Barique
| Barique | ||

|
||
|
||
| Data | ||
| surface | 122.13 km² | |
| population | 1,258 (2015) | |
| Chefe de Suco | Alexandrino Soares (election 2009) |
|
| Aldeias | Population (2015) | |
| Caunua | 249 | |
| Weubani | 189 | |
|
|
||
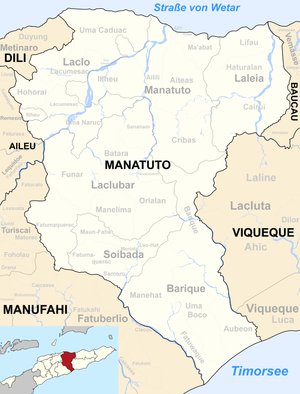
Barique is an East Timorese place and Suco in the Barique administrative office ( formerly Barique / Natarbora ) in the municipality of Manatuto . The place name is derived from the Malay word "Perigi" , which means "source".
The place
Barique is located in the interior of Timor in Suco Barique, about 66 km as the crow flies southeast of the state capital Dili and just 37 km south of the municipal capital Manatuto . The place is at an altitude of 301 m . Just a little further south are the villages of Caunua and Weubani ( Webani ). The only road of the sucos connects Barique with the southern coastal road, one of the main routes of East Timor. However, this is interrupted again and again. For the parliamentary elections in East Timor in 2007 , the ballot boxes had to be brought to Barique with porters and horses and then picked up again. In Barique there is a primary school ( Escola Primaria Barique ), a health post and a helipad.
The Suco
| Barique | ||
| places | position | height |
| Barique | 8 ° 50 ′ S , 126 ° 4 ′ E | 301 m |
| Caunua | 8 ° 51 ' S , 126 ° 4' E | 303 m |
| Weubani | 8 ° 51 ' S , 126 ° 4' E | 303 m |
A total of 1258 people (2015) live in Suco Barique, of which 663 are men and 595 women. The population density is 10.3 inhabitants / km². There are 240 households in the Suco. Almost 45% of the population name Tetum Terik as their mother tongue. Over 34% speak Habun , 8.5% Midiki , over 8% Idaté , 2.5% Tetum Prasa , minorities Galoli , Mambai or Lolein .
Before the 2015 territorial reform, Barique had an area of 114.22 km². Now there are 122.13 km². The Suco forms the north of the administrative office of the same name. Here it extends to the administrative offices of Laleia (Suco Cairui ) and Manatuto (Suco Cribas ). In the west are the administrative offices Laclubar (Sucos Fatumaquerec and Orlalan ) and Soibada (Suco Samoro and Leo-Hat ), further south the Suco Manehat and in the southwest Barique borders on the Suco Fatuwaque . To the east is the Lacluta administrative office (municipality of Viqueque ) with its sucos Ahic and Laline . Almost the entire length of the border is formed by the Rio Dilor , the most important river in the region. The Melac and Leci , headwaters of the Dilor, have their source in the north of Barique. The Melac forms the border with Laline. The Leci leaves Barique for Laline and there flows into the Leec , which together with the Melac forms the Dilor. Shortly afterwards the Buco river , which has its source in the Suco Orlalan, meets the Dilor. A left tributary of the Buco is the Nabaonada. It flows along the border between the Sucos Leo-Hat and Barique. The Tacabucan rises in Barique and flows into the Dilor. The Ribeira Culacao rises in the northeast of Manehat and then roughly follows the border between the Sucos Fatuwaque and Barique up to its confluence with the Dilor. A right tributary of the Culacao is the Motobeca . The Dilor forms a larger lake with several small islands at one point on the border with Viqueque. The Haeraun , a tributary of the Laleias, has its source in the north-west of Barique . The Haeraun flows north into the Suco Cribas. Most of the Sucos landscape is mountainous. In the north the mountains reach heights of over 1100 m .
The two Aldeias Caunua and Weubani are located in the Suco .
history
Barique was one of the traditional kingdoms of Timor, ruled by a liurai . It appears on a list by Afonso de Castro , a former governor of Portuguese Timor , listing 47 empires in 1868. During the rebellion in Cowa , Barique gave arms to the Portuguese colonial power.
In the Second World War, the bombed Australian Air Force on May 17, 1943 Place Barique with B-25 bombers in the fight against the Japanese .
In 1976 Barique was a retreat for the FALINTIL , who fought against the Indonesian invaders. Here they founded a base de apoio , a resistance base that offered refuge for refugees from Natarbora, Laclubar, Barique and Same . The base was later destroyed by the Indonesians.
In 1981 700 families from Barique and the entire Viqueque district at that time were to be deported to Atauro . The intervention of the Lacluta administrator ultimately prevented families from his sub-district from having to go to the island. Many of the others died of hunger, disease and climate change. It was not until 1985/1986 that some of the deportees returned to their old homeland.
politics
In the 2004/2005 elections , Estevão dos Anjos was elected Chefe de Suco. In the 2009 elections won Alexandrino Soares .
Web links
- Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Barique ( tetum ; PDF; 7.94 MB)
- Results of the 2015 census for the Suco Barique (tetum; PDF)
- Seeds of Life: Suco information sheets Barique (tetum)
- UCA, May 12, 2009, Priest revives faith on horseback in remote region. About the work of the local priest on horseback
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Direcção-Geral de Estatística : Results of the 2015 census , accessed on November 23, 2016.
- ↑ Geoffrey Hull : The placenames of East Timor. In: Placenames Australia (ANPS): Newsletter of the Australian National Placenames Survey, June 2006, pp. 6 & 7, ( memento of February 14, 2017 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on September 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b List of polling stations for the parliamentary elections in East Timor 2007 (PDF file; 118 kB)
- ↑ UNMIT map of the Manatuto district, August 2008 ( Memento from December 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF file; 567 kB)
- ↑ Fallingrain.com: Directory of Cities, Towns, and Regions in East Timor
- ↑ Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Barique ( tetum ; PDF file; 7.94 MB)
- ↑ Direcção Nacional de Estatística: Population Distribution by Administrative Areas Volume 2 English ( Memento from January 5, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) (Census 2010; PDF; 22.6 MB)
- ↑ Jornal da Républica with the Diploma Ministerial n. 199/09 ( Memento of February 3, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (Portuguese; PDF; 323 kB)
- ↑ TIMOR LORO SAE, Um pouco de história ( Memento from 20050829140354)
- ↑ East Timor - PORTUGUESE DEPENDENCY OF EAST TIMOR ( Memento of February 21, 2004 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ History of Timor - Technical University of Lisbon ( Memento of the original from March 24, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF file; 805 kB)
- ↑ a b "Chapter 7.3 Forced Displacement and Famine" ( Memento from November 28, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF file; 1.22 MB) from the "Chega!" Report of the CAVR (English)
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2004/2005 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2009 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )