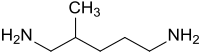
2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry - 1: 1 mixture of enantiomers | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 16 N 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 116.21 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.86 g cm −3 at 25 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−50 to −60 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4588 (25 ° C, 589 nm) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane MPMD is a branched aliphatic primary diamine which u. a. is used as a building block for vitamins , as a raw material for diisocyanates , as a hardener for epoxy resins and as a diamine component for polyamides .
Occurrence and representation
As early as 1902, the Austrian chemists Adolf Franke and Moritz Kohn published a synthesis for 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane from 1,3-dibromobutane by Kolbe nitrile synthesis with potassium cyanide to form 2-methylglutaronitrile
and subsequent hydrogenation with sodium in boiling ethanol .
The 2-methyleneglutaronitrile formed in the dimerization of acrylonitrile by head-to-tail linkage gives 2-methylpentamethylenediamine in 80% yield along with 3-methylpiperidine (18%) when hydrogenation is complete.
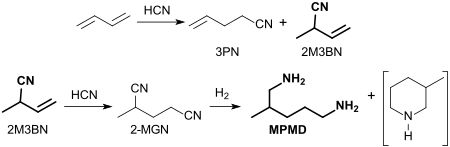
Of Ni 0 - phosphorus - complexes catalyzed than hydrocyanation indicated, addition of hydrogen cyanide HCN to 1,3-butadiene yields a mixture of positionally isomeric pentenenitriles with the main component of 3-pentenenitrile 3PN (precursor for adiponitrile ) and the main minor component of 2-methyl- 3-butenenitrile 2M3BN.
Further hydrocyanation of 2M3BN leads to 2-methylglutaronitrile 2-MGN, which is hydrogenated to the target compound 2-methylpentane-1,5-diamine (in addition to a little 3-methylpicoline).
The synthesis of 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane from a waste product of adiponitrile (starting material for the nylon 6.6 -diamine component hexamethylenediamine HMDA, and to a lesser extent also for the The dicarboxylic acid component adipic acid appears to be the most economical option.
properties
2-Methyl-1,5-diaminopentane is a colorless, clear liquid with an amine-like odor, the aqueous solutions of which are alkaline (pH 12.1 in 5% solution at 25 ° C).
Applications
MPMD as a functional chemical
Corrosion inhibitor : like other diamines, e.g. B. Isophoronediamine , 2-methyl-1,5-pentamethylenediamine is an effective corrosion protection agent in aqueous media in contact with iron surfaces.
Cooling lubricant : in drilling cutting emulsions , 2-methylpentane-1,5-diamine suppresses oxidation and discoloration of the machined metal surfaces and extends the service life of milling, drilling and cutting tools.
MPMD as a building block
As a branched aliphatic diamine, 1,5-diamino-2-methylpentane is suitable for the preparation of diisocyanates by reaction with phosgene . Compared to hexamethylene diisocyanate HDI, MPMD diisocyanate reduces the melting temperature and increases the flexibility of hot melt adhesives .
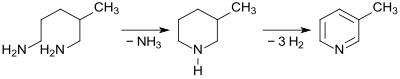
Because of its wide availability, 1,5-diamino-2-methylpentane is a preferred starting material for the B vitamins nicotinic acid and nicotinamide (niacinamide). For this purpose, the diamine MPMD is cyclized practically quantitatively (> 99.5% yield) to 3-methylpiperidine MPI on a zeolite contact with elimination of ammonia at 335 ° C. , which is then cyclized on a palladium - magnesium chloride - aluminum oxide contact at 280 ° C. , 3% yield is dehydrated to 3-methylpyridine (β-picoline) .
The reaction sequence can also be carried out in two reactors connected in series without isolating the intermediate product MPI and then gives 3-methylpyridine in 99.1% yield.
In the further Niacinamidsynthese β-picoline is a ammoxidation using oxygen and ammonia at 330 ° C in 95% yield 3-cyanopyridine transferred, the biotechnologically by immobilized Rhodococcus bacteria of the species Rhodococcus rhodochrous is virtually quantitatively converted to nicotinamide.
MPMD as a reactive component in polymers
The incorporation of the branched diamine 2-methyl-1,5-pentanediamine into polymeric materials disrupts the parallel arrangement of the polymer chains and hinders or prevents the formation of crystalline structures. MPMD-containing polymers therefore have lower glass transition temperatures or melting temperatures. They are usually easier to process and in many cases have improved material properties.
Epoxies : 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane is a fast and efficient hardener even at low temperatures and shortens the gel time while maintaining the mechanical strength of epoxy resins.
Polyurethanes and polyureas : 2-Methyl-1,5-pentamethylene diamine may be used as chain extender (engl. Chain extender ) and crosslinking agent (engl. Cross-linker ) can be used in polyurethanes. MPMD reacts with diisocyanates to form polyureas.
Polyamides : in aliphatic polyamides, the incorporation of the asymmetric diamine 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane causes a significant reduction in the melting temperature (nylon 6,6: T M = 265 ° C; nylon MPMD, 6: T M = 184 ° C) , and quenching (rapid cooling) of the melt causes the MPMD-containing polyamide to solidify amorphously . This makes such polyamides suitable as hot-melt adhesives, for powder coatings and 3D printing . In partially aromatic polyamides ( polyphthalamides with terephthalic acid PTA or isophthalic acid as dicarboxylic acid components), 2-methyl-1,5-pentanediamine lowers the crystallinity and improves mechanical properties, e.g. B. the flexural strength, and increases the transparency. The proportion of expensive reactants, e.g. B. Isophthalic acid can be reduced with the addition of MPMD.
Manufacturer and trade name
2-methylpentamethylenediamine was originally developed and brought to market by DuPont . Today it is a product of Invista , which belongs to the US company Koch Industries and markets MPMD under the brand name DYTEK® A.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 2-methylpentane-1,5-diamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 22, 2020 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ a b c d e Technical Information, DYTEK® A Amine. Invista, March 5, 2018, accessed April 22, 2020 .
- ↑ Entry on 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane at TCI Europe, accessed on April 22, 2020.
- ↑ Data sheet 1,5-diamino-2-methylpentane from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 22, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ A. Franke, M. Kohn: About a synthesis of alkylated glutaric acids from β-glycols . In: monthly Chem. Band 23 , 1902, pp. 740-746 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01524932 .
- ↑ A. Franke, M. Kohn: About a synthesis of alkylated pentamethylene diamines and alkylated piperidines from β-glycols . In: monthly Chem. Band 23 , 1902, pp. 877-885 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01536355 .
- ↑ Patent US3408397 : Methyl pentamethylene diamine process. Filed June 1, 1965 , published October 31, 1967 , Applicant: National Distillers and Chemical Corp., Inventor: J. Feldman, M. Thomas.
- ↑ Patent EP2041075B1 : Process for making 3-pentenenitrile from butadiene. Filed July 13, 2007 , published March 25, 2015 , Applicant: Invista Technologies S.à.rl, Inventors: T. Foo, SS Kristjansdottir, RJ McKinney, R. Ozer.
- ↑ N. Herrmann, D. Vogelsang, A. Behr, T. Seidensticker: Homogeneously catalyzed 1,3-diene functionalization: A success story from laboratory to miniplant scale . In: Chem. Cat. Chem. Band 10 , no. 23 , 2018, p. 5342-5365 , doi : 10.1002 / cctc.201801362 .
- ↑ Patent US4987263 : Preparation of 2-methylpentadiamine. Applied on August 12, 1988 , published January 22, 1991 , applicant: Rhone-Poulenc Chimie, inventor: G. Cordier.
- ^ Adiponitrile plans Shanghai Invista - Archive. Polyestertime, February 25, 2019, accessed April 24, 2020 .
- ↑ Patent EP0691955B1 : Process for the production of 3-methylpiperidine and 3-methylpyridine by catalytic cyclization of 2-methyl-1,5-diaminopentane. Applied on March 30, 1994 , published on May 28, 1997 , applicant: Lonza AG, inventor: J. Heveling, E. Armbruster, W. Siegrist.
- ↑ Patent US5719045 : Process for preparing nicotinamide. Applied on October 31, 1996 , published on February 17, 1998 , applicant: Lonza AG, inventors: J. Heveling, E. Armbruster, L. Utiger, M. Rohner, H.-R. Dettwiler, RJ Chuck.