Imazalil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
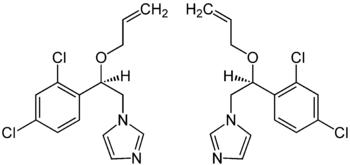
|
||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) -form (left) and ( S ) -form (right) | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Enilconazole | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 14 Cl 2 N 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 297.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.243 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
52.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
347 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water (18 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Imazalil - INN enilconazole - is a systemic fungicide from the group of imidazoles . It was developed by the Belgian company Janssen Pharmaceutica . The substance is also used in the form of its salts, e.g. B. sold as imazalil nitrate or imazalil sulfate.
synthesis
2,4-dichloroacetophenone is reacted with bromine in boiling methanol to give 2,4-dichlorophenacyl bromide , which is then condensed with imidazole to give 2,4-dichloro-α- (1-imidazolyl) acetophenone. Its reduction with sodium borohydride in boiling methanol gives 1- (2,4-chlorophenyl) -2- (1-imidazolyl) ethanol, which is finally alkylated with allyl chloride and sodium hydride in boiling dimethylformamide to give imazalil .
Mode of action
Enilconazole inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol by blocking the 14-demethylation of lanosterol . This changes the cell membrane and thus the permeability of yeast , mold and dermatophytes . In addition, the uptake of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid building blocks is inhibited and fatty acid metabolism and oxidative and peroxidative enzyme systems are disrupted. This leads to cell membrane damage and cell death. Enilconazole has a fungistatic effect, and in high concentrations also fungicidal . In addition, enilconazole is also effective against gram-positive bacteria .
use
Plant protection
Imazalil is used in the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants. The substance is contained in dressings for cereal seeds . It has a good effect against the streak disease in barley .
In Switzerland, Imazalil can be used in the greenhouse in the form of incense cones against powdery mildew on tomatoes and cucumbers. It is also part of an approved preparation for the treatment of seed potatoes. It is also found in wound closures for fruit and ornamental trees. In Germany Imazalil is only approved for the dressing of grain seeds. In Austria imazalil is next to the seed treatment for the protection of seed potatoes before Fusarium storage decay , Phomafäule and silver scurf used.
Preservatives
Similar to thiabendazole , orthophenylphenol or biphenyl , Imazalil protects citrus fruits from the formation of mold . As far as they are subject to the EU marketing standard, citrus fruits treated with Imazalil must be labeled. Treated peel should not be eaten. Imazalil does not yet have an E number .
Veterinary medicine
In veterinary medicine, Imazalil is sold under the brand name Imaverol ad us. vet. Used as a broad spectrum antimycotic against fungal diseases of the skin ( dermatomycoses ) and the nose ( sinunasal aspergillosis ) as well as in the aspergillosis of birds . It is given topically .
toxicology
Experimental animals were given as a symptom of acute poisoning one goose bumps . Imazalil seems to stimulate the hair follicles through the nervous system . There were also coordination disorders, low blood pressure, tremors and vomiting. Contact dermatitis has occurred in some susceptible individuals . The oral LD 50 was 227 mg / kg body weight (female rats) and 343 mg / kg body weight (male rats).
In long-term studies in rats, there were slight changes in the liver values , the weight gain was reduced and effects on the bilirubin balance were ascertainable. Otherwise no effects of imazalil administration were observed.
Imazalil is metabolized in the body and excreted within a few days; it does not accumulate in adipose tissue. The WHO specifies a permitted daily dose of 0.03 mg / kg.
The American environmental protection agency (EPA) classifies Imazalil as probably carcinogenic because adenomas of the liver and adenomas combined with carcinomas were found in animal experiments . Adenomas and carcinomas of the thyroid gland were also found in rats after administration of Imazalil . According to the EPA, a possible increased risk exists only for people who handle Imazalil directly or who pack citrus fruits.
Imazalil caused reproductive and developmental disorders in mice.
In its safety data sheet, Bayer indicates the toxicity of the pesticide for trout: according to this, 50% of the test organisms perish after an exposure time of 96 hours and a water content of 1.48 mg / l.
Environmental impact
Birds are relatively insensitive to Imazalil, the LD 50 for ducks or quails is around 6000 mg / kg body weight. For fish, however, it is poisonous, the LC 50 for trout is 2.5 mg / L. An oral LD 50 of 40 µg / bee was determined for bees , so imazalil is not considered to be toxic to bees.
The half-life for degradation in the soil is about half a year. Imazalil stays in the soil and does not wash out.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on Imazalil in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on 1- [2- (allyloxy) -2- (2,4-dichlorophenyl) ethyl] -1H-imidazole in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturer or distributor can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Imazalil data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 12, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e EXTOXNET: Pesticide Information Profile Imazalil (English, as of 1996).
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for imazalil nitrate : CAS number: 33586-66-2, PubChem : 443088 , Wikidata : Q72482245 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to imazalil sulfate: CAS number: 58594-72-2, EC number: 261-351-5, ECHA InfoCard: 100.055.755 , GESTIS substance database : 496440 , PubChem : 173636 , ChemSpider : 151546 , Wikidata : Q27278652 .
- ↑ Synthesis of Imazalil ( Memento of the original from February 23, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed December 24, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on enilconazole at Vetpharm, accessed on May 25, 2017.
- ↑ a b c Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Imazalil (aka enilconazole) in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 16, 2016.
- ↑ Residues of pesticides in citrus fruits from January to May 2010
- ↑ EPA: RED Facts Imazalil (PDF; 63 kB), as of February 2005, accessed on August 18, 2009.
- ↑ T. Tanaka: Reproductive and neurobehavioral effects of imazalil administered to mice. In: Reprod Toxicol . 9 (1995), pp. 281-288.
- ↑ Bayer CropScience Safety Data Sheet in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006, as of January 22, 2013, accessed on March 15, 2013.
- ↑ Werner Perkow: Active substances in pesticides and pesticides . 3rd edition, Erg. Current issue April 1996, Paul Parey publishing house.



