Geltinger Birk
|
NSG Geltinger Birk
|
||
|
Geltinger Birk Nature Reserve (2014) |
||
| location | Nieby and Gelting , Schleswig-Holstein , Germany | |
| surface | 7.73 km² | |
| Identifier | No. 8 | |
| WDPA ID | 70923 | |
| Geographical location | 54 ° 47 ' N , 9 ° 55' E | |
|
|
||
| Setup date | December 23, 1986 | |
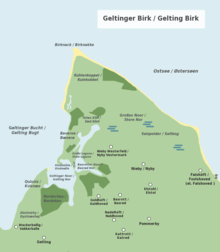
The Geltinger Birk ( Danish Gelting Birk ) has been a nature reserve on the Schleswig-Holstein Baltic Sea since 1986 . It is located - northeast of Gelting - mainly in the area of the municipality of Nieby on the Geltinger Bay at the exit of the Flensburg Fjord .
Surname
The northern part of the peninsula is Geltinger 1494 as Barkö and 1519 as Berckoe referred. The field name is probably in Danish . birk for birch ( mnd . berke ) and ø for island back. The meaning is therefore birch island, since the area used to be an island. At the same time, the area around Gelting formerly formed a Birk , i.e. a legally independent district separated from the Harde after Birkrecht , which was first attested in 1494, but is probably older.
Description of the area
With its area of around 773 hectares, the nature reserve in the Geltinger Bay (Baltic Sea water area) and on a peninsula (it is a so-called Höft ) is the largest in the Schleswig-Flensburg district . The area belongs to the Schleswig-Holstein Nature Conservation Foundation .
Of the total area, around 260 hectares are below sea level . The landscape is characterized by bodies of water (Geltinger Noor ), beach lakes, swamps, forests, salt marshes , dunes , beaches and spit hooks . The nature reserve also includes the shallow water areas with seagrass meadows bordering the land . The Schleswig-Holstein Nature Conservation Foundation uses herds of horses ( Koniks ), cattle ( Scottish highland cattle , Galloways ) and sheep in parts of the area to preserve the pastureland .
history
The Geltinger Birk is a spit hook that was created during the formation of a compensatory coast due to sediment drift through currents parallel to the coast. In order to be able to use the Birk for agriculture, the first dike was built there in 1581 on the Schleswig-Holstein Baltic Sea coast, which separated the Geltinger and Beveroer Moor from the Baltic Sea. Then the drainage of the low lying area began. The first dike was later destroyed by a storm surge. In 1750 the Grahlensteindamm was built as a second dike. With the Charlotte windmill built in 1826 after the Great Noores were dyed , it was then possible for the first time to drain the Birk over a large area. To date, the water level has been lowered to 3.20 meters below sea level. Extensive preparations are currently underway for the controlled watering of the birch. To do this, u. a. Dikes and pumping stations built. Since September 16, 2013, lake water has been let into the Birk through a pipe north of the town of Falshöft in order to raise the water level to one meter below sea level. In this way, lagoons and salt marshes should be created again. This measure is one of the largest nature conservation projects that are currently being planned or implemented in Schleswig-Holstein.
Significance relevant to nature conservation
The birch is an important area for bird migration and the breeding of around two hundred species . In addition, over 90 species of birds breed here. That is why it is a popular destination for ornithologists . The area is also interesting from a botanical point of view: there are rare and protected species such as the sea kale ( Crambe maritima ) and the sea thistle ( Eryngium maritimum ).
The nature reserve is also part of two significantly larger areas that belong to the European Natura 2000 network of protected areas: It is in the FFH area DE-1123-393 coastal areas of the Flensburg Fjord from Flensburg to Geltinger Birk and in the European bird sanctuary DE-1123-491 Flensburg Fjord .
tourism
The area is accessible to tourists via several circular routes. Every year around 50,000 to 80,000 tourists visit the nature reserve. There are various circular hiking trails. Cycling in the nature reserve is permitted along designated paths. There is a small exhibition on the Geltinger Birk in the integrated station Geltinger Birk , which is maintained by the Naturschutzbund Deutschland (NABU) and the municipality of Nieby , among others . From here, the Birk and other nature reserves in the region are looked after by full-time employees of the station ( State Office for Agriculture, Environment and Rural Areas ). These offer information and tours or arrange tours.
literature
- Manfred and Dorothea Diehl: Nature reserves on the Baltic coast of Schleswig-Holstein. In reports of the association "Nature and Homeland" and the Natural History Museum in Lübeck, issue 19/20, Lübeck 1986.
Web links
- Integrated station Geltinger-Birk e. V.
- History of Geltinger Birk , Friends of the Integrated Station Geltinger Birk eV, accessed on March 10, 2020
- Wildpferde Association, Geltinger Birk e. V.
- NABU nature reserve and Information Hut Geltinger Birk
- Kathrin Weber: Magical landscape on the fjord: The Geltinger Birk. NDR , July 27, 2011, accessed on March 18, 2013 .
- Nature conservation in the municipality of Nieby
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b State ordinance on the "Geltinger Birk" nature reserve of December 23, 1986
- ↑ Wolfgang Laur: Historisches Ortsnamelexikon von Schleswig-Holstein , 2nd edition, Neumünster 1992, p. 155
- ↑ Uwe Muuß, Marcus Petersen: The coasts of Schleswig-Holstein. Neumünster 1974, ISBN 3-529-05301-5 .
- ↑ "Geltinger Birk" nature reserve - NABU Schleswig-Holstein. Retrieved October 2, 2017 .
- ↑ a b Rieke Scholz, Franziska Stoll: Coastal adaptation processes in the German Baltic Sea Region . ISBN 978-3-939206-14-9 , pp. 57 .
- ↑ a b c Technical plan for coastal protection on the Baltic Sea coast. (PDF) State Office for Coastal Protection, National Park and Marine Protection Schleswig-Holstein, May 15, 2017, p. 13 , accessed on February 10, 2017 .
- ^ Rieke Scholz, Franziska Stoll: Coastal adaptation processes in the German Baltic Sea Region . ISBN 978-3-939206-14-9 , pp. 57 .
- ↑ Technical plan for coastal protection on the Baltic Sea coast: figures data facts. (PDF) Ministry for Energy Transition, Agriculture, Environment and Rural Areas of the State of Schleswig-Holstein, February 7, 2014, accessed on October 2, 2017 .
- ↑ World Database on Protected Areas - coastal areas of Flensburg Fjord from Flensburg to Geltinger Birk SAC (English)
- ↑ World Database on Protected Areas - Flensburger Förde Special Protection Area (English)