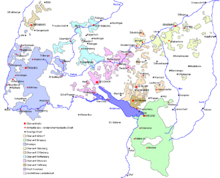
Swabian Austria
Swabian Austria was the mostly Upper Swabian part of Upper Austria . From 1490 on it comprised the possessions of the House of Habsburg in the Duchy of Swabia until the Peace of Pressburg in 1805. Swabian Austria was legally and territorially part of the Swabian Confederation , Swabian Empire and partly of the Austrian Empire , within the Holy Roman Empire . In the 500-year history of Upper Austria and its Swabian Austria sub-area, the Habsburgs only partially succeeded in proclaiming the area a crown land .
History and location
The Habsburg possessions west of the Lech in today's areas of Bavarian Swabia , Upper Swabia , Southern Baden , Eastern Switzerland , Upper Alsace , Vorarlberg and in the Territoire de Belfort were referred to as Vorderösterreich or Vorlande for short . The ancestral castle of the Habsburgs, the Habsburgs, is located in these foreland .
The Swabian-Austrian part of the foreland was the Margraviate of Burgau , the Landgraviate of Nellenburg , parts of the later Principality of Fürstenberg , the Reichslandvogtei of Swabia , the County of Hohenberg , Tettnang , Ehingen and five other Danube towns, Mengen , Munderkingen , Riedlingen , Saulgau and Waldsee . In addition, there were in part the spiritual territories of the Upper Swabian prelate bank of the Benedictines , Premonstratensians and Cistercians , who had submitted to the emperor in Vienna with regard to property rights.
The Habsburgs' original Swiss holdings were lost very early on. The defeats of the Habsburg dukes at the battles at Morgarten (Leopold I, 1315), at Sempach (Leopold III, 1386) and at Näfels (Albrecht III, 1388) were decisive for this. In 1415 they lost Aargau as a result of Duke Friedrich IV's ostracism , Rapperswil in 1458 , Thurgau in 1460 and Winterthur in 1467 . With the acquisition of Tyrol and finally all of Vorarlberg, the Habsburgs were able to establish a territorial connection between Austria and Upper Austria and to compensate for the loss of power.
Treaty of Neuberg 1379
The real founder of Front Austria was Leopold III. of Habsburg Austria , who fell in the battle of Sempach . In the Treaty of Neuberg of September 25, 1379 the area was determined. Albrecht III. Austria received under and above the Enns (without Wiener Neustadt and the County of Pitten, but with Steyr and the Salzkammergut); Leopold III. Styria (with the area of Wiener Neustadt), Carinthia, Krain, the Windische Mark, Istria, Tyrol and the Vorlande. With the Neuburg partition agreement, two Habsburg lines (Albertine line, Leopoldine line) were established. The lost battle at Sempach had a devastating impact on the politics of the Habsburgs in their home countries. Therefore the union took place all possessions again until 1493 by Maximilian I .
In 1490 the foreland government with its seat in Ensisheim in Alsace was subordinated to the central administration for Tyrol and the foreland with its seat in Innsbruck , created by Maximilian I. In 1651, Freiburg im Breisgau became the seat of the government of Upper Austria. Swabian Austria remained subordinate to the central administration in Innsbruck. The Habsburgs did not succeed in transforming the area into a closed crown land , such as the Fürstete Grafschaft Tirol, for example.
In the four large administrative units of Swabian Austria - the Margraviate of Burgau, Landvogtei of Swabia, Landgraviate of Nellenburg and the County of Hohenberg - there were 528 witch trials between 1493 and 1711 , around 90 of which were around 90 , at the secular courts that were administered directly and undivided by Habsburg % against women. 80% of the proceedings took place in the County of Hohenberg .
Peace of Pressburg 1805
After the first for the Empire Russia devastating and Austria defeat in the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805, also Battle of Three Emperors called, was the same year the Treaty of Pressburg closed. There, and finally in 1815, all areas of Upper Austria came to the Grand Duchy of Baden , the Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Bavaria .
With the division of Swabian Austria and the territorial retreat of Habsburg into the Austrian heartlands that remained to him, the Bavarian Wittelsbach land gains were able to record beyond the Lech border and were elevated to the rank of Kings of Bavaria. The people of Württemberg, originally only present around today's state capital Stuttgart , expanded their area to Lake Constance and were also elevated to kings.
Administrative division 1790
- Oberamt Hohenberg (formerly Grafschaft Hohenberg ) - areas on the upper Neckar around the administrative headquarters Rottenburg am Neckar ( Horb am Neckar , Oberndorf am Neckar ) and on the western edge of the Swabian Alb ( Schömberg , Spaichingen )
- Oberamt Nellenburg (former Landgrafschaft Nellenburg ) - areas from the northwest of Lake Constance ( Stockach , the administrative center, Radolfzell ) over the Hegau ( Aach ) to the Danube ( Mengen ), rule Gutenstein , Saulgau , areas in the vicinity of Riedlingen in today's Biberach district , whereby Stockach and the Hegau belong to Baden.
- Oberamt Altdorf (former Landvogtei Schwaben ) - administrative seat Weingarten , areas from the eastern north shore of Lake Constance via the Schussental ( Waldsee ) to the Ostalb ( Schelklingen , the city of Riedlingen ), also in the western Allgäu the area around the imperial city of Leutkirch in the Allgäu (Gebrazhofen) in today's Ravensburg district
- Oberamt Tettnang (formerly Reichsgrafschaft Tettnang ) - a closed area on the central northern shore of Lake Constance around Tettnang and Wasserburg am Bodensee , which included part of the former territory of the Counts of Montfort .
- Oberamt Günzburg (formerly Margraviate Burgau ) - in addition to the administrative seat of Günzburg, other areas in today's Bavarian administrative district of Swabia ( Krumbach (Schwaben) , Weißenhorn , Burgau , Ziemetshausen ) in today's district of Günzburg and in today's Alb-Danube district ( Ehingen )in Baden-Württemberg
literature
- Franz Quarthal : Land estates and land taxation in Swabian Austria (writings on Southwest German regional studies, vol. 16), Stuttgart: Müller & Gräff 1980, XXXVIII + 514 pp.
- Franz Quarthal: The best, most loyal and most affectionate subjects. On the history of the Swabian-Austrian estates. In: Contributions to regional studies 1979 (Issue 1), pp. 1–33.
- Paul Rothmund: The five Danube cities in Swabian Austria , dissertation, Tübingen 1955.
- Johannes Dillinger : "Bad people". Witch persecution in Swabian Austria and Kurtrier in comparison, Trier 1999
Web links
- Swabian Austria in aeiou
- History of Swabia up to the end of the 18th century - §41 The Habsburg possessions: Swabian Austria and the foreland
Individual evidence
- ^ Franz Quarthal : When Swabia was ruled from Austria. On the history of the Habsburg possessions in southwest Germany. In: Schöne Schwaben 10/11, 1996 (Issue 6), pp. 34–39.
- ↑ Johannes Dillinger: Witches' persecutions in Swabian Austria of December 13, 1999, accessed on July 10, 2010