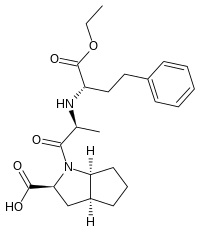
Ramipril
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Ramipril | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(2 S , 3a S , 6a S ) -1 - {( S ) - N - [( S ) -1-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl] alanyl} -octahydrocyclopenta- [ b ] pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 32 N 2 O 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 416.51 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
109 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water (11.2 mg l −1 at 25 ° C), slightly soluble in methanol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Ramipril is a medicine in the group of ACE inhibitors that is used to treat arterial hypertension (high blood pressure), heart failure and to prevent heart attack . Ramipril belongs to a group of so-called second generation ACE inhibitors . Ramipril itself is an inactive prodrug . After activation to ramiprilat by hydrolytic cleavage of ethanol, its active principle is based on the inhibition of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
chemistry
The connection comes from the pharmaceutical research of the former Hoechst AG (Hoe 498). It was filed for a European patent in 1983 and was also patented in the USA. In 1984 the inventors Volker Teetz, Rolf Geiger, Rainer Henning and Hansjörg Urbach reported on their synthesis in a specialist journal.
The model of the active ingredient was the ACE inhibitor enalapril , whose proline part is replaced by the bicyclic unnatural amino acid (all- S ) -octahydrocyclopenta [b] pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid (2-azabicyclo [3.3.0] octane-3-carboxylic acid) was replaced. In other words: the proline part was fused with a cyclopentane ring . The basic structure also contains the α- amino acid ( S ) - alanine , which is often present in ACE inhibitors , the amino group of which is linked to the C-2 atom of the ethyl 4-phenylbutyric acid ester. The compound could also be viewed as a derivative of ( S ) -homophenylalanine.
synthesis
The bicyclic building block was created by alkylating pyrrolidinocyclopentene with a chlorinated serine derivative . The reaction product was treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, all protective groups being split off, and an iminium salt formed. This was catalytically hydrogenated. In this case, the addition of the hydride hydrogen atom takes place on the same side as the hydrogen atom present on the adjacent bridgehead atom, i.e. H. the two five-membered rings are cis -linked (cf. e.g. Decalin ). They form a concave partial structure. The carboxylic acid group (COOH) protrudes 'inside' the folded molecule, in other words it occupies the endo position.
The endo-cis acid formed exclusively , a racemate , was converted into the benzyl ester. This racemate could with chiral auxiliaries, i. H. be broken down into the enantiomers via salts with chiral acids : (R, S, S) - and (S, S, S) -2-azabicyclo [3.3.0] octane-3-carboxylic acid benzyl ester. The latter was used for peptide linkage.
The larger building block was created by the addition of L-alanine benzyl ester, i. H. with ( S ) configuration , built up on ethyl 4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-enoate with ( E ) configuration.
This prochiral molecule can be linked to the 'front' or 'rear' with the NH 2 group of the chiral amino acid ester, whereby diastereomers with ( S, S ) - and ( R, S ) -configuration can be formed. The reaction product at room temperature consists of a mixture of both stereoisomers. The desired ( S, S ) -diastereomer predominates (approx. 2: 1). At a higher temperature, a chemical equilibrium is established , which could be used to further enrich the ( S, S ) -compounds. On the principle of a diastereoselective synthesis planning, i. H. chiral economy, this reaction step is the critical step.
Hydrogenolysis in the presence of a palladium catalyst removed the benzyl protecting group and also reduced the keto group, so that the aimed carboxylic acid was obtained. This has now been condensed with the bicyclic proline derivative. Finally, the remaining benzyl protective group was again removed by hydrogenolysis.

pharmacology
Ramipril is an inactive prodrug, which was achieved by esterifying the free carboxylic acid function with ethanol . This ethyl ester is hydrolyzed in the organism in the liver by esterases , whereby the active, so-called ramiprilat (better would be 'ramipril diacid') is formed. In the structural formula, the active metabolite is shown as a dicarboxylic acid; Since it also contains a basic NH atom, the compound must preferably be present as a zwitterion under physiological conditions .
The mechanism of action of ramipril based on the fact that its metabolite ramiprilat inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme ( inhibited ). With the zinc ion contained as a cofactor , it forms a stronger complex than angiotensin I , which is less converted into angiotensin II . This causes a decrease in the tone of blood vessels, and therefore a decrease in blood pressure. The decrease in the angiotensin II level also leads to a reduction in the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex and thus to an influence on the water balance.
Analytics
The reliable qualitative and quantitative determination of ramipril is possible after appropriate sample preparation by combining HPLC with mass spectrometry .
Therapeutic use
application areas
Ramipril is used individually (monotherapy) and in combination with other antihypertensive drugs (combination therapy, especially with diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide or calcium channel blockers ), mainly for the treatment of high blood pressure. It is also considered the first choice for the treatment of heart failure. Ramipril has also been shown to be effective in the prophylaxis (prevention) of myocardial infarction in several clinical studies .
Ramipril is also used in veterinary medicine to treat heart failure .
An extension of walking distance, probably through vasodilation , has been described.
Side effects
Most of the side effects of ramipril have been associated with slower breakdown and accumulation of bradykinin due to ACE inhibitors . These include skin reactions such as B. exanthema and hives , also angioedema . Serious allergic skin reactions, however, are only very rarely observed.
Airway side effects often include a dry cough. Hoarseness and a sore throat can also occur. Asthma attacks and shortness of breath can also occur, albeit rarely.
As a result of the main action of ramipril, it may decrease blood pressure too much. As a result, dizziness, headache, and drowsiness may occasionally be observed. Severe cardiovascular events such as chest tightness , myocardial infarction and syncope have only been reported in isolated cases.
Functional kidney dysfunctions can occasionally be observed through interference with the water and electrolyte balance. Proteinuria (excretion of proteins in the urine), however, has only rarely been observed.
Since ramipril in pregnancy can, among other things growth and bone formation disorders associated with the child cause with increased mortality, ramipril should not be used at this time and should be replaced by other suitable therapeutic measures.
Interactions
Ramipril enhances the blood sugar lowering effects of insulin and oral antidiabetic drugs and the blood count-altering effects of immunosuppressants .
By interfering with the water and electrolyte balance, the elimination of electrolytes can be slowed down, causing them to accumulate in the body. This should be taken into account especially in the case of therapy with lithium or potassium-sparing diuretics, since the simultaneous use of ramipril can increase the plasma level of lithium or potassium critically.
When combined with other antihypertensive drugs, increased blood pressure lowering should be taken into account.
Trade names
Delix (D), Hypren (A), Lannapril (A), RamiLich (D), Triatec (CH), Tritace (A), Vasotop (D, Vet.) Vesdil (D), numerous generics (D, A, CH )
- In combination with hydrochlorothiazide : Delix plus (D), Hypren plus (A), Lannapril plus (A), Triatec comp. (CH), Tritazide (A), Generics (D, A, CH)
- In combination with furosemide : Lasitace (A)
- In combination with amlodipine : Tonotec (D), Generika (D)
- In combination with Piretanid : Trialix (CH), Arelix ACE (D), Generika (D)
- In combination with Felodipine : Unimax (D), Delmuno (D)
- In combination with atorvastatin and acetylsalicylic acid : Sincronium (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 5TH EDITION . tape 5.0-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b Entry on ramipril in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Ramipril data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Specialist information Delix (PDF; 120 kB) as of September 2010, accessed on March 6, 2012.
- ↑ Volker Teetz et al. Eur. Pat. Application 79022 (1983) for Hoechst AG. Chemical Abstracts Vol. 100 (1984), 52012h.
- ^ V. Teetz, R. Geiger, R. Henning, H. Urbach: Synthesis of a highly active angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor: 2- [N - [(S) -1-ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl] -L-alanyl] - (1S, 3S, 5S) -2-azabicyclo [3.3.0] octane-3-carboxylic acid (Hoe 498) . Pharmaceutical Research / Drug Research, Vol. 34 (1984), pp. 1399-1401.
- ↑ Dubey R, Ghosh M: Simultaneous Determination and Pharmacokinetic Study of Losartan, Losartan Carboxylic Acid, Ramipril, Ramiprilat, and Hydrochlorothiazide in Rat Plasma by a Liquid Chromatography / Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method. , Sci Pharm. 2014 Nov 30; 83 (1): 107-24, PMID 26839805
- ↑ Gupta VK, Jain R, Lukram O, Agarwal S, Dwivedi A: Simultaneous determination of ramipril, ramiprilat and telmisartan in human plasma using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. , Talanta. 2011 Jan 15; 83 (3): 709-16, PMID 21147310
- ↑ M McGrae: "Improving walking performance in peripheral artery disease"; JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association, 2013; 309 (5): 487-488; PMID 23385276 .


