Yegorlyk
|
Jegorlyk Егорлы́к, Большо́й Егорлы́к (Bolshoi Jegorlyk, Great Jegorlyk) |
||
|
Egorlyk at Stanitsa Novotroitskaya |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 05010500312107000016716 | |
| location | Stavropol Region , Rostov Oblast , Kalmykia ( Russia ) | |
| River system | Don | |
| Drain over | Manych → Don → Sea of Azov | |
| source | 30 km south of Stavropol 44 ° 46 ′ 2 ″ N , 42 ° 4 ′ 43 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 580 m | |
| muzzle |
Proletarsk Reservoir 25 km northwest of Salsk Coordinates: 46 ° 32 '58 " N , 41 ° 51' 3" E 46 ° 32 '58 " N , 41 ° 51' 3" E |
|
| Mouth height | 13 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 567 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 1.3 ‰ | |
| length | 448 km | |
| Catchment area | 15,000 km² | |
| Drainage at the Nowy Jegorlyk gauge |
MQ |
38.2 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Kalaly, Rassypnaya, Bolshaya Sandata | |
| Right tributaries | Tashla, Bolshaya Kugulta, Bashanta | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Sengileevskoye, Egorlykskoye, Novotroitskoye | |
| Small towns | Solnechnodolsk | |
| Communities | Novotroitskaya , Krasnogwardeiskoye | |
|
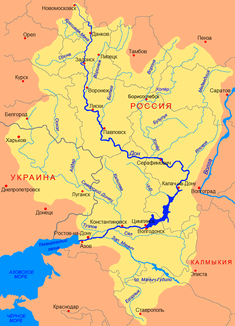
Location of the Jegorlyk (Егорлы́к) in the southern catchment area of the Don |
||
The Jegorlyk ( Russian Егорлы́к, Большо́й Егорлы́к ( Bolshoi Jegorlyk ); also "Great Jegorlyk") is a 448 km long left tributary of the Manych in Russia .
course
The Jegorlyk rises in the foothills of the Greater Caucasus about 30 km south of the city of Stavropol , in the Stavropol Heights at about 580 m altitude on the northeast flank of the 831 m high mountain Strischament . It initially flows in a north-westerly direction through the mountainous area in the southwest of the Stavropol region . To the southwest of Stavropol, the river - is diverted from the original bed for a few kilometers into a right side valley, in which the Sengileevskoye Lake used to be, which was converted into the much larger Sengileevskoye reservoir . The reservoir is mainly fed by the 50-kilometer-long Nevinnomyssk Canal , which takes water from the Kuban near Nevinnomyssk in order to direct it into the Jegorlyk Basin. Some of the water from the canal, bypassing the reservoir, also flows directly into the Jegorlyk below the lake via a branch canal, where it powers a small hydroelectric power station .
In the further course of the Jegorlyk, other smaller reservoirs were built, such as the Jegorlyk Reservoir (Jegorlykskoe Reservoir) a few kilometers below at the village of Sengilejewskoje and the Novotroitsk Reservoir (Novotroitskoje Reservoir) at the Stanitsa Novotroitskaya . The Jegorlyk flows through the steppe landscape , which is gradually becoming more level, in a north-easterly, then almost in a westerly direction. At Privolnoye it reaches Rostov Oblast , where it turns again in a north-easterly to north-easterly direction. On a short section it marks the border with the Republic of Kalmykia .
25 km northeast of the city Salsk finally ends of Yegorlyk River in just 13 m high in the Don creek Manytsch that as the boundary between for a common definition of Europe and Asia is considered. The Manych is dammed up on this section, as is the lower reaches of the Jegorlyk to the Proletarsk Reservoir (Proletarskoje Reservoir). However, this part of the reservoir is practically completely silted up by the sedimentation of the Jegorlyk. Previously, the dammed up Jegorlyk lower course was several hundred meters wide. Above the dammed section, the river is 50 to 100 meters wide and two meters deep; its flow velocity is 0.4 m / s.
The most important tributaries of the Jegorlyk are Taschla, Bolshaya Kugulta (Great Kugulta) and Baschanta from the right and Kalaly, Rassypnaja and Bolshaya Sandata (Great Sandata) from the left.
There are no cities directly on the river, but apart from Stavropol and Salsk, the city of Isobilny is also nearby. The larger towns of Solnechnodolsk ( urban-type settlement ), Novotroitskaya and Krasnogwardeiskoje ( district administrative center ) are located directly on the river .
Hydrology
The catchment area of the river covers 15,000 km².
The mean flow rate in the village of Nowy Jegorlyk near the mouth is 38.2 m³ / s. Before the completion of the Newinnomyssk Canal in 1948 and thus the supply of up to 75 m³ of water per second, the Jegorlyk in the lower reaches of the river dried out for up to 3–4 months in the summers. The flow rate, which has since increased several times over the natural one, has led to increased lateral and deep erosion of the river bed and sand deposits in other places, mainly from the middle reaches to the siltation of the Proletarsk reservoir.
fauna
The settlement of neozoa in the catchment area of the Jegorlyk is worth mentioning . These include the spotted catfish ( Ictalurus punctatus , "Channel catfish"), which was imported from the USA ( Arkansas ) for fish farming in the 1970s and which subsequently spread outside of the fish farms. Another fish is the gudgeon species Romanogobio pentatrichus , which migrated independently from the Kuban, its original area of distribution, via the Nevinnomyssk Canal.
Use and infrastructure
The Jegorlyk is not navigable.
The entire length of the river flows through intensively agricultural area, for which the water is used for irrigation . The largest part is taken from the Novotroitskoye Reservoir via the Right Jegorlyk Canal (Prawo-Jegorlykski kanal) .
Several small hydropower plants were built on the upper reaches of the river, which are now operated by the Filiate Kuban-Wasserkraftwerk-Kaskade (Kubanski kaskad GES) from RusHydro :
- Sengilejewskoje hydropower plant ( Sengilejewskaja GES , power 15 MW , built 1949–1953 at the outlet of the Nevinnomyssk Canal to the Jegorlyk)
- Jegorlyk hydropower plant ( Jegorlykskaja GES , 30 MW, 1956–1962)
- Jegorlyk-2 hydropower plant ( Jegorlykskaja GES-2 , 14.2 MW, 1994-2010)
- Novotroitsk hydropower plant ( Novotroitskaya GES , 3.68 MW, 1950–1953)
The construction of the Jegorlyk-2 hydropower plant ( Jegorlykskaja GES-2 ), which began in 1994, was initially delayed due to financial difficulties, was resumed in 2005 after being taken over by RusHydro and completed at the end of 2010. The reservoir of the Novotroitsk hydropower plant is also used for the cooling water supply of the Stavropol thermal power plant (Stavropolskaja GRES) , which is operated by OGK-2 and is the largest in the North Caucasus with an output of 2400 MW.
A number of other reservoirs directly on the Jegorlyk or in its valley basin are used for fish farming, for example at Ptitschje north of Isobilny.
The upper reaches of the Jegorlyk is crossed by a branch of the M29 trunk road , which connects the regional capital Stavropol to the main route between Nevinnomyssk and Kochubeevskoye . The railway line from Kropotkin ( Kawkasskaya station ) to Stavropol and Elista crosses the river below Novotroitskaya and Isobilny, the regional road R269 ( Rostov-on-Don -) Bataisk - Stavropol near the village of Besopasnoye , which follows the middle course on the left .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Article Jegorlyk in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Jegorlyk in the State Water Register of the Russian Federation (Russian)
- ↑ Article Newinnomyssk Canal in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ A. Mišvelov, E. Olejnikov: channel ' nyj somik verchnego i srednego tečenija r. Bol ʹ šoj Egorlyk . In: Rossijskij žurnal biologičeskich invazij . No. 1 , 2008 ( The spotted catfish of the upper and middle reaches of the Great Jegorlyk ; Russian, PDF ).
- ↑ Area expansion of freshwater fish in the waters of Russia on the website of the Zoological Institute of the RAN (Russian)
- ↑ Sengileevskoye hydropower plants on the RusHydro website (Russian)
- ↑ Press release ( Memento of the original from July 17, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. by RusHydro on December 29, 2010 (Russian)
- ↑ Stavropol thermal power plant on the OGK-2 website (English, Russian)