Mercaptoethanol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Mercaptoethanol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 6 OS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a characteristic odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 78.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.12 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<−50 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
157 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
9.72 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4985 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Mercaptoethanol (according to IUPAC nomenclature: 2-sulfanylethanol , also known as thioglycol ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of thiols and alcohols . The fabric has an extremely unpleasant odor of hydrogen sulfide .
Extraction and presentation
For the large-scale synthesis of mercaptoethanol, ethylene oxide is reacted with hydrogen sulfide at temperatures of 140–180 ° C. and pressures of 10–25 bar.
As a catalyst and solvent is thiodiglycol used. The complete reaction takes place in adiabatically operated stirred tank or tubular reactors. The purification and work-up of the product is usually carried out by vacuum distillation in downstream columns .
properties
Physical Properties
Mercaptoethanol has a relative gas density of 2.69 (density ratio to dry air at the same temperature and pressure ) and a relative density of the vapor-air mixture of 1.01 (density ratio to dry air at 20 ° C and normal pressure ). In addition, 2-sulfanylethanol has a vapor pressure of 1.38 hPa at 20 ° C, 2.91 hPa at 30 ° C, 5.77 hPa at 40 ° C and 10.80 hPa at 50 ° C. Furthermore, the dynamic viscosity is 3.4 mPa · s at 20 ° C
Chemical properties
2-sulfanylethanol is a difficult to ignite, colorless liquid from the group of thiols and alcohols . It is readily soluble in water and with most organic solvents . In addition, mercaptoethanol is hygroscopic and quickly splits off highly toxic hydrogen sulfide on contact with water or acid . Violent reactions can also occur on contact with oxidizing agents . An aqueous solution of concentration 500 g / l at 20 ° C has a pH value in the range of 4.5 - to. 6
use
Mercaptoethanol is used in organic chemistry as a nucleophile in substitution and addition reactions and as a sulfur donor . It is also used for the synthesis of heterocycles such as 1,3-oxathiolanes . These in turn serve as protective groups for aldehydes and ketones .
Another area of application for 2-sulfanylethanol is polymer modification . Here it is used as a chain transfer reagent , to modify end groups and as a crosslinker.
In biochemistry , mercaptoethanol is used as an enzyme modulator and is used here e.g. B. as a stimulator of glutathione biosynthesis . The substance is also used in the purification of enzymes , DNA and RNA and is often added to culture media to promote growth and differentiation. In the PVC industry , 2-sulfanylethanol is also often used as a tin stabilizer .
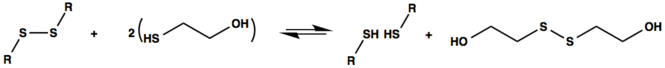
Mercaptoethanol is also used to reduce proteins and thus destroy disulfide bridges. This destroys the tertiary structure, which can be advantageous for the SDS page , for example . It reacts with proteins as follows:
safety instructions
The vapors of mercaptoethanol can form explosive mixtures with air when heated above the flash point. The substance is classified as hazardous to the aquatic environment. Mercaptoethanol is mainly absorbed through the airways and skin . This leads to strong irritation and chemical burns to the mucous membranes and skin. In addition, a disorder of the central nervous system has been proven. In in vitro tests on cell cultures one was mutagenic effect detected.
Mercaptoethanol has a lower explosion limit (LEL) of approx. 2.3 vol.% And an upper explosion limit (UEL) of approx. 18 vol.%. The ignition temperature is 295 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T3. With a flash point of 68 ° C, mercaptoethanol is considered hardly inflammable.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Entry on 2-mercaptoethanol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 17, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases, pp. 8-42.
- ↑ a b c Entry on 2-sulfanylethanol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on February 17, 2019.
- ↑ a b Patent WO2016024012 : Process for the production of 2-mercaptoethanol. Published on February 18, 2016 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: Ralf Böhling, Michael Hayer, Alwin Rehfinger, Andreas Deckers, Michael Triller.
- ^ 2-mercaptoethanol. In: BASF product search. BASF SE, 2014, accessed on February 17, 2019 .