Diaminodinitroethylene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diaminodinitroethylene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 4 N 4 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 148.08 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
from 180 ° C decomposition |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, slightly soluble in acetonitrile and cyclohexanone , soluble in DMSO , dimethylformamide and N -methylpyrrolidone |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Three isomeric structures can be formulated for diaminodinitroethylene . Of the possible isomers 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene ( 1 ), trans -1,2-diamino-1,2-dinitroethylene ( 2 ) and cis -1,2-diamino-1,2-dinitroethylene ( 3 ) so far only the former is synthetically accessible.
1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7 or DADE) is an energy-rich chemical compound that is suitable as a basis for insensitive and at the same time highly explosive explosives . For the two 1,2-diamino-1,2-dinitroethylene isomers, only theoretical, quantum chemical calculations have been made so far. Real production and characterization of the two compounds is still pending.
history
The synthesis of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene derivatives was described as early as 1992. Starting from 1,1-diiodo-2,2-dinitroethylene , the corresponding 1,1-dialkylamino-2,2-dinitroethylene compounds can be obtained by conversion with alkylamines . The reaction with ammonia gave the ammonium salt of cyanodinitromethane as the reaction product and thus not the basic compound 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene. 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) was first synthesized in 1998 at the FOI (Swedish Defense Research Agency). With a yield of <10%, this synthetic route is not commercially viable despite the cheap starting material 2-methyl-imidazole .
Extraction and presentation
The production of diaminodinitroethylene is only carried out in small batch sizes, which results in a relatively high price for the compound. An optimized synthesis with a yield of> 90% starts from 2,6-dihydroxy-4-methylpyrimidine , which is converted into a tetranitro intermediate by nitration in nitrating acid . The intermediate product is then hydrolytically split into the target compound, dinitromethane and carbon dioxide . The starting compound 2,6-dihydroxy-4-methylpyrimidine can be obtained by cyclizing acetamidine hydrochloride with diethyl malonate in the presence of sodium and ethanol .
A control of the turnover is possible here via liquid chromatographic separation using special graphite columns.
properties
Physical Properties
1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene forms yellow crystals. The connection shows a polymorphic behavior. The α-form is present at room temperature, which converts to the β-form when heated to 114 ° C. This phase transition is reversible. A further conversion to the γ form is observed at 173 ° C. The γ form is metastable and only slowly and incompletely converts to the low temperature form α on cooling. No melting point can be found for the compound, as DSC measurements indicate a strongly exothermic decomposition reaction from 180 ° C. Single-crystal investigations on the α-form crystallized from NMP / water revealed a monoclinic crystal structure. The presence of electron-depressing and electron-withdrawing groups in the molecule leads to altered bond lengths. The bond length of the carbon-carbon bond is 145.6 pm between the typical bond lengths for a single bond with 154 pm and double bond with 134 pm. The compound therefore does not have a pure double bond structure. Two resonance structures can be formulated, whereby the polar imine structure is more present. This is also confirmed by the observed chemical properties such as B. in electrophilic additions.
There are two strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds between the NH and NO functions in the molecule. This results in a planar basic structure of the molecule. In the crystal lattice, a wave-like layer structure forms due to intermolecular hydrogen bonds. The crystal structure of the β-form is orthorhombic. The γ-shape shows a monoclinic crystal lattice with the space group P2 1 / n.
The compound is practically insoluble in water. In other solvents such as acetone , ethyl acetate or acetonitrile , the solubility is low at <0.5 g / 100 ml. Better solubilities are observed in dimethylformamide with 21 g / 100 ml, in N- methyl-2-pyrrolidone with 32 g / 100 ml and in dimethyl sulfoxide with 45 g / 100 ml.
The molar enthalpy of formation is Δ f H 0 = −130 kJ / mol. The NMR spectra of the compound are quite simple. The 1 H-NMR spectrum shows a broad peak resulting from the NH protons only at 8.77 ppm. In the 13 C-NMR spectrum there are two peaks at 128.5 ppm for the carbon atom substituted by nitro groups and at 158.8 ppm for the carbon atom bearing the amino groups.
Thermal stability and explosiveness
1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene shows no melting point when heated. In thermoanalytical measurements, a two-stage decomposition with a heat of decomposition of −1427 J / g is observed from 180 ° C. The decomposition mechanism has been considered theoretically with regard to the intermediate compounds that occur and leads to the final products carbon monoxide , nitrogen and water .
Important explosion indicators such as the heat of the explosion , the detonation speed or the detonation pressure were estimated using various calculation methods or determined experimentally using various measurement methods. The calculated values for the heat of explosion are between 4442 J g −1 and 4884 J g −1 , for the detonation velocity between 8453 m s −1 and 8869 m s −1 and for the detonation pressure between 29.3 GPa and 34 , 0 GPa. The experimentally determined values for the detonation energy are 4860 J · g −1 , the detonation velocity between 8325 m · s −1 and 8405 m · s −1 and the detonation pressure 28.4 GPa. The connection is sensitive to impact with an impact energy of 11 - 40 Nm . The impact sensitivity depends on the grain size distribution of the tested material. No friction sensitivity could be determined up to a friction force of 353 N. The connection can be ignited by laser irradiation . This effect can be enhanced by adding up to 5% activated carbon .
Chemical properties
The compound has acidic properties. Deprotonation can occur in the presence of bases. The pK a value is around 10.6. When reacted with potassium hydroxide solution at low temperatures, the potassium salt can be isolated as a white, crystalline solid. Heating to 70 ° C with potassium hydroxide leads to basic hydrolysis, with the potassium salt of dinitromethane and urea being formed.
Due to the large polarity differences in the molecule, there are interesting aspects for chemical reactions. The compound can be further nitrated using nitric acid in the presence of acetic anhydride or trifluoroacetic anhydride . The resulting tetranitro compound is thermally unstable. Decomposition is relevant from room temperature. The compound can be stored for about a week at −20 ° C. Decomposition in ammoniacal acetonitrile solution gives the ammonium salt of trinitromethane and nitroguanidine .
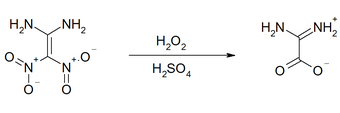
The halogenation with N -bromosuccinimide or N -chlorosuccinimide takes place analogously to the nitration to the carbon atom bearing the geminal nitro groups and to an amino group. The oxidation with 30% hydrogen peroxide in sulfuric acid or with trifluoroacetic acid leads to the release of nitrous acid and nitrous oxide to diaminoacetic acid.
1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene can be used as a starting material for the production of tetrazoles . The reaction with trimethylsilyl azide in DMSO enables the formation of the tetrazole ring with the formation of 5-amidinotetrazole. The potassium salt of tetrazole-5-carboxamide can be obtained by basic hydrolysis. Reaction of this with methyl iodide gives the two isomers 1-methyl-tetrazole-5-carboxamide and 2-methyl-tetrazole-5-carboxamide.
use
Due to its acidic properties, FOX-7 can be reacted with basic and nucleophilic substances to produce other high-energy substances. The reaction with guanidinium chloride in the presence of potassium hydroxide solution gives the guadidinium salt G (FOX-7). The higher nitrogen content in the molecule causes a higher gas development during thermal decomposition, which enables use in propellants .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n A.J. Bellamy: FOX-7 (1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene) in struc. Bond. 125 (2007) 1-33. doi : 10.1007 / 430_2006_054 (Structure & Bonding, Vol. 125: High energy density materials , Ed.Thomas M. Klapötke . Springer 2007, doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-540-72202-1 , ISBN 978-3-540- 72201-4 , p. 14, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e Koehler, J .; Meyer, R .; Homburg, A .: Explosivstoffe , tenth, completely revised edition. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, p. 69, ISBN 978-3-527-32009-7 .
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of 1,1-ethenediamine, 2,2-dinitro- in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 19, 2019, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ P. Politzer, MC Concha, ME Grice, JS Murray, P. Lane, D. Habibollazadeh: Computational investigation of the structures and relative stabilities of amino / nitro derivatives of ethylene in J. Mol. Struct. 452 (1998) 75-83, doi : 10.1016 / S0166-1280 (98) 00136-5 .
- ↑ K. Baum, SS Bigelow, Nguyen Nghi Van, TG Archibald, R. Gilardi, JL Flippen-Anderson, C. George: Synthesis and reactions of 1,1-diiododinitroethylene in J. Org. Chem. 57 (1992) 235– 241, doi : 10.1021 / jo00027a042 .
- ↑ a b c N.V. Latypov, J. Bemm, A. Langlet, U. Wellmar, U. Bemm: Synthesis and reactions of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene in Tetrahedron 54 (1998) 11525-11536, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (98) 00673-5 .
- ↑ NV Latypov, M. Johansson, E. Holmgren, EV Sizova, VV Sizov, AJ Bellamy: On the Synthesis of 1,1-Diamino-2,2-dinitroethene (FOX-7) by nitration of 4,6-dihydroxy- 2-methylpyrimidine in Org Process Res Dev . 11 (2007) 56-59, doi : 10.1021 / op068010t .
- ↑ M. Anniyappan, MB Talawar, GM Gore, S. Venugopalan, BR Gandhe: Synthesis, characterization and thermolysis of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) and its salts in J. Hazard. Mat. B137 (2006) 812-819, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2006.03.034 .
- ↑ B. Buszewski, M. Michel, S. Cudzilo, Z. Chylek: High performance liquid chromatography of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene and some intermediate products of its synthesis in J. Hazard. Mat. 164 (2009) 1051-1058, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2008.09.018 .
- ↑ H. Cai, Y. Shu, H. Huang, B. Cheng, J. Li: Study on Reactions of 2- (Dinitromethylene) -4,5-imidazolidinedione in J. Org. Chem. 69 (2004) 4369-4374 , doi : 10.1021 / jo030395f .
- ↑ a b Klapötke, TM: Chemistry of High-Energy Materials , 2nd Edition, 2012 Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin / Boston, ISBN 978-3-11-027358-8 , pp. 11-13, (accessed via De Gruyter Online).
- ↑ PB Kampa, M. Herrmann: Temperature resolved X-ray diffraction for the investigation of the phase transitions of FOX-7 in Part. Part. Syst. Char. 22 (2005) 418-422, doi : 10.1002 / ppsc.200501006 .
- ↑ U. Bemm, H. Östmark: 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene. A novel energetic material with infinite layers in two dimensions in Acta Cryst. C 54 (1998) 1997-1999, doi : 10.1107 / S0108270198007987 .
- ↑ a b c J. Evers, TM Klapötke, P. Mayer, G. Oehlinger, J. Welch: α- and β-FOX-7, Polymorphs of a High Energy Density Material, Studied by X-ray Single Crystal and Powder Investigations in the Temperature Range from 200 to 423 K in Inorg. Chem. 45 (2006) 4996-5007, doi : 10.1021 / ic052150m .
- ↑ a b c G. Herve; G. Jacob: Novel illustrations of the specific reactivity of 1,1-diamono-2,2-dinitroethene (DADNE) leading to new unexpected compounds in Tetrahedron 63 (2007) 953-959, doi : 10.1016 / j.tet.2006.11. 031 .
- ↑ M.-J. Crawford, J. Evers, M. Göbel, TM Klapötke , M. Mayer, G. Oehlinger, JM Welch: γ – FOX-7: Structure of a high energy density material immediately prior to decomposition in Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics 32 (2007 ) 478-495, doi : 10.1002 / prep.200700240 .
- ↑ A. Gindulyte, L. Massa, L. Huang, J. Karle: Proposed Mechanism of 1,1-Diamino-Dinitroethylene Decomposition: A Density Functional Theory Study in J. Phys. Chem. A 103 (1999) 11045-11051, doi : 10.1021 / jp991794a .
- ↑ a b c d e f g W.A. Trzcinski, S. Cudzilo, Z. Chylek, L. Szymanczyk: Detonation properties of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene (DADNE) in J. Hazard. Mat. 157 (2008) 605-612, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2008.01.026 .
- ↑ Fang, X .; McLuckie, WG: Laser ignitibility of insensitive secondary explosive 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene (FOX-7) in J. Hazard. Mat. 285 (2015) 375-382, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2014.12.006 .
- ↑ a b c d G. Herve; G. Jacob; N. Latypov: The reactivity of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) in Tetrahedron 61 (2005) 6743-6748, doi : 10.1016 / j.tet.2005.05.010 .
- ↑ a b Kangzhen Xu, Jirong Songa, Fengqi Zhao, Haixia Ma, Hongxu Gao, Chunran Changa Yinghui, Rena Rongzu Hu: Thermal behavior, specific heat capacity and adiabatic time-to-explosion of G (FOX-7) in J. Hazard . Mat. 158 (2008) 333-339, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2008.01.077 .