Neuhof (Zossen)
|
Neuhof
City of Zossen
Coordinates: 52 ° 8 ′ 18 ″ N , 13 ° 28 ′ 35 ″ E
|
|
|---|---|
| Height : | 44 m |
| Incorporation : | April 1, 1974 |
| Incorporated into: | Wünsdorf |
| Postal code : | 15806 |
| Area code : | 033702 |
|
Neuhofer Dorfstrasse, view to the southwest
|
|
Neuhof is part of the municipality of Wünsdorf , a district of the city of Zossen in the Teltow-Fläming district ( Brandenburg ). Neuhof was probably rebuilt around 1700 and was an independent municipality until 1974 when it was incorporated into Wünsdorf. In 2003 Wünsdorf, including its Neuhof district, was incorporated into the town of Zossen.
Geographical location
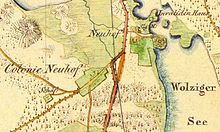
Neuhof is located about nine kilometers south of the center of Zossen on the B 96. The district borders the Wolziger See in the east in its entirety . Lindbrück, a district of the town of Zossen, is located to the south and east of the Wolziger See. To the west is the district of Sperenberg and, over a short distance, the district of Klausdorf (both districts of the municipality of Am Mellensee ). The district of Wünsdorf is north of Neuhof. The new residential areas stretch from the old town center to the Großer Wünsdorfer See . In 1939 the size of the district is given as 296 ha.
history
A farm or dairy was probably built in 1700/1701 near Wolziger Mühle . In any case, in 1701 this location was already referred to as auffm Neuen-Hoffe , in 1753 as Neuhoff, olim Woltziger Mühle ; on the other hand, Bratring writes: "Established in 1747". The Wolziger Mühle was on the right bank of the Notte River, which flows from the Wolziger See to the Großer Wünsdorfer See . The Wolziger Mühle may have been built on the site of a medieval village. The name Neuhof is self-explanatory. In the Urmes table sheet 1: 25,000 (sheet Wünsdorf, No. 3847) from 1840, a larger property is drawn on the left bank of the Notte river and opposite the Wolziger Mühle and is called Neuhoff . A sheep farm near the Wolziger Mühle is mentioned as early as 1655. It was on the road that is now called Märkischer Weg, about 100 meters west of the fork in the Märkischer Weg and Wünsdorfer Weg. It is still recorded in the original table sheet from 1841. In 1745 the sheep farm seems to belong to the Vorwerk or to be connected with it. In 1749, in addition to the Meier (the Vorwerk), the Müller (the Wolziger Mühle), the Shepherd (the Shepherd's farm) and four house people, a wine master is also mentioned. However, it is a one-time mention. Neither in later documents nor in the Schmettauschen card is a winemaker named or a vineyard shown. In 1753 there were plans to make a break with 387 acres of 169 square rods arable and to give them to 12 families from Klein Ziescht (then the Electorate of Saxony , today part of the municipality of Baruth / Mark ). In 1757/8 the alley-shaped Neuhof colony was actually built between the sheep farm and the Neuhof farm along today's Neuhofer Dorfstraße. In 1801 Neuhof had 14 fireplaces (= households) and 103 residents. This year a jug is mentioned for the first time. It is likely to have stood on today's B 96 across from today's manor house. On the Urmes table sheet from 1841 the new location is called Colonie Neuhof . The Vorwerk consists of three buildings, one building is roughly in line with today's manor house, two buildings are at right angles to it and delimit a courtyard open to the north. A star-shaped system can be seen on a small peninsula in the lake, probably a park or garden. The owner (or leaseholder / bailiff) of the Vorwerk Neuhof was a certain Bethge, who also initiated the construction of the Neuhof colony, allegedly at the suggestion of Frederick the Great .
According to Bratring, the Neuhof Vorwerk was still an official Vorwerk at the beginning of the 19th century, administered by the bailiff Rehfeld. The value was then estimated at 5100 thalers. In 1837 the Neuhof Vorwerk was owned by a certain Hintze.
In 1848, the Adlershorst forestry was built in the forest west of the town center and south of today's B 96. In the original table sheet from 1841, a forester's field is already drawn in at the location of the later forester's house, but not yet a building. This part of the district was separated as part of the Kummersdorfer Forest and came to the Fernneuendorf district. Today the location belongs to Sperenberg.
In 1850 there were already 15 houses in the colony and manor. In 1864 the landowner was named D. Ehrlich. In 1861 the inn belonging to Gut Neuhof is leased. In 1868 D. Ehrlich offered the inn, the sheep farm and the dairy farm as well as fields and meadows for sale on the "Dominium Neuhof". In 1870 the property was auctioned on account of debt. This included the manor, inn, a forge, the sheep farm and a day laborer's house, as well as 914.72 acres of land. In 1873 and 1875 a landowner is called Beussel. Beussel was the owner of the manor in Zossen and in 1872 bought the building "Zu Haus Zossen". In 1874 the sheep farm was given up by the landowner Beussel. In 1876 the Wolziger Mühle, which was previously free of parishes, came to the Neuhof parish. In 1877 the Neuhof estate was merged with the Neuhof colony and the Adlershorst forestry to form the Neuhof municipality. The Neuhof manor house, reminiscent of French models, was built around 1890.
From around the 1930s, the Neuhof villa colony was built in the area around the Great Wünsdorfer See, which also has several representative buildings with extensive gardens. Also in the 1930s, the Halpaus canning factory settled on the former estate. The farm buildings of the estate were converted into warehouses and factories, and the estate building was used as an administration building. From 1939 onwards, canned meat was mainly supplied to the Wehrmacht.
At the end of the Second World War, on April 21, 1945 there was still heavy fighting near Neuhof. On the same day, the bunker rooms of the Army High Command near Wünsdorf were occupied. It had been evacuated the day before.
After the Second World War, 155 hectares of state forest were expropriated, of which 128 hectares were divided. The canning factory was also converted into a VEB . In 1956 it produced canned vegetables, fruit and fish with 149 employees. In 1959 a Type I LPG was established with initially seven members. In 1961 there were 44 members, and the LPG cultivated 145 hectares of agricultural land. In 1973 the Neuhof plant belonged to the VEB Havelland fruit and vegetable processing company in the Potsdam district. There was also the steel construction Neuhof production department of the VEB (B) Hochbaukombinat Potsdam and the state forestry company.
After the fall of the Wall, a holiday home and leisure facility was built on the estate. The factory buildings were almost all demolished. The former manor house and later administration building was renovated and converted into a representative restaurant. The area and the manor house have been vacant and for sale for several years.
In 1990, the “Wünsdorfer Werkstätten gGmbH” for disabled people was established in the northwestern area of the Neuhofer district. According to its own information, it employs 300 disabled employees and 80 carers.
Schlotthorst
In 1777 the civil servant Gerresheim submitted the plan to build a two-family house at Schlotthorst (also Schlothorst; a peninsula protruding into the Wolziger See only around 500 meters northeast of the "Colonie Neuhoff") for approval. The house was completed a year later. On the Urmes table of 1841 the "establishment" is referred to as the Invalidenhaus . Around 1860 two residential buildings and two farm buildings are already mentioned. In 1858 the small settlement had eight residents.
Population development from 1583 to 1971 (from the historical local dictionary)
| year | Residents |
|---|---|
| 1772 | 85 |
| 1801 | 103 |
| 1817 | 79 |
| 1840 | 141 |
| 1858 | 171 |
| 1895 | 263 |
| 1925 | 284 |
| 1939 | 379 |
| 1946 | 490 |
| 1964 | 470 |
| 1971 | 486 |
Administrative affiliation
In the 18th century the place belonged to the Zossen office ; this had emerged in 1490/1 from the medieval rule of Zossen . With the development of the district order in Brandenburg, it was counted as part of the Teltow district. With the dissolution of the Zossen office in 1872, the last dependencies were eliminated. With the unification of the manor district and the municipality district in 1877, Neuhof was now an independent municipality within the Teltow district. When the Teltow district was dissolved in 1952, Neuhof was assigned to the Zossen district . In 1974 Neuhof was incorporated into Wünsdorf and has been part of Wünsdorf ever since. From 1992 to 2003 Wünsdorf was administered by the (new) Zossen office. With the legally mandated incorporation of Wünsdorf (as a district) into the city of Zossen and the dissolution of the Zossen office in 2003, Neuhof became part of the municipality of Wünsdorf.
Monuments and sights
monument
The only monument in the area is the representative Neuhof manor house , built around 1890 . It is a transversely rectangular building with central and side projections and flat side extensions. The ground floor on a low plinth has high rooms, and above it is a mansard roof with lavishly designed windows in the side elevations.
Natural monuments
A group of trees consisting of four oaks (0.2 km south of the station, east of the railway line) is protected as a natural monument because of its age and size.
Personalities
- Frieda Kassen (* 1895 in Neuhof (Zossen); † 1970 in Bremen), German politician (SPD), member of the Bremen citizenship
- Ernst-Joachim Gießmann (* 1919 in Berlin; † 2004 in Neuhof), German physicist, professor and rector in Magdeburg, state secretary and minister for higher education in the GDR, professor in Berlin-Wartenberg
supporting documents
literature
- Lieselott Enders and Margot Beck: Historical local dictionary for Brandenburg. Part IV. Teltow. 395 p., Hermann Böhlaus successor, Weimar 1976.
- Gerhard Schlimpert : Brandenburg name book part 3 The place names of the Teltow. 368 p., Hermann Böhlaus successor, Weimar 1972.
- Wilhelm Spatz: The Teltow. Part T. 3., History of the localities in the Teltow district. 384 pp., Rohde, Berlin 1912.
Individual evidence
- ^ Service portal of the state administration Brandenburg - City of Zossen
- ↑ a b Main statutes of the city of Zossen from March 4, 2009 PDF ( Memento of the original from December 13, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Friedrich Wilhelm August Bratring: Statistical-topographical description of the entire Mark Brandenburg: for statisticians, businessmen, especially for cameramen Vol 2 containing the Mittelmark and Ukermark. VIII, 583 S., Berlin, Maurer, 1805 Online at Google Books
- ↑ Schlimpert (1972: p. 141/2)
- ^ Berthold Schulze: Property and settlement history statistics of the Brandenburg authorities and cities 1540-1800. Supplement to the Brandenburg office map. Individual writings of the historical commission for the province of Brandenburg and the imperial capital Berlin, Volume 7, 190 pp., Im Kommissionsverlag von Gsellius, Berlin, 1935.
- ↑ Spatz (1912: p. 205)
- ↑ August von Sellentin: Topographical-statistical overview of the government district of Potsdam and the city of Berlin: Compiled from official sources. 292 pp., Verlag der Sander'schen Buchhandlung, 1841.
- ↑ Enders & Beck (1976: p. 3)
- ↑ Teltower Kreisblatt of July 17, 1867, p. 222 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ^ Teltower Kreisblatt dated October 12, 1861, p. 7 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ^ Teltower Kreisblatt dated October 17, 1868, p. 332 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ^ Teltower Kreisblatt dated August 10, 1870, p. 275 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ↑ Teltower Kreisblatt of October 7, 1876, p. 324 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ↑ A small excerpt from the history of the district court ( memento of the original from June 13, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Teltower Kreisblatt of April 25, 1874, p. 135 full-text search of the Prussian official press
- ↑ Teltower Kreisblatt from January 20, 1876, p. 26 full text search of the Prussian official press
- ^ Carsten Preuß and Hiltrud Preuß: The manor houses and mansions in the Teltow-Fläming district. 243 pp., Lukas Verlag, Berlin, 2011 ISBN 978-3-86732-100-6 (pp. 146–9)
- ↑ What happened on April 20 and 21, 1945?
- ↑ Wünsdorfer Werkstätten gGmbH Recognized workshop for disabled people
- ↑ a b Enders and Beck (1976: pp. 203-207)
- ↑ Fourth law on state-wide municipal area reform concerning the districts Havelland, Potsdam-Mittelmark, Teltow-Fläming (4th GemGebRefGBbg) of March 24, 2003, § 19
- ↑ List of monuments of the State of Brandenburg for the district of Teltow-Fläming (as of December 31, 2011) PDF ( Memento of the original from September 23, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Landkreis Teltow-Fläming Natural Monuments - Trees PDF ( Memento of the original dated December 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.