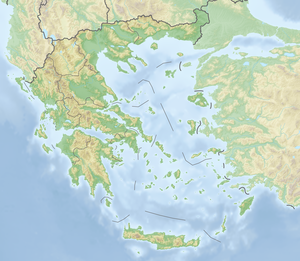
Ionian islands
| Ionian islands | ||
|---|---|---|
| View on Corfu | ||
| Waters | Mediterranean Sea | |
| Geographical location | 38 ° 25 ′ N , 20 ° 30 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| Number of islands | approx. 50 | |
| Main island | Corfu | |
| Location of the Ionian Islands archipelago | ||
The Ionian Islands ( Greek Ιόνια Νησιά Iónia Nisiá , after the seven main islands in Greek often also called Eptánisa Επτάνησα or Eptánisos Επτάνησος, in German “Seven Islands” or rarely “Heptanesos”) are a group of islands in the Greek west coast of the Ionian Sea Albania extends in the north to the Peloponnese in the south. The northern islands (main islands from north to south: Corfu , Paxos , Lefkada , Ithaka , Kefalonia and Zakynthos ) form what is now the Greek region of the Ionian Islands ; Kythira (together with Andikythira) belongs to the prefecture of Piraeus in the Attica region . The Ionian Islands also include some coastal islands in the south of the Peloponnese region .
The name has nothing to do with Ionia (Greek: Ἰωνία or Ἰωνίη), a classic Greek landscape on the west coast of Asia Minor. This is written with an omega ω, in contrast to the omicron in the name of the island group.
history
Until 1797 the islands belonged to the Republic of Venice . After the conquest of Venice by Napoléon Bonaparte , they came under French rule and in 1800, under the Russian-Ottoman protectorate, they formed the Republic of the Ionian Islands , the first modern Greek state. From 1807 to 1814 they were again under Napoleonic rule, after the fall of Napoleon the British took power over what was initially known as the "United States of the Seven Islands". Under the British protectorate, the domestically autonomous “United States of the Ionian Islands” was formed in 1817. In 1864, after a vote in parliament, the Ionian Islands joined the Greek state , which has been independent since 1830 , to which they have belonged ever since.
Culture
Corfu did not arrive until 734 BC. In the Greek culture area. In contrast, Lefkada, Ithaka, Kefalonia and Zakynthos were already an integral part of the early Greek Mycenaean culture . Later they formed the western border of the Eastern Roman Empire. During the Venetian rule there was a lively cultural exchange. The Venetian language was spoken until the 1950s.
As part of Napoleonic France and then English protectorate, these two epochs also left cultural traces. Austria also had geographical influence with the port of Trieste, from which the islands were connected to Central Europe. Numerous conservatories testify to the importance of classical music to this day, better-known pieces from the Ionian School are the Olympic Anthem and the Hymn to Freedom (Greek national anthem) .
geography
Belong to the Ionian Islands region
- the Kerkyra regional unit with
- the Lefkada regional unit with
- the regional unit of Kefalonia with
- The Echinaden in front of the Acheloos estuary, including Oxia , are spread over the districts of Kefalonia and Ithaka.
Belong to the Peloponnese region
Belong to the Attica region in the Islands regional unit
The island of Sason , which is now called Sazan , officially belonged to the Republic of the Ionian Islands until 1914 . However, it lies in the Adriatic Sea. During the First World War, the island was occupied by Italy and then went to Albania.
With the Flora Ionica project, the University of Vienna has been researching the flora of the islands since 1985.