Turanose: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
added pubchem ID, SMILES, CSID, StdInChI and StdInChIKey that match the structure shown in the Chembox |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
[[ja:ツラノース]] |
[[ja:ツラノース]] |
||
[[pt:Turanose]] |
[[pt:Turanose]] |
||
[[sr:Turanoza]] |
|||
Revision as of 16:28, 20 August 2012
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
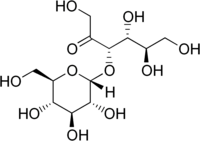
| IUPAC name
(3S,4R,5R)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-3-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyhexan-2-one
| |
| Other names
α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-D-fructopyranose
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.108 |
| MeSH | turanose |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Turanose is a reducing disaccharide. The D-isomer is naturally occurring. Its systematic name is α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-D-fructofuranose. It is an analog of sucrose not metabolized by higher plants, but rather acquired through the action of sucrose transporters for intracellular carbohydrate signaling. In addition to its involvement in signal transduction, D-(+)-turanose can also be used as a carbon source by many organisms including numerous species of bacteria and fungi.[2][3][4][5][6]
References
- ^ Turanose - Compound Summary, PubChem
- ^ Sinha, A.K.; et al. (2002). "Metabolizable and non-metabolizable sugars activate different signal transduction pathways in tomato". Plant Physiol. 128 (4): 1480–1489. doi:10.1104/pp.010771. PMC 154275. PMID 11950996.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Gonzali, S.; et al. (2005). "A turanose-insensitive mutant suggests a role for WOX5 in auxin homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana". Plant J. 44 (4): 633–645. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02555.x. PMID 16262712.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Sivitz, A.B.; et al. (2007). "Arabidopsis sucrose transporter AtSUC9. High-affinity transport activity, intragenic control of expression, and early flowering mutant phenotype". Plant Physiol. 143 (1): 188–198. doi:10.1104/pp.106.089003. PMC 1761979. PMID 17098854.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Loreti, E.; et al. (2000). "Glucose and disaccharide-sensing mechanisms modulate the expression of α-amylase in barley embryos". Plant Physiol. 123 (3): 939–948. doi:10.1104/pp.123.3.939. PMC 59056. PMID 10889242.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ D-Turanose at Sigma-Aldrich
