Sababurg Zoo
| Sababurg Zoo | ||
|---|---|---|
| place | Sababurg 1 34369 Hofgeismar |
|
| surface | 130 ha | |
| opening | 1973 | |
| Animal species | about 80 | |
| Individuals | approx. 900 | |
| Visitor numbers | 352,000 (2019) | |
| organization | ||
| management | Uwe Pietsch | |
| Sponsorship | District of Kassel | |
|
View from the zoo to the Sababurg |
||
| www.tierpark-sababurg.de | ||
|
|
||
Coordinates: 51 ° 32 ′ 43 " N , 9 ° 32 ′ 7" E
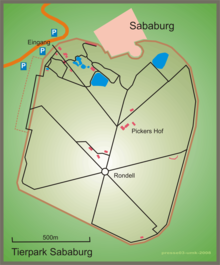
The Sababurg zoo is a wildlife park on the Sababurg (formerly also called Zapfenburg ) in the Reinhardswald in the northern Hessian district of Kassel . It was created as a zoo in 1571 ( Thiergarten an der Zapfenburg ) and has been known as the Sababurg zoo since 1973 . With an area of around 130 hectares, it is one of the largest and oldest wildlife parks in Europe. Long oak avenues run through the park, which is bordered by the Sababurg primeval forest to the west . The park also houses native animal species that are threatened with extinction, and species-appropriate husbandry is strived for through spacious outdoor enclosures.
Geographical location
The Sababurg zoo is part of the Beberbeck district of Hofgeismar , in the core area of the Reinhardswald, between Beberbeck , about 4 km west-southwest, and Gottsbüren , a district of Trendelburg, about 4.5 km north-northwest . It spreads out directly below the Sababurg, which stands on a basalt dome, and is located between 275 m (at the entrance in the north) and 355 m above sea level. NN (near the Kasseler Tor in the south). The Donnebach , a small, right-hand tributary of the Holzape , flows through the eastern and northern park areas in a south-east-north-west direction . West to the park borders of the unincorporated area Gutsbezirk Reinhardswald belonging jungle Sababurg .
History - 1571 to 1973

The Sababurg , built as a Zappenburg from 1334 , underwent a renovation and expansion into a Renaissance hunting lodge with stud from 1490 by Landgrave Wilhelm I (1466–1515) . In the following 70 years, extensive horse paddocks and pastures were built below the castle, now known as the "Zapfenburg" . Landgrave Wilhelm IV (1532–1592), who was very interested in natural sciences, had the site enclosed between 1567 and 1571 with a five-kilometer-long and three-meter-high wall made of rubble stones . For hunting and research, part of the area was equipped with aurochs , fallow deer , white red deer , chamois , elk and reindeer . In addition to the paddocks for the stud horses, the Thiergarten at the Zapfenburg , which is not open to the public , was created, the first of its kind in Europe.
In 1724, Landgrave Carl von Hessen (1654–1730) had the horse stud moved to Beberbeck. Parts of the zoo continued to be used as pasture, while the game gates were covered with trees.
After the occupation by French soldiers from 1760 to 1763 during the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the Sababurg was only used as a forester's house and fell into disrepair. Under Landgrave Friedrich II (1720–1785), the park was redesigned around 1770, in keeping with the Baroque zeitgeist, making it suitable for parforce hunting . A roundabout was created , towards which six aisles led from the surrounding wall in a star shape, which can still be recognized today as oak avenues . With this redesign, the avenue that runs almost straight from Holzhausen to Sababurg was moved to a path outside the zoo. At that time, the zoo was actually no longer one because the Hessian landgraves had lost interest in it at the end of the 18th century. Most of the trees were cut down and the game gates removed in order to obtain more pasture space for Beberbeck horse breeding.
Horses were bred in Beberbeck until 1928 and the Sababurg zoo was used exclusively as pasture, after which it was used as an agricultural area for the Prussian state domain of Beberbeck. After 1945, when Beberbeck and Sababurg including the former zoo belonged to the Hessian Hofgeismar and thus to the district of Kassel, there were increased efforts to revive the zoo as such. The onset of tourism around the Sababurg , the ruins of which were converted into an upscale hotel and restaurant in 1959, and the diplomatic hunts introduced in Reinhardswald at the time of the Hessian Prime Minister Georg-August Zinn (1901–1976) encouraged public and political interest in reactivation. The zoologist Hans Georg Picker played a key role in the conceptual design and rebuilding of the zoo . Under his leadership and the sponsorship of the district, the zoo was reopened in 1973.
History - since 1973
concept













Basically, the old, still existing zoo wall was retained as the outer border of the new wildlife park. It was restored along its entire length and only broken through on the southwest flank for an additional outdoor area. The entrance is in the northwest corner of the area, right next to the large parking lot.
The layout of the zoo and the route largely correspond to the last baroque complex. The roundabout in the southern third of the park forms its center again, from which six oak-lined avenues lead to the outer wall. Two further avenues are located in the first third behind the entrance, so that the park is strictly divided into eight areas almost symmetrically. Six of them are partially forested, 10 to 20 hectares of wild meadows.
There are aviaries at the roundabout and along the southwest wall . The created water areas include two larger ponds, a branched small pond system for otters as well as a basin each for penguins and raccoons. A bird of prey station was set up on the slope of the castle hill .
In addition to animal husbandry and breeding facilities, the zoo's infrastructure also includes a petting zoo and playgrounds, a zoo museum, a culture and church barn, the Pickers Hof school farm and an inn.
Today's concept for the zoo includes three main topics:
-
Urwildpark : In addition to keeping the endangered, native wild animal species, livestock breeds that are thought to have a certain resemblance to their extinct ancestors, such as the Heck cattle, are kept. To commemorate the historical career, different species of deer are kept as in the times of the landgraves. The wildlife park includes the following species:
- Eurasian river otter ( Lutra lutra )
- European pond turtle ( Emys orbicularis )
- European fallow deer ( Dama dama )
- Dybowski deer ( Cervus nippon hortulorum )
- European red deer ( Cervus elaphus elaphus )
- Maral deer (Asiatic red deer) ( Cervus elaphus sibiricus )
- Elk (North American Red Deer) ( Cervus canadensis nelsoni )
- Exmoor pony ( Equus ferus )
- Przewalski's horse (Thaki) ( Equus ferus przewalskii )
- Heck horse ( Equus ferus f. Caballus )
- Heck cattle ( Bos primigenius f. Taurus )
- Mouflon (European wild sheep) ( Ovis ammon musimon )
- Eurasian lynx ( Lynx lynx )
- Reindeer (caribou) ( Rangifer tarandus )
- Wolverine (Järv, Bear Marten) ( Gulo gulo )
- West Caucasian Ibex (Tur) ( Capra caucasica )
- European bison ( Bison bonasus )
- Wild boar ( Sus scrofa )
- Wolf ( Canis lupus )
- Archepark : Old domestic and farm animal breeds have often become economically insignificant for our agriculture and are threatened with extinction. Special importance is attached to their rearing and keeping.
- Children's zoo : Young visitors in particular should be able to meet the animals up close. For this purpose, various petting facilities were set up. The exotic species kept here such as Humboldt penguins , Tasmanian Bennett wallabies (kangaroos), budgies, ring-tailed lemurs and meerkats deviate from the basic concept of the zoo, but are very popular with visitors.
Livestock
Previously occurring in all zones of Europe and Asia, the wisent (European bison) was considered extinct in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century. In addition to other zoological institutions, the Sababurg zoo is also involved in protecting this species from extinction.
The result of the attempts at breeding images of the Heck brothers, the Heck horse and the Heck cattle, is also kept. In addition to a herd of tail horses, the zoo is home to the endangered Przewalski horse from the Asian steppe and the Exmoor pony from the moors of southwest England.
To the European and Asian domestic species of deer in the zoo include Dybowski deer , Maralhirsche and Wapiti -Hirsche and fallow deer and red deer (both in white color variants) and the reindeer are very difficult to keep the outside its Nordic home, and special food is instructed. The zoo founder Landgrave Wilhelm IV already found out about this when his herd of reindeer, which was transported by ship from Lapland to the Reinhardswald, arrived severely decimated and the rest of them only survived a few weeks. On the second attempt, the herd was looked after by an experienced Samin from the start , who then lived in the zoo with her reindeer. When the last reindeer died, the young Samin also disappeared. As a reminder of their fate, there is a sculpture of Samin on the roundabout with a corresponding inscription. In 2013, a four-animal group of elks was relocated to a 53,000 m² enclosure.
The population of native wild animals is supplemented by a pack of wolves , lynxes , wolverines , otters , wild boars , West Caucasian ibexes and mouflons . The domestic animals kept in the zoo include donkeys , East Prussian Skudden and Thuringian forest goats as well as red high cattle , German saddle pigs , leash goose and German Peking duck .
Birds of prey station
On the castle hill directly below the Sababurg at the highest point of the zoo there is a terraced bird of prey facility . Various birds of prey live here between the end of March and the end of October and are shown in their natural flight movements by a falconer . The stock of the complex includes white- tailed eagles , golden eagles , steppe eagles , buzzard , red kite , saker falcon , peregrine falcon , desert buzzard , bald eagle , eagle owl and snowy owl . Most of the birds are on loan from the Hellenthal Bird of Prey Station , but there are now some of their own owls among them. The air show takes place Tuesday through Sunday from 11:30 a.m., 2:00 p.m. and 4:15 p.m.
Picker's yard
The spiritual father of the zoo, zoologist Hans Georg Picker, had already created a pet garden in 1985 to show endangered old breeds. In 2006 the Sababurg zoo received the first construction phase of a school farm : Pickers Hof .
With a financial outlay of the State of Hesse amounting to 341,000 euros and 181,000 euros from EU funds, a courtyard with stables, aviaries and exercise areas for small animals was created. A multifunctional building with kitchen, group room and grain store is also part of the courtyard, and traditional craft techniques were used in the construction. The courtyard is heated by a pellet heating system. Power is supplied by a photovoltaic system.
Cattle, pigs, goats, sheep, ducks and geese live in the school farm, which shows practically how people work and live on a farm. To make this clear, old farm animals were acquired for the zoo, such as red high cattle , linen sheep , Thuringian forest goats and German saddle pigs. In addition to the salmon chicken and the Vorwerk chicken , the German Peking duck and the leash goose are kept in the yard.
museum
The museum in the park was originally designed as a natural history, hunting and forest history exhibition. Today's zoo museum shows the history of the wildlife park on the Sababurg , reports on horse breeding there and the people living in the Reinhardswald, in order to come to the Brothers Grimm at the end of a tour , who also spent a time on the edge of the Reinhardswald between 1806 and 1811.
The museum is housed in a half-timbered house from 1610. The Saxon long hall house stood in Gottsbüren until 1979 and was rebuilt in the Sababurg zoo in the spring of 1980 . The museum has been rebuilt since 2005, with a new ambience to make the exhibition space and the presentations more modern and friendlier. The first part, the ground floor of the museum, was inaugurated in May 2009. The short tour shows the history of the hunt, the creation and use of the zoo.
Documentation is provided on the upper floor to provide information about the conservation and breeding of animal species. Other exhibition themes are the profession of animal keeper, the Sababurg primeval forest as the first nature reserve in Hesse with its hat oak and the history of the former Beberbeck stud.
Directly below is an old, restored half-timbered barn from Ostheim near Liebenau . The zoo administration has moved in here since 2009, informing visitors on site. Events and educational work with school classes and interested groups are planned on the top floor.
In 2007 the Sababurg Zoo received 32,500 euros from the municipal financial equalization scheme for the further redesign of the museum. The Hessian Ministry of Science and Art took over more than half of the total eligible costs.
Culture and art
Above in the direction of Pickers Hof on the left is the old wild barn . This half-timbered barn was restored in 2007 and inaugurated as a culture and church barn. Lectures are held in their hall and, in the summer months, short services are held on every Sunday and public holiday, and fairytale services are held at longer intervals.
Actions and attractions
The zoo's offerings have been steadily expanded in recent years: the bird of prey station described above was inaugurated in 1999, the school farm followed in 2006, the culture barn in 2007, the museum expansion in 2009, and in 2011 a new facility for penguins and the new monkey climbing world . In 2012, the rabbit and kangaroo enclosures were renewed, a walk-in budgie aviary built and the old penguin enclosure converted into a raccoon paradise. In 2013 the new meerkat and dwarf goat stable was inaugurated.
Since 2005, a medieval market has been held regularly in late summer and in the run-up to Christmas. More than 20,000 visitors come to the two-day markets each year.
Visitors
Since the reopening of the zoo in 1973, the number of visitors has increased every year. For example, between 1998 and 2004 the number of visitors increased from 105,000 to 148,000. In 2005, the zoo welcomed the 4.5 millionth guest and thus reached an annual average of 140,000 visitors. In 2008 the number of visitors was around 180,000, in 2011 over 250,000 and in 2014 already 320,000. After 327,457 visitors in 2016, a new record was set in 2019 with 352,000 visitors.
Transport links
The Sababurg zoo can be reached via Kreisstraße 55, which leads from Hofgeismar past the Beberbeck district , the Sababurg primeval forest and the park to the Gottsbüren district of Trendelburg ; From the park you can drive on this street and then on the county road 56 up to Sababurg . Since June 2015 there has been a type 2 charging point in the zoo's car park.
Two bus lines of the North Hessian Transport Association (NVV) drive the park from Hofgeismar and Reinhardshagen .
Individual evidence
- ^ Section The zoo - a cultural monument , accessed on December 28, 2015, at tierpark-sababurg.de
- ^ Section fairy-tale location , accessed on December 28, 2015, at tierpark-sababurg.de
- ↑ a b Urwildpark in animal Sababurg on tierpark-sababurg.de
- ↑ Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ a b c Sleeping Beauty Castle Sababurg ( Memento of the original from August 17, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on sababurg.de
- ↑ a b Peter W. Foth, Sababurg Zoo - A small guide through a large park , Hofgeismar, 2007
- ↑ Hans G. Picker: Sababurg Zoo - History of the 400-year-old "Thiergarten an der Zapfenburg" (see literature )
- ↑ Pickers Hof opens its doors - school farm in the zoo ready ( memento from October 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), information according to the press release of the district committee of the Kassel district, from June 1, 2006
- ↑ Medieval Spectaculum ... , on foerderverein-tierpark-sababurg.de
- ↑ HNA, press release of December 28, 2009
- ↑ HNA, press release from January 19, 2012
- ↑ HNA, press release from January 27, 2015
- ↑ HNA, press release from October 23, 2017
- ↑ Article at HNA-online , accessed in February 2020.
- ↑ Federal Network Agency - charging station card. Retrieved April 18, 2020 .
literature
- Hans Georg Picker: Sababurg zoo - history of the 400-year-old "animal garden at the Zapfenburg" with forest and hunting museum, guide through the wildlife park for endangered animal species and the children's zoo , Kassel, 1975
Web links
- Literature about Sababurg Zoo in the Hessian Bibliography
- Tierpark Sababurg (official homepage), at tierpark-sababurg.de