Fritz Arlt
Fritz Arlt (born April 12, 1912 in Niedercunnersdorf ; † April 21, 2004 in Seeg ) was a German National Socialist functionary in a leading position involved in ethnic cleansing in Poland, head of the volunteer control center in the east, head of the refugee control center and, after 1945, an employers' association in youth education centers.
Life
Fritz Arlt's parents were conservative- pietist , and some of the relatives came from Upper Silesia . From 1926 to 1932 he was educated in a Christian boarding school and was active in the German Freischar . In 1929 he joined the Hitler Youth from the Young Socialists .
1932 with Schelsky to the SA
Arlt joined the NSDAP in 1932 ( membership number 1,376,685) and - together with the same old Helmut Schelsky - joined the SA . The transfer of power to the NSDAP experienced Arlt as a student against whom, because of an SA-brawl, a strained by the police Relegation process ran (NSDAP representation: he "belonged to the overthrow of the auxiliary police readiness Captain rust."). The relegation procedure was discontinued in April 1933. Arlt studied philosophy with Arnold Gehlen in Leipzig, he received his doctorate in 1936 with him and Otto Reche . Arlt studied here in a generation of students that would later form the elite in the Reich Security Main Office. In December 1934 Arlt became an unpaid employee of the Racial Political Office (RPA) established that year .
- 1933 chairman of the student union.
- 1934 head of the district office for race and population policy of the Leipzig district. Beginning of surveys on the population structure of the Jews in Leipzig, his dissertation topic from 1935/36.
Hans-Joachim Schoeps , Joachim Wach and Fritz Borinski belonged to his circle of friends - according to a later self - testimony .
1936 with "Folk Biological Studies" for SD
In 1936 Arlt completed “Folk Biological Investigations” in Leipzig. Arlt's investigation was a detailed breakdown of the place of residence of people who had indicated in the 1933 census that they were of Jewish faith, as well as those whom Arlt assigned to part of the "Jewish race" on the basis of further research. Arlt recorded the data of these people on index cards and presented the concentration of residence he found georeferenced - a procedure which allowed the data of the individual to be selected and was taken up by the SD as a model for Eichmann's task (a contact conversation with the SD is documented below) :
"Dr. Arlt is old Pg . He has an excellent knowledge of Judaism. During his time in Leipzig, he categorically recorded all full, three-quarter, half and quarter Jews. Dr. Arlt carried out on its own initiative. He intends to set up the same card index first for Upper Silesia and finally for all of Silesia and asked for the support of the SD (...) Dr. Arlt offered to teach some SD members New Hebrew. (...) The speaker II 112 of the SD-OA Südost already spoke to Dr. Arlt got in touch. A direct discussion with the head of Department II 112 in Berlin is considered appropriate. "
In August 1936, after completing his studies, Arlt moved from Leipzig to Breslau; in the local RPA in the Gau Silesia he was head of department and district training director, in the University of Breslau Arlt was a lecturer for " racial studies ". At the suggestion of Martin Staemmler, he was appointed as his representative in the Gauamt for Race and Population Issues. In addition to family politics and racist propaganda, he carried out special assignments for President Wagner on border policy.
Arlt published his racist theses in Der Weltkampf , an anti-Semitic magazine, which was later acquired by the NSDAP High School under the technical director Kurt Wagner .
1937 appointed to the management staff of the higher SS and police leaders
In 1937 the Polish-speaking Arlt was hired by the SS , where he worked in the command staff of the Higher SS and Police Leaders (HSSPF) Upper Silesia . At the same time he began working with the Canaris office .
From 1937, the SD was collecting information for a possible war against Poland. A special wanted book for Poland , which included about 61,000 names of Polish intelligentsia , had been created. Franz Six set up the Central Office II P (Poland) in Amt II. Before setting up the Central Office II P (Poland) of the SD, Herbert Hagen had thought about “possible connections to Poland” and noted that “it was important to know people in Poland who would give precise information about a complete record of Judaism in Poland can give ”.
Marriage to Ida Maria Hübsch.
"Race, people and genes in Silesia"
In early 1938, complained the Gauleiter of the Gau Silesia Josef Wagner at the Reich Ministry of Science, Education and Culture that the breed composition of Silesia in popular and semi-scientific representations is often wrong: Silesia was "Nordic", not "ostisch", this was by studies of Wroclaw Scientifically proven professor of racial studies Egon Freiherr von Eickstedts and his staff. He demanded that such representations be prevented in the future. Fritz Arlt is responsible for further information.
The Reich Ministry commissioned the publications office in Berlin-Dahlem in cooperation with the Northeast German Research Foundation (NODFG), which were responsible for the control of scientific publications in the field of Eastern research , to make themselves knowledgeable. Johannes Papritz from the Publication Office asked racists such as Otto Reche and Fritz Lenz as well as Hermann Aubin , the Breslau representative of the NODFG, to assess the Silesia investigation. In 1938, Arlt and Heinrich Tewes started a series of booklets entitled “People, Race, Hereditary Value” in Silesia, but later, together with Tewes, contributed to the publication of Eickstedt's Silesian investigation: “Race, People, Hereditary Property in Silesia” and probably also provided practical and organizational assistance .
The assessment was negative due to personal animosity towards Eickstedt and justified methodological criticisms, which were mainly contributed by Lenz, but also by Otmar Freiherr von Verschuer . The Reich Ministry concealed its source and added a statement by the "Commissioner for the entire intellectual and ideological training of the NSDAP". On instructions from Berlin, Arlt was forced to withdraw from the project in 1943 by Wagner's successor Fritz Bracht .
Censorship or withdrawal of the series of booklets was not found necessary, also because Martin Staemmler had campaigned for them. The attempt at censorship on the racial studies of Silesia, which the group around Arlt attempted, failed because of official and party official decrees.
This investigation of Silesia, the z. B. also integrated the mapping of church registers by the NSLB, is the counterpart to Arlt's racial knowledge of "foreign races".
1938 “Folk Biological Studies”, instructions for mass deportation
In 1938 Arlt was appointed Gau Commissioner for the RPA in Gau Silesia . In the same year Arlt's "Folk Biological Investigations" were published. In these he suggested expelling the Leipzig Jews as foreigners and deporting them to their places of origin in Poland .
The proposed Arlt procedure was in 1938 in a combination of German and Polish government through deportations carried out en masse. The reaction time of the Polish government in the context of these first mass deportations in 1938 made it clear that the government of Poland also had updated census data from 1931 - selectable according to religion and mother tongue.
On the evening of October 29, 1938, the Polish government ordered that German citizens be deported from Posen and Pomerania . The German government argued that deporting Aryans would exacerbate the conflict, whereupon the Polish government deported only Jewish Germans.
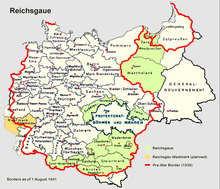
1939 “Population and Welfare” in the Generalgouvernement
In August 1939, Arlt was still working on the so-called Jewish card index in Breslau, for which he summoned the Jewish historian Willy Cohn , who was later deported to Auschwitz and murdered , and made use of his knowledge. He also requisitioned relevant books from his extensive library "against his word of honor".
Arlt took part in a Brieger battalion in the attack on Poland . During the attack on Poland, the SD confiscated the census data in the University of Warsaw. In October 1939, Arlt became head of the “Population and Welfare” department under the occupation regime of the Governor General of Poland, Hans Frank .
In the spring of 1940, 15,000 Poles were deported to the Generalgouvernement every month from the Warthegau , with Arthur Greiser significantly involved . In a film interview for the BBC in 1997, in the 31st minute of the 48:20 minute film, Arlt commented on the victims of these deportations, who after their arrival were under his responsibility as head of the Office for "Population and Welfare" in the General Government:
- 30:49 Fritz Arlt: Evacue trains came night after night, which brought the so-called resettlement center, of which Mr. Eichmann was the boss , to the Generalgouvernement, people were thrown out of the trains, whether on the market square, at the train station, wherever it was, and nobody cared about it.
- 31:13 So we got a phone call from the district chief, that's the district administrator. He said now I don't know what to do anymore.
- So again and so many came along, I have neither an apartment, nor food, nor anything else.
- 32:25 When I think of Frank, I have to say: he was a tragically funny character. Frank was a very intelligent fellow, was a good musician and pianist. Mr. Frank was someone who attached great importance to presentation and representation. Which is why they mockingly called the King of Poland.
- 35:12 Dr. Fritz Arlt: helped deal with the problem of Baltic Germans who did not want to relocate
- 35:19 In our interview with him, Dr. Arlt that he wanted to help the occupied population.
- 35:29 But this letter about the ethnically German peasants shows a different character of Arlt.
- 35:43 He has the dictation mark A for Arlt, we reminded him of the existence of this letter.
- 35:49 Yes, what else should I do, you ask!
- 35:55 The letter led to the fact that Ringführer (Wehrwirtschaftsführer) of the ethnic Germans were sent to a concentration camp.
- 36:03 Question: But what was a concentration camp for you now? When you say the admission should be in a concentration camp?
- 36:09 Arlt: What was a concentration camp for me ?, Exactly in the term: A camp in which people who somehow pose a threat to order have been concentrated.
- 36:35 Question: Did you feel at the time that it might be a severe punishment?
- 36:39 Arlt: Excuse me, that was known to the people, so they probably had to expect it.
- Arlt: I don't know, I've never been a warehouse manager.
- 36:58 Speaker: Dr. Arlt joined the NSDAP in 1932, is he ashamed to have been in the NSDAP today?
- 36:59 Arlt: I am not ashamed that I became a National Socialist, but rather I went there with an absolute consideration based on the situation analysis.
The “Population and Welfare” department was responsible for the sanatoriums and nursing homes in which old and sick patients were murdered, for example the sick from the Chelm psychiatric institution on January 12, 1940.
In July 1940 Arlt attested in the "Volkspolitischen Informationsdienst" (Volkspolitischen Informationsdienst) published by the Government of the Generalgouvernement, internal administration "Population and Welfare" (Cracow 1940) overview of the population situation in the Generalgouvernement and the occupied area overpopulation: The area of the Generalgouvernement is less than one Fifth of good arable land, but the population density, at 126 people per square kilometer, almost approaches that of the German Empire. “That is too much both in terms of the natural flooring and in terms of its industrial preparation and furnishing. (…) The General Government is an overpopulated area ” (p. 20). "From history and practical population policy, the population scientist knows three ways to solve the problem of overpopulation" , continued Arlt: The first possibility is "the decimation of the population through temporary emigration (seasonal migration)" . This was accomplished through the massive recruitment of forced laborers for German armaments and agriculture. Arlt calls the second “solution” “final emigration” . This, Arlt concluded, was not possible because of the war.
Arlt referred to the third solution, physical destruction, in the form of deliberations. They concerned the increase in the mortality of the most vulnerable victims of the Nazi regime, infants and over 65-year-olds, and the "number of the generally weak, the infirm and sick in the other age groups" (p. 9). Arlt referred to these as "the layers most subject to the withering process" . Later Arlt was head of the Central Institute for State Research in Upper Silesia and also head of the Upper Silesia branch of the Reich Commissioner for the Consolidation of German Ethnicity .
Arlt was transferred from the Wehrmacht to the SS in 1940 .
In preparation for June 22, 1941: the "Volunteer Control Center East"
The head of the SS main office, Gottlob Berger , had entrusted his friend Fritz Arlt with the formation of the "volunteer control center east".
In the "Freiwilligen-Leitstelle Ost" (Volunteer Control Center East), non-Russian combat units were brought together in the force of foreign volunteers of the Waffen SS from Eastern Europe. From this team, a Reiner Olzscha , medical advisor and Obersturmbannführer in office D 3 of the SS main office is still known today , because he was also active as a journalist. He was responsible for Muslim units of the SS and therefore fled to the West at the end of the war together with his ideological chief, the Mufti .
Central Institute for Upper Silesian Regional Research
In 1941, after Bracht took over as staff leader of the BdRRFSS / RKF, Arlt set up the main offices for ethnicity issues, schools and education, as well as the central institute for Upper Silesian regional research.
Retreat to the front
In 1943, Arlt said he fell victim to intrigues in the NSDAP and German racial studies. He reported to the troops, was trained on assault guns and took part in battles of the SS Panzer Division "Das Reich" . In 1944 he was wounded and took over the volunteer control center East (for Balts, Ukrainians, White Ruthenians, Cossacks) of the SS. At the end of the war he was taken prisoner with a Ukrainian volunteer unit.
After October 1, 1944: the "refugee control center"
Gottlob Berger was the organizational creator of the Waffen SS ; In addition to his diverse functions, Berger was appointed head of the prisoner-of-war system by Heinrich Himmler on October 1, 1944 . In this function, Berger had allowed American prisoners to be cared for by the German Red Cross under Ernst-Robert Grawitz in April 1945 . The “Volunteer Control Center East” became the “Refugee Control Center”.
In November 1944, SS-Obersturmbannführer Arlt was nominated for promotion to Standartenführer by his superior, SS-Obergruppenführer and Police General Ernst-Heinrich Schmauser . At the end of January 1945, however, because he was too young, his application for promotion was rejected. In January 1945 the 14th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (Galician No. 1) was reorganized as the 1st Ukrainian Division of the Ukrainian National Army , a formality that only took place on paper (but later saved the lives of the soldiers ). In May 1945, the division went into British captivity. In contrast to most of the other Eastern European volunteer associations, the majority of their members were not extradited to the Soviet Union, but were allowed to emigrate to Canada and Australia.
In 1945 the “German Red Cross” was largely dissolved by the occupying powers, and the DRK was banned in the French and Soviet occupation zones. In the new application to the Central Committee of the National Red Cross Societies on June 26, 1952, the circumstance was described as follows: “This national society, founded in 1921 under the name 'German Red Cross', which extended its activities to the entirety of German territory, was Dissolved in the summer of 1945 by an order of the occupation authorities. ”.
After 1945
Arlt was denazified in Munich in 1949 as a so-called “ fellow traveler ” ; Before that, he had done studies for the Americans on German relations with the East and on psychological warfare.
After 1945, Arlt and his friends Schelsky and Wagner played a key role in setting up the tracing service of the German Red Cross . From 1954 to 1957, Arlt was head of the “Educational Work and Sociopolitical Issues” department at the Institute for the German Economy in Cologne . He was also a member of the management of the Confederation of German Employers' Associations .
The state Franco-German Youth Office (DFJW) elected him as a deputy member of the Board of Trustees; in January 1966 he resigned from the committee after public pressure.
Arlt published four books on social and economic policy with the last Federal Minister for Internal German Relations , Dorothee Wilms .
From 1972 to 1978 Arlt worked as a freelance management consultant.
Writings by Fritz Arlt
- Folk-biological studies on the Jews in Leipzig. Hirzel, Leipzig 1938 (Archive for Population Science and Population Policy, Supplement 4)
- The subjugation of the Gentiles. A program picture from the library of the Breslau Jewish lodges . At the same time a contribution to the psychology of Judaism. Journal “Der Weltkampf” , published by the Institute for Research into the Jewish Question, vol. 15, 1938, pp. 199–202
- Overview of the population in the Generalgouvernement. 1940
- Tasks and paths of business in youth education Deutsche Industrieverlagsgesellschaft 1955
- with Dorothee Wilms : Young workers answer: Young workers and salaried employees express their views on profession and work, society and education. A contribution to youth social work inside and outside the company. Westermann, 1962
- Poles, Ukrainians and Jews in the General Government for the occupied Polish territories in 1939/1940 in Upper Silesia in 1941/1943 and in the freedom struggle of the oppressed Eastern peoples. Documents, statements by Poles, Ukrainians and Jews. Corrections of counterfeiting. Memories from an insider. Scientific book service Herbert Taege, Lindenhorst 1995, ISBN 3-000001182
literature
- Ernst Klee : The Personal Lexicon for the Third Reich: Who Was What Before and After 1945? Fischer TB, Frankfurt 2005, ISBN 3-596-16048-0 .
- Roger Uhle: New people and pure race. Walter Gross and the Race Political Office of the NSDAP (RPA) 1934–1945 . Dissertation RWTH Aachen 1999.
- Götz Aly , Susanne Heim : thought leaders of annihilation. Auschwitz and the German plans for a new European order. Fischer-Taschenbuch 11268, Frankfurt 1993, ISBN 3-596-11268-0 .
- Bogdan Musial : German civil administration and persecution of Jews in the Generalgouvernement . Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden 1999, ISBN 3-447-04208-7 ; 2nd edition, ibid. 2004, ISBN 3-447-05063-2 .
- Stephan Wendehorst: Building Blocks of a Jewish History of the University of Leipzig. Simon Dubnow -Institute for Jewish History and Culture, Leipziger Universitätsverlag, 2007, ISBN 3-86583-106-0 .
- Miroslaw Sikora: Art. Fritz Arlt, in: Michael Fahlbusch , Ingo Haar , Alexander Pinwinkler (eds.): Handbook of the völkisch sciences. Actors, networks, research programs. With the collaboration of David Hamann, Vol. 1, Berlin 2017, ISBN 978-3-11-042989-3 , pp. 28-38.
Web links
- Literature by and about Fritz Arlt in the catalog of the German National Library
Individual evidence
- ^ Frank Mecklenburg: career of Fritz Arlt. In: Jürgen Matthäus , Klaus-Michael Mallmann (ed.): Germans, Jews, Genocide. The Holocaust as Past and Present. Scientific Book Society , Darmstadt 2006, ISBN 3-534-18481-5 .
- ↑ Mecklenburg: career of Fritz Arlt : "Arlt should never become a civil servant or state employee, but remain in the service of the party until 1945."
- ↑ a b c d e f Arlt 1995, p. 143
- ↑ Bogdan Musial: German civil administration and the persecution of Jews in the Generalgouvernement . Wiesbaden 1999, p. 380
- ↑ Michael Wildt : Generation of the Unconditional. The leadership corps of the Reich Security Main Office. Hamburg 2002.
- ↑ Bundesarchiv Berlin, R 58/991 cf. On Fritz Arlt's curriculum vitae: Berlin Document Center , Faszikel Arlt (approx. 150 sheets), quoted from: Götz Aly, Karl Heinz Roth: The complete collection: census, identification, weeding out under National Socialism Fischer, Frankfurt am Main 2000, ISBN 3-596-14767-0 . ( English version ) online at books.google.com
- ↑ Quoted from: Gerhard Paul: Until then, he had no idea about Jewish affairs.
- ↑ a b c d e Arlt 1995, p. 144
- ↑ Detlev Franz: The political context of the investigation of Silesia. In: Arbeitskreis Universitätsgeschichte 1945–1965 (Ed.): Elements of a different university history. Mainz 1991.
- ↑ See Willy Cohn: No right, nowhere. Diary of the fall of Wroclaw Jewry 1933–1941. Vol. 2, p. 673 f., P. 876 f. Böhlau, Cologne / Weimar / Vienna 2006 (Newer Research on Silesian History 13.2), ISBN 3-412-32905-3 .
- ↑ "The Nazis. A Warning from History “The first 20 month in Poland v.youku.com
- ^ Kościan and euthanasia in Poland at www.deathcamps.org
- ↑ Quotations from: Götz Aly, Karl Heinz Roth
- ↑ Gottlieb Berger in the spelling of October 19, 1945 as a witness in Nuremberg nizkor.org
- ^ Poles, Ukrainians and Jews: in the General Government for the occupied Polish territories in 1939/40 and in Upper Silesia in 1941/43 and in the freedom struggle of the oppressed Eastern peoples; Documents, statements by Poles, Ukrainians and Jews, corrections of forgeries, memories of an insider / Fritz Arlt
- ↑ with Georg Cleinow : Turkestan. The Political, Historical and Economic Problems of Central Asia. Koehler & Amelang, Leipzig 1942; also: online , for collaboration with Richard Hartmann (orientalist) , with the Mufti u. a. in an SS “Working Group Turkestan”, section “Islam”. In Engl. - The whole chapter p. 333ff. reports Olzscha's statements about those involved ( Bertold Spuler and many others); from p. 348–368 there is an excerpt from the O. report in German on the "Feldmullahs", ie SS clergymen for the indoctrination of these troops. From: Bundesarchiv Berlin-Zehlendorf , No. A 54.7 R. 920. Olzscha himself sat as a “consultant for Arabia” in the “foreign department” of the Reich Medical Association
- ↑ on the complex of Muslim SS people: with further literature ( Memento from May 2, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) and on their further organization in Munich after 1945
- ↑ Recognition of the DRK by the International Committee of the Red Cross in Geneva on June 26, 1952 (PDF; 124 kB)
- ↑ a b c Arlt 1995, p. 145.
- ^ Name of the week . In: Die Zeit , No. 2/1966 (His troop "Das Reich" had committed serious war crimes in France.)
- ↑ Herbert Taege is a former security guard at the Dachau concentration camp who publishes historical revisionist books; see. geschichtsthemen.de
- ↑ place of birth of A. written with 1 number; so wrongly adopted by Wendehorst 2007.
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Arlt, Fritz |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German National Socialist functionary |
| DATE OF BIRTH | April 12, 1912 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Niedercunnersdorf |
| DATE OF DEATH | April 21, 2004 |
| Place of death | Seeg |