Unicorn (constellation)
|
Unicorn constellation |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Monoceros |
| Latin genitive | Monocerotis |
| Abbreviation | Mon |
| Right ascension | 05 h 55 m 52 s to 08 h 11 m 24 s |
| declination | −11 ° 22 ′ 08 ″ to + 11 ° 56 ′ 00 ″ |
| surface | 481,569 deg² rank 35 |
| Completely visible | 78.7 ° N to 78.5 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | winter |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 0 |
| Brightest star (size) | β monocerotis (3.76) |
| Meteor streams | |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
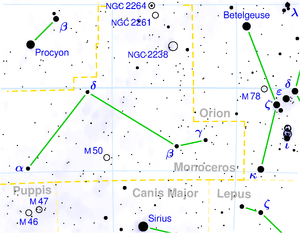
The unicorn ( Greek Monoceros ) is a constellation south of the celestial equator .
description
The unicorn is a relatively nondescript constellation east of the prominent Orion and north of the bright star Sirius in the Big Dog . It only contains two stars that are brighter than the 4th magnitude .
The ribbon of the Milky Way runs through the unicorn , so it contains a number of foggy objects, such as the open star cluster M50 and the Rosette Nebula .
history
The unicorn is not one of the classic 48 constellations of antiquity .
It is attributed to the Dutch cartographer Petrus Plancius , who in 1612 created a celestial globe on which he depicted eight new constellations, including Monoceros Unicornis .
Jacob Bartsch included it in his Planisphaerium Stellaris as Unicornus in his star maps in 1624 and ascribed a Christian motif to it: The unicorn is mentioned several times in the Latin Bible ( Vulgate ) ( Psalmi iuxta LXX 21:22, 28: 6, 91:11 ; Isaiah 34: 7); however, modern Bible translations speak of buffalo here. Plancius himself did not leave his reasons for introducing these constellations. In the Bestiaire Divin de Guillaume from the 13th century, it says that the unicorn lies quietly and can be caught when a virgin enters its hunting grounds. The unicorn is supposed to represent Jesus Christ and his horn the divine truth.
Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers and Ludwig Ideler pointed out, however, that the constellation was described before 1564. According to Joseph Scaliger , it is said to be depicted on an ancient Persian celestial globe.
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | F. | Names or other designations | Size (mag) | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | 5 | 3.76 | 691 | B3 V + B3ne | |
| α | 26th | Lukida , Lucida | 3.94 | 144 | K0 III |
| γ | 5 | 3.99 | 645 | K3 III | |
| δ | 22nd | 4.15 | |||
| ζ | 29 | 4.36 | 1853 | G2 Ib | |
| ε | 8th | 4.39 | 128 | A5 IV | |
| 13 | 4.47 | 1510 | A0 Ib | ||
| 18th | 4.48 | 373 | K0 III | ||
| 15th | 4.66 | 1023 | O7 | ||
| 28 | 4.69 | 473 | K4 III | ||
| 17th | 4.77 | 485 | K4 III | ||
| 20th | 4.91 | 211 | K0 III | ||
| 27 | 4.93 | 250 | K2 III | ||
| 3 | 3 monocerotis | 4.94 | 980 | B5 III | |
| 19th | 4.99 | 1117 | B1 V | ||
| 2 | 5.04 | 328 | A6m | ||
| HR 2205 | 5.06 | 1204 | B2 V | ||
| 10 | 5.06 | 1354 | B2 V | ||
| HR 2508 | 5.08 | 1310 | M1 II | ||
| HR 2395 | 5.09 | 537 | B5 Vn | ||
| 25th | 5.14 | 202 | F6 III | ||
| HR 2334 | 5.19 | 951 | K1 II | ||
| HR 2142 | 5.19 | 919 | B2 Vne | ||
| HR 2469 | 5.21 | 378 | M0 III | ||
| HR 2639 | 5.22 | 682 | M2 III | ||
| HR 2375 | 5.22 | 211 | A3 V | ||
| 7th | 5.27 | 824 | B2 V | ||
| HR 2267 | 5.36 | 511 | K1 III | ||
| HR 2154 | 5.37 | 2132 | B5 IV | ||
| HR 2381 | 5.43 | 870 | K2 III | ||
| HR 2572 | 5.44 | 485 | A4 IV | ||
| 21st | 5.44 | 261 | F2 V | ||
| HR 3014 | 5.49 | 238 | K5 III |
α Monocerotis is a 144 light-years distant, orange shining star of the spectral class K0 III.
γ Monocerotis is 645 light years away and belongs to the spectral class B2 IV.
Multiple stars
| system | Sizes (mag) | distance |
|---|---|---|
| β | 4.5 / 5.4 / 5.6 | 7.3 / 2.8 " |
| ε | 4.4 / 6.7 | 13.3 " |
β Monocerotis is a multiple star system 691 light years away. Three stars of the spectral class B3 orbit a common center. Since the stars are relatively far apart, they can already be observed with a small telescope . Wilhelm Herschel discovered the system in 1781 and described it as one of the most beautiful sights in the sky.
ε Monocerotis is a binary star system 128 light years away. The two components belong to the spectral classes A5 and F5. The system can also be observed with a small telescope.
Variable star

| star | Size (mag) | period | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| U | 5.8 to 7.2 | 92 days | Semi-regularly variable |
| T | 5.6 to 6.6 | 27.025 days | Cepheid |
| R. | 10 to 12 | ||
| V838 | 6.75 to 15.74 |
U Monocerotis is a semi-regularly variable star 4000 light-years away that changes its brightness over a period of about 92 days.
T Monocerotis is 8000 light years away and belongs to the luminous group of the Cepheids . Its brightness changes within a period of 27 days.
Both stars can barely be seen with the naked eye during their maximum brightness. Binoculars are required for minimum observation.
R Monocerotis is a variable star in the middle of the open cluster NGC 2261 . Due to its low brightness of 10 to 12 mag, you need a medium-sized telescope to observe it.
V838 Monocerotis is about 20,000 light years away. In January 2002 the Hubble telescope observed a violent burst of brightness.
Messier and NGC objects
| NGC | Size (mag) | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2323 | 7th | Open star cluster | Messier 50 |
| 2232 | 3.9 | Open star cluster | |
| 2236 | 7.5 | Open star cluster | |
| 2237 | 14th | Emission nebula | Part of the rosette nebula |
| 2244 | 5.8 | Open star cluster | Part of the rosette nebula |
| 2250 | 8.9 | Open star cluster | |
| 2251 | 7.3 | Open star cluster | |
| 2261 | 10.0 | Reflection fog | Hubble's Variable Nebula |
| 2264 | Open star cluster | Christmas tree fog | |
| 2269 | 10.0 | Open star cluster | |
| 2286 | 7.5 | Open star cluster | |
| 2301 | 8.0 | Open star cluster | |
| 2324 | 8.5 | Open star cluster | |
| 2335 | 7.2 | Open star cluster | |
| 2343 | 6.7 | Open star cluster | |
| 2353 | 7.1 | Open star cluster |
M 50 is an open star cluster 3000 light years away. It contains about 100 stars and can already be observed with prism binoculars . The telescope is a very beautiful sight.
The open star cluster NGC 2244 is 5000 light years away. He can also be observed with binoculars. Around the star cluster lies NGC 2237, the famous Rosette Nebula . The relatively young, bright stars of the star cluster stimulate the surrounding gas clouds to glow. However, only the densest regions can be seen in the telescope. Complex structures only become visible in long-exposure photographs.
NGC 2261 is 3000 light years away. In larger telescopes, one of its stars appears like a small comet . It is a reflection nebula called the "Hubble Nebula" or Hubble Nebula . Since the stimulating star is variable and its light is transmitted differently by the surrounding dust clouds, the brightness and size of the nebula change over weeks and months.
NGC 2264 is a star cluster 3000 light years away. Because of its triangular, pointed arrangement, it is also known as the “Christmas tree star cluster”. Its stars are surrounded by a gas nebula in which there are dark clouds of dust and gas. One of the dark clouds is the so-called Cone Nebula because of its shape .
NGC 2301 is 2,500 light years away. To resolve the star cluster, you need a telescope.
NGC 2324 is a star cluster 15,000 light years away. A large number of stars can be seen in larger telescopes.