Intel Xeon (Broadwell)
| << Intel Xeon >> | |
|---|---|
| Production: | since 2015 |
| Producer: | Intel |
| Processor clock: | 1.6 GHz to 3.5 GHz |
| QPI cycle: | 4.8 GT / s to 9.6 GT / s |
| L3 cache size: | 6 MiB to 55 MiB |
| Instruction set : | x86 / Intel 64 ( AMD64 ) |
| Microarchitecture : | Intel Broadwell micro-architecture |
| Base: | Base 2011-3 , base 1150 |
| Name of the processor core: | Broadwell-EX |
The Intel Xeon series based on the Intel Broadwell microarchitecture is a family of 64-bit microprocessors for servers and workstations from Intel . These multi-core processors with two to 24 cores represent the successors of the core- based Xeon processors.
Three very different families of CPUs are manufactured:
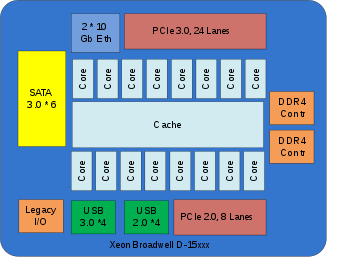
- Xeon D for micro servers with integrated peripherals (SoC or System-on-a-Chip ), four to 16 cores, 1.5 MB 3rd level cache per core, two DDR4 channels
- Xeon E3 for single-processor systems with integrated processor graphics, four cores, 1.5 MB 3rd level cache per core, two DDR4 RAM channels
- Xeon E5 and E7 for NUMA multi-processor systems with QPI connections, four to 22 cores, 2.5 MB 3rd level cache per core, four DDR4 RAM channels
The Xeons of the Broadwell generation now support DDR4 memory modules on four memory channels. A processor can support up to 1536 GB of RAM in up to twelve DIMM slots (depending on the size of the available modules).
- The Xeon D-Chip (4 to 8 cores) has a size of 14.76 mm × 10.85 mm - 160.24 mm²
The E5 and E7 variants are also called Broadwell-EP / EX . The chip is manufactured in three variants:
- "LCC": Low Core Count, 16.2 mm × 15.2 mm - 246.24 mm² - 3.2 billion transistors - 10 cores
- "MCC": Mid Core Count, 16.2 mm × 18.9 mm - 306.18 mm² - 4.7 billion transistors - 15 cores
- "HCC": High Core Count, 18.1 mm × 25.2 mm - 456.12 mm² - 7.2 billion transistors - 24 cores
Broadwell-EP / EX HCC
Image from Intel
Link to the image
(Please note copyrights )
The variants sold are created through testing and selection; So that the rejects in production are not too high, not all cores have to be functional and may be switched off. The cores are connected to one another and to the 3rd level cache working memory system with bidirectional ring buses. In the core area there are 256 kB 2nd level and 32 kB 1st level cache memory, outside the cores there are 2.5 MB per core in the 3rd level cache memory, as well as the controllers for QPI ports, DDR-RAM and PCI E 3.0
Models
A variety of models exist. The main parameters are:
- The first digit of the four-digit product code indicates how many processors of this type can be used in parallel on a motherboard (number of sockets as opposed to number of cores).
- Clock frequency (goes directly into the single-task performance and determines the performance of many programs)
- Cache size (increases data throughput)
- Number of cores (increases the number of tasks that can be processed simultaneously)
- Thermal Design Power: Power loss, limits the intended use, the higher the size, the larger the cooling system and power supply must be, increases with the clock frequency, the number of cores and the size of the cache. The models with an "L" after the 4-digit product code are low power versions with lower energy consumption for micro servers
- Integrated GPU: only interesting for workstations with low 3D graphics performance (see also Intel HD Graphics ), since graphics accelerators with high computing power are usually also plugged into CAD workstations
Xeon D-15xx
At the beginning of 2015, Intel brought out a series of “SoC” (System on a Chip) variants, the Xeon D series, which are intended as CPUs with an integrated chipset (peripheral connections such as PCI, USB, SATA and Ethernet) for micro servers. These CPUs are not the socket base 2011-3 E3, E5, E7 v4 series, but over a FCBGA 1667 called ball grid array -Lötsockel fixed to the main board connected. The CPUs only support two main memory channels instead of four in the large v4 variants and only one CPU per system. They are apparently positioned against newly developed server CPUs with ARM architecture.
Image: Block diagram of a Xeon D-15xx CPU
| Product Code | L3 cache | Tact | Release | Cores | TDP | integrated GPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-1518 | 6 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q4'15 | 4th | 35 W | no |
| D-1521 | 6 MB | 2.40 GHz | Q4'15 | 4th | 45 W | no |
| D-1527 | 6 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q4'15 | 4th | 35 W | no |
| D-1528 | 9 MB | 1.90 GHz | Q4'15 | 6th | 35 W | no |
| D-1529 | 6 MB | 1.30 GHz | Q2'16 | 4th | 20 W | No |
| D-1531 | 9 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q4'15 | 6th | 45 W | no |
| D-1537 | 12 MB | 1.70 GHz | Q4'15 | 8th | 35 W | no |
| D-1539 | 12 MB | 1.60 GHz | Q2'16 | 8th | 35 W | no |
| D-1541 | 12 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q4'15 | 8th | 45 W | no |
| D-1548 | 12 MB | 2.00 GHz | Q4'15 | 8th | 45 W | no |
| D-1577 | 24 MB | 1.30 GHz | Q1'16 | 16 | 45 W | no |
| D-1567 | 18 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q1'16 | 12 | 65 W | no |
| D-1559 | 18 MB | 1.50 GHz | Q2'16 | 12 | 45 W | no |
| D-1571 | 24 MB | 1.30 GHz | Q1'16 | 16 | 45 W | no |
| D-1557 | 18 MB | 1.50 GHz | Q1'16 | 12 | 45 W | no |
The following shows the CPU variants without integrated peripherals.
E3 v4 for single processor systems
The E3-1xxx-v4 variants only have two main memory channels and no QPI links, as they are built for single-socket systems. The CPUs lead out 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes into the system.
That's why you don't need the 2011v3 socket, but get by with a 1150 socket . Below is a block diagram of a typical E3 system:
| Product Code | L3 cache | Tact | Release | Cores | TDP | integrated GPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3-1285L v4 | 6 MB | 3.40 GHz | Q2'15 | 4th | 65 W | Intel Iris Pro Graphics P6300 |
| E3-1285 v4 | 3.50 GHz | 95 W | ||||
| E3-1278L v4 | 2.00 GHz | 47 W. | ||||
| E3-1265L v4 | 2.30 GHz | 35 W | ||||
| E3-1258L v4 | 1.80 GHz | 47 W. | Intel HD Graphics P5700 |
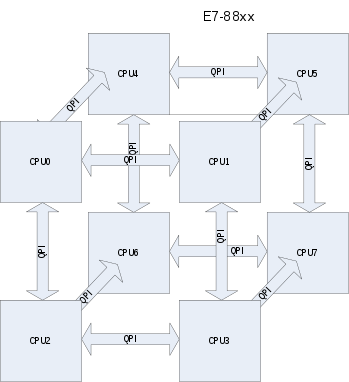
Broadwell EP / EX - the E5v4 and E7v4 families
The E5 variants (26xx and 46xx) are equipped with two QPI links for the socket-to-socket connections, the E7 variants (48xx and 88xx) are equipped with three QPI links. E5 and E7 variants have four DDR4 main memory channels and lead out 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes into the system. The following is a block diagram of an E5-26xx system:
| Product Code | L3 cache | Tact | Release | Cores | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E5-2699 v4 | 55 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 22nd | 145 W |
| E5-2695 v4 | 45 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q1'16 | 18th | 120 W |
| E5-2660 v4 | 35 MB | 2.00 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 105 W |
| E5-2680 v4 | 35 MB | 2.40 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 120 W |
| E5-2683 v4 | 40 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q1'16 | 16 | 120 W |
| E5-2687W v4 | 30 MB | 3.00 GHz | Q1'16 | 12 | 160 W |
| E5-2690 v4 | 35 MB | 2.60 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 135 W |
| E5-2697 v4 | 45 MB | 2.30 GHz | Q1'16 | 18th | 145 W |
| E5-2697A v4 | 40 MB | 2.60 GHz | Q1'16 | 16 | 145 W |
| E5-2698 v4 | 50 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 20th | 135 W |
| E5-2658 v4 | 35 MB | 2.30 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 105 W |
| E5-2650L v4 | 35 MB | 1.70 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 65 W |
| E5-2650 v4 | 30 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 12 | 105 W |
| E5-2648L v4 | 35 MB | 1.80 GHz | Q1'16 | 14th | 75 W |
| E5-2628L v4 | 30 MB | 1.90 GHz | Q1'16 | 12 | 75 W |
| E5-2630L v4 | 25 MB | 1.80 GHz | Q1'16 | 10 | 55 W |
| E5-2667 v4 | 25 MB | 3.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 8th | 135 W |
| E5-2623 v4 | 10 MB | 2.60 GHz | Q1'16 | 4th | 85 W |
| E5-2630 v4 | 25 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 10 | 85 W |
| E5-2618L v4 | 25 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q1'16 | 10 | 75 W |
| E5-2637 v4 | 15 MB | 3.50 GHz | Q1'16 | 4th | 135 W |
| E5-2640 v4 | 25 MB | 2.40 GHz | Q1'16 | 10 | 90 W |
| E5-2620 v4 | 20 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q1'16 | 8th | 85 W |
| E5-2608L v4 | 20 MB | 1.60 GHz | Q1'16 | 8th | 50 W |
| E5-2643 v4 | 20 MB | 3.40 GHz | Q1'16 | 6th | 135 W |
| E5-2609 v4 | 20 MB | 1.70 GHz | Q1'16 | 8th | 85 W |
| E5-2603 v4 | 15 MB | 1.70 GHz | Q1'16 | 6th | 85 W |
The QPI links form the interconnection between the main memory controllers of the different CPUs to form a non-uniform memory access computer: access to the four local memory channels of a CPU is faster than via QPI to the remote memory channels of other CPUs.
In an eight-CPU system, three CPUs are reached directly via a QPI link, three further CPUs (via two possible paths each) via an intermediary CPU, and the last diametrical CPU (via six possible paths each) via two intermediary CPUs .
| Product Code | L3 cache | Tact | Release | Cores | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E5-4669 v4 | 55 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q2'16 | 22nd | 135 W |
| E5-4667 v4 | 45 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q2'16 | 18th | 135 W |
| E5-4660 v4 | 40 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q2'16 | 16 | 120 W |
| E5-4655 v4 | 30 MB | 2.50 GHz | Q2'16 | 8th | 135 W |
| E5-4650 v4 | 35 MB | 2.20 GHz | Q2'16 | 14th | 105 W |
| E5-4640 v4 | 30 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q2'16 | 12 | 105 W |
| E5-4627 v4 | 25 MB | 2.60 GHz | Q2'16 | 10 | 135 W |
| E5-4620 v4 | 25 MB | 2.10 GHz | Q2'16 | 10 | 105 W |
| E5-4610 v4 | 25 MB | 1.80 GHz | Q2'16 | 10 | 105 W |
| E5-4628L v4 | 35 MB | 1.80 GHz | Q2'16 | 14th | 75 W |
| E7-4809 v4 | 20 MB | 2.10 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 8th | 115 W |
| E7-4820 v4 | 25 MB | 2.00 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 10 | 115 W |
| E7-4830 v4 | 35 MB | 2.00 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 14th | 115 W |
| E7-4850 v4 | 40 MB | 2.10 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 16 | 115 W |
| E7-8893 v4 | 60 MB | 3.20 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 4th | 140 W |
| E7-8891 v4 | 60 MB | 2.80 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 10 | 165 W |
| E7-8860 v4 | 45 MB | 2.20 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 18th | 140 W |
| E7-8867 v4 | 45 MB | 2.40 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 18th | 165 W |
| E7-8870 v4 | 50 MB | 2.10 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 20th | 140 W |
| E7-8880 v4 | 55 MB | 2.20 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 22nd | 150 W |
| E7-8890 v4 | 60 MB | 2.20 GHz | Jun 6, 2016 | 24 | 165 W |
| E7-8891 v4 | 60 MB | 2.80 GHz | Q2, 2016 | 10 | 165 W |
| E7-8893 v4 | 60 MB | 3.20 GHz | Q2, 2016 | 4th | 140 W |
| E7-8894 v4 | 60 MB | 2.40 GHz | Q1, 2017 | 24 | 165 W |
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ SemiAccurate: Xeon D-1500 Line SemiAccurate: Xeon D-1500 Line , article from March 9, 2015