Hawaii (island)
| Hawaii | |
|---|---|
| Hawaii from space | |
| Waters | Pacific Ocean |
| Archipelago | Hawaii |
| Geographical location | 19 ° 34 ′ N , 155 ° 30 ′ W |
| length | 150 km |
| surface | 10,432.47 km² |
| Highest elevation |
Mauna Kea 4205 m |
| Residents | 198,450 19 inhabitants / km² |
| main place | Hilo |
| Topography of Hawaii | |
Hawaii ( Hawaiian : Hawaiʻi , older also Owyhee , now also Big Island ) is the most easterly and with around 10,433 km² the largest island of the US state of Hawaii and the largest island of the United States . It also forms Hawaii County . The island is separated from the neighboring island of Maui to the northwest by the Alenuihaha Channel . In 2016, around 200,000 people lived on the Big Island, who mainly earn from tourism, but also from the cultivation of macadamia nuts, almost all of which come from this island, Kona coffee , papayas , bananas and other agricultural products as well as cattle breeding.
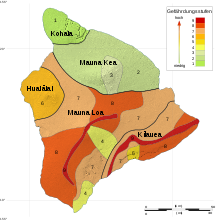
The geology and morphology of the island are shaped by volcanism, on the one hand by the two high volcanic mountains Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea , on the other hand by the much smaller but highly active Kīlauea .
Volcanism
The island, which is geologically and oceanographically part of the Hawaii-Emperor chain , consists of five large volcanoes: Kohala (extinct) in the north, Hualālai in the west (active, last eruption in the 19th century), Mauna Kea in the east (dormant) , Mauna Loa in the south and Kīlauea in the southeast. All are part of the latest in a series of volcanoes that formed the Hawaiian Islands as the Pacific plate moved over a localized hot spot in the Earth's mantle . Both Mauna Loa and Kīlauea are very active, with the current eruption of Kīlauea going on since 1983.
Some geologists name seven volcanoes that make up the island, adding Māhukona in the northwest and Lōʻihi in the southeast as parts of the island's base. Māhukona is the oldest shield volcano, which sank again after its extinction. The youngest volcano, Lōʻihi, which rises about 3000 meters above the sea floor, is located about 900 meters below the sea surface.
The 9200 hectare Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park was founded in 1916 and includes the western flank of Mauna Loa and the most active volcano on earth, the Kīlauea, with the side crater Puʻu ʻŌʻō , which has been continuously active since 1983 .
mythology
In Hawaiian mythology, the lava lake of Halemaʻumaʻu, which is embedded in the caldera of Kīlauea, is regarded as the seat of the volcano goddess Pele .
etymology
While in other Polynesian languages Hawai'i or related names such as Havaiki denote the ancestral seat, the word has no meaning of its own in the Hawaiian language .
astronomy
On the summit of Mauna Kea stands the Mauna Kea Observatory, one of the most important astronomical observatories of our time.
tourism

With 1,515,000 visitors in 2015, the island of Hawai'i is the third most visited Hawaiian Islands (after Maui with 2,540,000 and O'ahu with 5,340,000 visitors).
Hilo on the rainy east coast is the capital of the island with over 47,000 inhabitants and is primarily the starting point for excursions to the volcanoes and the orchid gardens ( Nani Mau Gardens ).
To the west of Hilo, at the end of Highway 220, lies the Ka Uao Waiānuenue waterfalls ( Rainbow Falls ). North of Hilo there are the waterfalls of 'Akaka ( Akaka Falls ). There are numerous black sand beaches, especially on the south side of the island.
Kailua-Kona on the sunny and rain-free west coast has white sandy beaches and has become the main tourist destination on the island. It houses numerous hotels, souvenir shops and restaurants. The place with approx. 12,650 inhabitants also has an international airport from which there are direct flights to Asia. Some museums and the oldest church in Hawaii, the Mokuʻaikaua Church , built from lava rock in 1823, opposite the Huliheʻe Palace , can be visited here. Every October, Kona hosts the legendary Ironman Hawaii competition.
The so-called Painted Church “St. Benedict's ” in Keokea, on Highway 11, is a painted wooden church. The missionary who built it was also a good painter. For lack of books, he painted the wooden walls of the church with biblical motifs.
Puʻuhonua o Hōnaunau was a burial place for chiefs and once a refuge for taboo breakers who were safe from persecution here.
Kealakekua Bay , at the end of Highway 160, is not only a good snorkeling area but also a historical site. Here in 1779 James Cook (Captain Cook) was slain by the Hawaiians.
Waimea / Kamuela has 6,000 residents and is the main town of the Parker Ranch , which is the largest privately operated ranch in the USA with more than 90,000 hectares of land and approximately 60,000 cattle.
The original statue of King Kamehameha I stands in Kapaʻau in northwest Hawaii .
Symbol of the island is the Lehua flower of 'Ōhi'a -tree which grows as the first tree on the new lava fields.
Sports
In Hawaii, the Ironman Hawaii World Championship in long-distance triathlon (3.86 km swimming, 180 km cycling, 42.195 km running) takes place every October in Kailua-Kona on the west coast .
Culture
The focus of the East Hawaii Cultural Center in Hilo is on engaging with local culture.
Picture gallery
- gallery
Hi'ilawe Falls in the Waipi'o Valley
Monument to King Kamehameha I in Kapaʻau
Web links
- Hawaii (island) in the Geographic Names Information System of the United States Geological Survey
- Suzanne Taylor Muzzin: New Technology Allows Geophysicist To Test Theory About Formation of Hawaii. In: phys.org , December 11, 2009
- Hawaiian hot spot has deep roots. In: phys.org , December 3, 2009
Individual evidence
- ↑ cf. Hawaii (island) in the Geographic Names Information System of the United States Geological Survey ; Encyclopaedia Britannica; or A dictionary of arts, sciences, and miscellaneous literature, Volume 8 . Edinburgh 1824, p. 284 ; Jared Sparks: Life of the Famous American Traveler John Ledyard . Leipzig 1829, p. 124
- ↑ United States Census Population Estimates 2016 US Census Bureau, accessed July 30, 2017.
- ↑ Macadamia Nut Facts. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
- ↑ Top 20 commodities, State of Hawaii, 2014 (PDF) US Government Statistics, accessed July 30, 2017.
- ↑ James G. Moore, David A. Clague: Volcano growth and evolution of the island of Hawaii . In: Bulletin of Geological Society of America . 104, No. 11, November 1992, pp. 1471-1484. doi : 10.1130 / 0016-7606 (1992) 104 <1471: VGAEOT> 2.3.CO; 2 . , P. 1471.
- ↑ Official writing according to the Hawaiian National Park Language Correction Act of 2000 (p. 939) ( Memento from August 14, 2013 on WebCite ) (PDF; 123 kB) (English).
- ^ Hawaiʻi in Hawaiian Dictionaries
- ↑ Annual Report 2016 Hawaii Tourist Authority, accessed July 3, 2017.
- ↑ US Census Bureau 2015 estimate, American Fact Finder, accessed July 31, 2017.
literature
- David Kalakaua, King of Hawaii: Legends and myths of Hawaii . Ed. and with an introduction by Hon. RM Daggett. Publisher: CL Webster & Company, New York 1888 ( digitized )