 2005 (second ballot) | ||
| Law and justice | ||
| Lech Kaczyński | ||
| be right | 8,257,468 | |
|
|
54.04% | |
| Platforma Obywatelska | ||
| Donald Tusk | ||
| be right | 7,022,319 | |
|
|
45.96% | |
| Powiat election results | ||
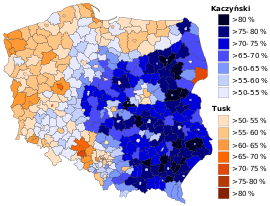
|
||
| President of the Third Polish Republic | ||
The presidential election in Poland in 2005 was the popular election of the Polish head of state on October 9 and October 23, 2005. In the second round of elections, the national -conservative Warsaw mayor Lech Kaczyński prevailed against the liberal-conservative politician Donald Tusk and became president for a five-year term elected to the Republic of Poland .
background
On December 23, 2005, the second five-year term of office of the President of the Republic of Poland Aleksander Kwaśniewski was to expire. According to the constitution , the incumbent was no longer allowed to stand for election. On May 23, 2005, the Sejm Marshal Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz ordered the presidential elections for October 9, 2005 with a possible second round on October 23.
The electoral rules were based on the current 1997 constitution . All citizens who were entitled to vote in parliamentary elections were given the right to vote, and those who had also reached the age of 35 by the day of the election were given the right to vote. The nominations had to show the written support of at least one hundred thousand eligible citizens. If no candidate had the necessary majority of over 50% of the validly cast votes on the first election day, a second election round would have to be called to which the two candidates who received the most votes in the first election round would be admitted ( runoff ). The Supreme Court was responsible for determining the validity of the election and for the President of the National Assembly to be sworn in .
The vote
The candidates
A total of sixteen candidates were able to show 100,000 signatures from the electorate within the set deadline (August 25, 2005, midnight) and were allowed to participate in the first round of voting after verification by the election committee:
- Henryka Teodora Bochniarz (* 1947) - holds a doctorate in economics, president of the employers' association, supported by the Democratic Party
- Marek Stefan Borowski (* 1946) - economist, member of the Sejm (since 1991), former Sejm Marshal (2001–2004), former Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister (1993–1994), Chairman of the Social Democracy of Poland
- Leszek Henryk Bubel (* 1957) - goldsmith, journalist, publisher, former member of the Sejm (1991–1993), self-proclaimed “leading anti-Semite of the republic”, supported by the Polish National Party
- Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz (* 1950) - doctor of law, university professor, acting Sejm Marshal (since 2005) and member of the Sejm (since 1989), former Foreign Minister (2001–2003), former Prime Minister (1996–1997), former Deputy Prime Minister, Attorney General and Attorney General (1993–1995), former member of the PVAP , supported by the Federation of Democratic Left
- Maciej Marian Giertych (* 1936) - qualified dendrologist and geneticist, titular professor, member of the European Parliament (since 2004), former member of the Sejm (2001-2004)
- Liwiusz Marian Ilasz (* 1961) - lawyer
- Lech Aleksander Kaczyński (1949–2010) - qualified lawyer, mayor of the capital Warsaw (since 2002), former minister of justice (2000–2001), former senator (1989–1991), former independent member of the Sejm (1991–1993), former advisor of President Wałęsa, former activist of the trade union “ Solidarność ” and opposition activist , supported by the national-conservative Law and Justice
- Jarosław Kalinowski (* 1962) - qualified animal breeder, chairman of the Polish Farmers' Party (since 1997), member of the Sejm (since 1993), former Deputy Prime Minister (2001-2003) and Minister of Agriculture (1997 and 2001-2003)
- Janusz Ryszard Korwin-Mikke (* 1942) - philosopher, columnist, libertarian politician of the Union for Realpolitik
- Andrzej Zbigniew Lepper (1954–2011) - farmer, entrepreneur, chairman of the self-defense union (since 1992) and the party of the same name, former member of the PVAP (1978–1980)
- Daniel Tomasz Podrzycki (1963–2005) - metal worker, trade union activist, supported by an alliance of secular, socialist, anarchist and communist parties
- Jan Pyszko (1930–2009) - qualified surgeon, activist of the Association of Poles Abroad, supported by the "Organization of the Polish Nation - Polish League"
- Zbigniew Eugeniusz Religa (1938–2009) - qualified cardiac surgeon, senator (1993–1997 and since 2001), conservatist, supported by the Center Party
- Adam Andrzej Słomka (* 1963) - qualified pedagogue, leader of the "Confederation of Independent Poland - Patriotic Group", a splinter group of the Confederation of Independent Poland
- Donald Franciszek Tusk (* 1957) - historian, Deputy Sejm Marshal (since 2001), Sejm Member (1991–1993 and since 2001), former Senator and Deputy Senate Marshal (1997–2001)
- Stanisław Tymiński (* 1948) - state-certified electrical engineer, web entrepreneur, supported by the "All-Polish Citizens' Coalition"
It is striking that seven of the candidates have run unsuccessfully in previous presidential elections: Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz and Stanisław Tymiński 1990, Leszek Bubel and Lech Kaczyński 1995, Jarosław Kalinowski 2000, and Janusz Korwin-Mikke and Andrzej Lepper 1995 and 2000.
Three candidates waived before the first ballot and were struck off the list of candidates: Zbigniew Religa on September 2, Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz on September 14 and Maciej Giertych on October 4, 2005. He died on September 24, 2005, the day before the parliamentary election Daniel Podrzycki as a result of a traffic accident and also dropped out of the list of candidates. As a result, twelve candidates stood for election, with the names of Giertych and Podrzycki on the already printed ballot papers.
Opinion polls
Initially, Cimoszewicz was considered the most promising candidate, followed by the far behind Lech Kaczyński, Andrzej Lepper and Zbigniew Religa. However, the negative mass media campaign based on allegations of fraud by Cimoszewicz's former assistant Anna Jarucka caused his opinion polls to plummet, mostly in favor of Donald Tusk. Then Cimoszewicz withdrew his candidacy on September 14th in this context.
1st ballot
| date | Institute | candidate | source | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henryka Bochniarz | Marek Borowski | Leszek Bubel | Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz | Maciej Giertych | Liwiusz Ilasz | Lech Kaczyński | Jarosław Kalinowski | Janusz Korwin-Mikke | Andrzej Lepper | Daniel Podrzycki | Jan Pyszko | Zbigniew Religa | Adam Słomka | Donald Tusk | Stanisław Tymiński | |||
| 1st - 4th July 2005 | TNS OBOP | 1 % | 4% | 0% | 31% | 4% | 0% | 16% | 2% | 0% | 15% | 0% | 0% | 14% | 0% | 8th % | 0% | |
| 4-8 August 2005 | TNS OBOP | 1 % | 5% | 0% | 26% | 3% | 0% | 21% | 2% | 1 % | 9% | 0% | 0% | 7% | 0% | 23% | 0% | |
| 4-9 August 2005 | Ipsos | 0% | 5% | 0% | 19% | 2% | 0% | 24% | 3% | 2% | 12% | 0% | 0% | 7% | 0% | 24% | 0% | |
| 25-29 August 2005 | TNS OBOP | 1 % | 2% | 0% | 24% | 3% | 0% | 21% | 3% | 1 % | 7% | 0% | 0% | 5% | 0% | 30% | 0% | |
| 8-12 September 2005 | TNS OBOP | 0% | 4% | 0% | 15% | 4% | 0% | 23% | 4% | 0% | 8th % | 0% | 0% | - | 0% | 41% | 1 % | |
| Sept. 29th - 3rd Oct 2005 | TNS OBOP | 1 % | 8th % | 0% | - | 1 % | 1 % | 34% | 3% | 2% | 9% | - | 1 % | - | 0% | 40% | 0% | |
2nd ballot
| date | Institute | candidate | source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lech Kaczyński | Donald Tusk | |||
| Sept. 29th - 3rd Oct 2005 | TNS OBOP | 47% | 53% | |
| 13-17 October 2005 | TNS OBOP | 43% | 57% | |
Official end result
| Ballot | candidate | Number of votes | % of valid votes | Supporting party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st ballot, October 9, 2005 | ||||
| Henryka Bochniarz | 188 598 | 1.26% | PD | |
| Marek Borowski | 1 544 642 | 10.33% | SdPl , UP , Z 2004 | |
| Leszek Bubel | 18 828 | 0.13% | PPN | |
| Liwiusz Ilasz | 31 691 | 0.21% | ||
| Lech Kaczyński | 4,947,927 | 33.10% | PiS | |
| Jarosław Kalinowski | 269 316 | 1.80% | PSL | |
| Janusz Korwin-Mikke | 214 116 | 1.43% | PJKM, UPR | |
| Andrzej Lepper | 2,259,094 | 15.11% | Samoobrona | |
| Jan Pyszko | 10 371 | 0.07% | ONP-LP | |
| Adam Słomka | 8 895 | 0.06% | KPN-FP | |
| Donald Tusk | 5 429 666 | 36.33% | PO | |
| Stanisław Tymiński | 23 545 | 0.16% | ECO | |
| Invalid votes | 99 661 | |||
| Since none of the candidates achieved the required majority, the second ballot was ordered for October 23, 2005, to which Donald Tusk and Lech Kaczyński were allowed. | ||||
| 2nd ballot, October 23, 2005 | Lech Kaczyński | 8 257 468 | 54.04% | PiS |
| Donald Tusk | 7 022 319 | 45.96% | PO | |
| Invalid votes | 155 233 | |||
| Lech Kaczyński was thus elected 4th President of the 3rd Republic of Poland . | ||||
After the election
On November 23, 2005, the Supreme Court determined the validity of the election on October 9 and 23; it did not go into the three irregularities found, as it was not able to determine any influence on the election result. On December 23, 2005, Lech Kaczyński took the oath of office to the National Assembly under the chairmanship of the newly elected Sejm Marshal Marek Jurek and in the presence of his predecessor Aleksander Kwaśniewski, followed by a speech by the President. Unlike his predecessor, Kaczyński supplemented the oath of office with a religious affirmation.
Footnotes
- ↑ postanowienie Marszałka Sejmu Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej z dnia 23 maja 2005 r. o zarządzeniu wyborów Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. May 23, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ Uchwała Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej a dnia 20 września 2005 r. w sprawie skreślenia z listy kandydatów na Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej w wyborach zarządzonych na dzień 9 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. October 6, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ a b Uchwała Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej z dnia 19 września 2005 r. w sprawie skreślenia z listy kandydatów na Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej w wyborach zarządzonych na dzień 9 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. September 19, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ Uchwała Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej z dnia 6 października 2005 r. w sprawie skreślenia z listy kandydatów na Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej w wyborach zarządzonych na dzień 9 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. October 6, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ Uchwała Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej z dnia 25 września 2005 r. w sprawie skreślenia z listy kandydatów na Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej w wyborach zarządzonych na dzień 9 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. September 25, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ a b TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie na trzy miesiące przed wyborami. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. July 10, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie na dwa miesiące przed wyborami. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. August 8, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ gazeta.pl: Sondaż prezydencki: Kaczyński i Tusk - po 24%; Sondaż parlamentarny PiS przed PO. In : zieloni2004.pl. August 9, 2005, accessed January 10, 2013 (Polish).
- ↑ TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie w ostatnich dniach sierpnia 2005 r. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. August 29, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie miesiąc przed wyborami 2005 r. tuż przed rezygnacją Włodzimierza Cimoszewicza ze startu wyborach. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. September 12, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie tydzień przed wyborami. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. October 3, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ TNS OBOP : Preferencje prezydenckie tydzień przed drugą turą wyborów. (No longer available online.) In: tnsglobal.pl. October 17, 2005, formerly in the original ; Retrieved January 10, 2013 (Polish). ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z Obwieszczenie Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej z dnia 10 października 2005 r. o wynikach głosowania i wyniku wyborów Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej, zarządzonych na dzień 9 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. October 10, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Obwieszczenie Państwowej Komisji Wyborczej z dnia 24 października 2005 r. o wynikach ponownego głosowania i wyniku wyborów Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. October 24, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ Uchwała Sądu Najwyższego z dnia 23 listopada 2005 r. w sprawie ważności wyborów Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej przeprowadzonych w dniach 9 i 23 października 2005 r. In: Dziennik Ustaw, sejm.gov.pl. November 23, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .
- ↑ 5 kadencja, Zgromadzenie Narodowe (December 23, 2005). In: 5 kadencja, Zgromadzenie Narodowe (23.12.2005). December 23, 2005, accessed January 5, 2013 .












