Indus
|
Indus Sindhu, Sindh |
||
| Data | ||
| location | PR China , India , Pakistan | |
| River system | Indus | |
| Confluence of | Source streams at Sênggêkanbab in the Gar district in the Transhimalaya 31 ° 25 ′ 7 ″ N , 81 ° 35 ′ 48 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 5300 m | |
| muzzle |
Arabian Sea at Sindh Coordinates: 23 ° 59 ′ 11 " N , 67 ° 26 ′ 13" E 23 ° 59 ′ 11 " N , 67 ° 26 ′ 13" E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 5300 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 1.7 ‰ | |
| length | 3180 km | |
| Catchment area | 980,000 km² | |
| Drain |
MQ |
3850 m³ / s |
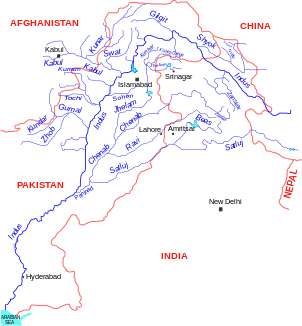
| Left tributaries | Zanskar , Yapola , Suru , Astor , Siran , Haro , Sohan , Panjnad | |
| Right tributaries | Kabul , Shyok , Shigar , Gilgit , Gomal , Kurram | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Diamer-Basha Reservoir (under construction), Tarbela Reservoir , Jinnah Reservoir , Chasma Reservoir , Taunsa Reservoir , Guddu Reservoir , Sukkur Reservoir , Kotri Reservoir | |
| Big cities | Hyderabad | |
|
River bed of the Indus at Skardu |
||
|
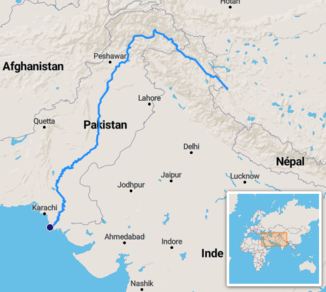
Course of the Indus |
||
|
Mouth of the Zanskar (from above) into the Indus (from left) in Ladakh |
||
The Indus ( Sanskrit सिन्धु Sindhu , Urdu سندھ Sindh ) is the longest river on the Indian subcontinent at 3,180 km and the most important river in Pakistan .
River course
The upper reaches of the Indus arise in the Chinese Transhimalaya in Tibet from the confluence of glacial streams at Sênggêkanbab and in the People's Republic of China bears the official name Sênggê Zangbo ( Tibetan སེང་གེ་ གཙང་ པོ Wylie seng ge gtsang po ), which one also flows through Large community carries. The river breaks through the Himalayas and then flows through the Tarbela Reservoir (254 km²; 13.69 km³) and the provinces of Punjab and Sindh in Pakistan. There it forms a delta of 7800 km² below Hyderabad and then flows into the Arabian Sea . In its middle reaches the river is the basis for extensive irrigation systems for agriculture. There the largest agricultural irrigation area on earth is supplied by a large number of dams and canals . The river meanders very strongly in the middle and lower reaches . A treaty between India and Pakistan ( Indus Water Treaty 1960 ) regulates the water supply. The amount of water carried varies greatly due to the monsoons .
Dams
The following dams are located along the course of the Indus River (sorted in the direction of discharge):
- Diamer-Basha Reservoir (under construction)
- Tarbela dam
- Jinnah Dam
- Chasma Dam
- Taunsa dam
- Guddu dam
- Sukkur Dam
- Kotri Dam
etymology
The name “Indus” goes back to the ancient Greek , more precisely: the Ionian dialect , which did not know the sound “h” ( Ἰνδός Indos ) and Old Persian ( Hinduš ) from the Sanskrit word सिन्धु sindhu meaning “river”. The name "India" is derived from the name of the river. The name of the Indus in the South Asian languages (e.g. Urdu سندھ Sindh ) is derived directly from the Sanskrit form. The province of Sindh , located on the lower reaches of the Indus, also got its name from the river.
history
The early Indus culture in the valley of the Indus River, one of the oldest civilizations in the world, is also called the Indus civilization. The Indus marks the extreme eastern limit of the empire of Alexander the Great . With his army he went down the Indus.
In 2010, in the wake of the flood disaster in Pakistan, the entire course of the river was flooded.
See also
literature
- James L. Wescoat Jr .: The Indus River Basin as a Garden . In: The garden art . tape 24 , no. 1 , 2012, p. 33-41 .
Web links
- Pakistan Water Gateway: Indus basin ( Memento of April 4, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Article Indus in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)