Water lily plants
| Water lily plants | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

White water lily ( Nymphaea alba ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Nymphaeaceae | ||||||||||||
| Salisb. |

The water lily plants (Nymphaeaceae) are a family of plants in the order of the water lily-like (Nymphaeales). With 58 (to 75) species in five genera , the Nymphaeaceae are one of the small families of flowering plants. Outside of the polar climatic zones, it is only found in freshwater worldwide.
Description and ecology
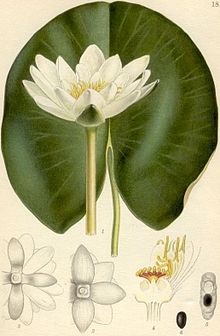

Appearance and leaves
Most of the species in the Nymphaeaceae family are perennial , rarely annual , herbaceous plants . They are all aquatic plants anchored in the bottom of the water with adventive roots with creeping or upright, branched or unbranched rhizomes , which can be bulbous and thickened, as persistence organs that form stolons in some species. The rhizodermis is divided into long and short cells. There is no secondary growth in thickness . They have scattered vascular bundles without cambia and without trachea . The sieve tube plastids have no protein crystalloids. A milky sap is present in the plants . There are very clear air chambers in the vegetative parts of the plant.
Underwater and floating leaves can be used as leaves . The alternate and spiral leaves are simple and petiolate. The simple leaf blade is often heart-shaped to circular, shield-shaped (peltat) and network-veined. The leaf margin is smooth or spiky-serrated. There may be stipules .
blossoms
The flowers are solitary, lateral on often long pedicels on or above the water level, they rarely bloom below the water level. The large, hermaphrodite, more or less radial symmetry flowers are often fragrant. The petals are partially helical (acyclic). The bracts can continuously change into nectar leaves and these into stamens. The inflorescence usually consists of two circles. The five or 20 to 50 free, mostly green sepals can be corolla-like ( Nuphar ). The five ( Nuphar ) or 15 to 50 petals are yellow or white over pink to purple and blue; they are seldom missing. There are 40 to 80 centripetally developing, spirally arranged, free stamens , 11 to 20 of which can be staminodes (in Nuphar there are nectar-forming scales). The stamens are broad to slender. The anthers are tetrasporangiat and a connective appendage may be present. The five to 35 above to semi-permanent under constant carpels (carpels) are partially or completely fused. There are ten to a hundred ovules per carpel. The scars sit directly, usually without a stamp, in a circle on a disc.
The flowers are open during the day or night, depending on the species. The pollination is done by insects (mostly beetles , Entomophilie ).
Fruits and seeds
The fleshy fruits, often surrounded by the bracts, are berry-like and contain a few or many seeds. The fruits, which are often embedded in the fleshy flower base, usually open by swelling of the inner mucus. The seeds have a small endosperm and usually an aril . The embryo is relatively small. The seeds of many species can swim through air pockets in the aril and the seed wall. There are two fleshy seed leaves ( cotyledons formed).
The ingredients are ellagic acid and gallic acid .
Systematics
The Nymphaeaceae family was founded in 1805 by Salisb. in Ann. Bot. (King & Sims), Published 2 June 1805, p. 70. The Barclayaceae HLLi , Euryalaceae J.Agardh and Nupharaceae A.Kerner used to be independent families whose genera are now assigned to the Nymphaeaceae.


Subfamilies with genera
In the family Nymphaeaceae there are two subfamilies with five genera and 58 to 75 species:
- Subfamily Nupharoideae M. Ito (Syn .: Nupharaceae A.Kerner ): It contains only one genus with eight to eleven species:
- Lake roses ( Nuphar Sm. , Syn .: Nymphozanthus Rich. ): It contains two sections with eight to eleven species. It is widespread in the northern hemisphere in the Holarctic and in directly adjacent subtropical areas.
- Subfamily Nymphaeoideae : It contains four genera with about 48 (up to 60) species:
- Barclaya Wall. (Syn .: Hydrostemma Wall. ): The four or so species are common in Southeast Asia.
-
Euryale Salisb. : It contains only one type:
- Barbed water lily ( Euryale ferox Salisb. ): It occurs from Kashmir to Assam and China .
- Water lilies ( Nymphaea L. , Syn .: Castalia Salisb. , Leuconymphaea Kuntze ): It is divided into two groups, five sub-genera and contains about 40 (up to 53) species. The spread is almost worldwide.
- Giant water lilies ( Victoria Lindl. ): The only two species are common in South America .
use
Some species, but especially hybrids, are used as ornamental plants in parks and gardens. The red Barclaya longifolia and Barclaya motleyi are used as aquarium plants . The flowers of Nymphaea odorata are popular because of their strong scented flowers, especially in the morning.
In some species, the subterranean plant parts are eaten raw or cooked or starch is extracted from them ( Nuphar advena , Nuphar japonicum , Nuphar lutea , Nuphar polysepala , Nuphar pumila , Nymphaea alba , Nymphaea odorata , Nymphaea tetragona , Nymphaea tuberosa ). In some species, the seeds are used raw, cooked or roasted to make flour ( Nuphar advena , Nuphar lutea , Nuphar polysepala , Nuphar pumila , Nymphaea alba , Nymphaea odorata , Nymphaea tetragona , Nymphaea tuberosa ). The leaves of Nuphar lutea , Nuphar pumila and Nymphaea odorata are cooked or, in some species, eaten raw. A soft drink is made from the flowers of Nuphar lutea and Nuphar pumila . Roasted seeds of Nymphaea alba serve as a coffee substitute. The flower buds of Nymphaea odorata are eaten cooked as vegetables or pickled.
The healing properties of some species have been studied.
swell
- The family of Nymphaeaceae in APWebsite . (engl.)
- The Nymphaeaceae family at DELTA by L. Watson & MJ Dallwitz. (Section description)
- Leslie Watson, 2008: Nymphaeaceae in the Western Australian flora .
- Bernard Verdcourt: Nymphaeaceae , Flora of Tropical East Africa , Royal botanic gardens Kew, 1989, 12 pages.
- John H. Wiersema, C. Barre Hellquist: Nymphaeaceae - the same text online as the printed work , In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico , Volume 3 - Magnoliidae and Hamamelidae , Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 1997, ISBN 0-19-511246-6 .
- Dezhi Fu, John H. Wiersema, Donald Padgett: Nymphaeaceae , p. 115 - the same text online as the printed work , In: Wu Zhengyi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Ed.): Flora of China , Volume 6 - Caryophyllaceae through Lardizabalaceae . Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2001, ISBN 1-930723-05-9 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Nymphaeaceae in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved January 3, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Walter Erhardt , Erich Götz, Nils Bödeker, Siegmund Seybold: The great pikeperch. Encyclopedia of Plant Names. Volume 2. Types and varieties. Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart (Hohenheim) 2008, ISBN 978-3-8001-5406-7 .
- ↑ Christel Kasselmann : aquarium plants. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart 1995; 2nd edition 1999, ISBN 3-8001-7454-5 , pp. 148-150.
- ↑ a b c Entries on Nymphaeaceae in Plants For A Future
Web links
- Entry with the Flora of Zimbabwe . (English)
- Entry in the Tree of Life project. (English)



