Global environmental changes and future scenarios
Global environmental changes and future scenarios refer to scientific studies of the state of the terrestrial biosphere , taking into account the balance of nature ( biomes , ecosystems , climate , geology , hydrology , material cycles ) as well as man-made influencing variables (e.g. population growth , use of raw materials and energy , input of substances in the environment , land use ) in their interactions in order to be able to predict model surveys with the probable statistical trends for future development . Existing influences on the natural environment, such as environmental pollution and damage , unusual changes in flora and fauna , land use or the reduction of the "wilderness" are also assessed and included in the considerations. The data basis comes from globally distributed measuring stations for environmental observation . As a rule, the commissioned researchers model different scenarios assuming different political, economic and technological development directions .
Such studies only became feasible through computer simulations , which enable people to meaningfully process the enormous amounts of data from the highly complex systems and use them to perform calculations.
The clients are mostly associations of committed scientists, governments or the United Nations . The goals are primarily to create a resilient basis for a sustainable global environmental policy .
The studies published since the middle of the 20th century have all come to similar conclusions: Since 1972 it has been assumed that global ecosystem services - i.e. the benefits that humans can derive from the life communities on earth - are at great risk. The positive scenarios became increasingly rare and improbable over the decades. The available data was validated and verified again and again on the basis of actual developments .
The scenarios of all studies show that only extremely committed and short-term innovative countermeasures could prevent a global, no longer controllable global environmental catastrophe .
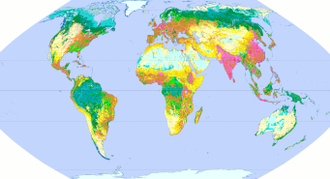
| Anthromes of the earth | |
|
Natural and anthropogenic biomes in the early 21st century (Ellis and Navin Ramankutty , 2008) |
Various studies over the decades
The data surveys and calculations carried out since the 1950s prove that human activity has a decisive influence on the changes on planet earth . Among other things, this led to completely new ecological considerations of the world: Instead of just looking at natural habitats, today the landscape types shaped by humans are also taken into account on a global level in the sense of smoothly merging degrees of hemerobicity (closeness to nature ↔ distant from nature).
It has been discussed since the beginning of the 21st century whether man has ushered in a new geological age. The name for it was provided by the chemist Paul Crutzen and the biologist Eugene Stoermer with their creation of the term Anthropocene .
Since 1956: International climate studies
"Mankind has started a large-scale geophysical experiment that has never existed in this form in the past, nor will it happen a second time in the future."
The beginning of global environmental studies is closely linked to research into climate change. In 1956 the Canadian physicist Gilbert Plass used computers for the first time to calculate possible global temperature profiles in the future. He found that, contrary to the theories existing at the time, global warming would occur much faster. It reached an increase of about one degree Celsius by the year 2000.
In 1960, the German meteorologist Fritz Möller developed the first complete climate model. From 1960 the data situation improved dramatically due to the use of earth observation satellites . The Russian geographer Mikhail Ivanovich Budyko was the first climate researcher who, on the basis of his model, assumed a serious threat to mankind from man-made climate change.
International recognition as a global problem began with the 1st World Climate Conference in 1979. This resulted in a fundamental declaration and the initiation of the World Climate Research Program and the establishment of the Intergovernmental Committee on Climate Change ( IPCC ) by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) and the world organization for Meteorology (WMO) in 1988.
Since then, hundreds of model calculations have been carried out by the IPCC, but also by a number of other organizations, with increasingly more likely and more accurate results.
Since the early 1990s at the latest, there has been a very broad consensus in science about the reality of climate change and its anthropogenic causes. Controversial debates about the alleged uncertainties of the studies, which are often fueled by business representatives and politicians, only take place outside the sciences.
The consequences of global warming affect all areas of nature and human life. Direct and unequivocally occurring consequences are rising sea levels , melting glaciers , shifting climate and vegetation zones , changing the occurrence of precipitation , stronger or more frequent weather extremes such as floods , storms and droughts ; Spread of parasites and tropical diseases and more environmental refugees .
Further possible consequences - such as a further acceleration of the mass extinction - are intensively investigated and discussed. They are often the subject of further studies.
1964-1974: International Biological Program
The International Biological Program (IBP) was the first large-scale ecological research program . The most ambitious part of the program was a basic inventory of biocenotic relationships, food chains, and energy and material flows for entire biomes. Although the results of the program were assessed as rather a failure by many scientists and no groundbreaking advances in knowledge were associated with it, it was of important importance for the organization and management of the later ecological studies.
The UNESCO program Man and the Biosphere ( MAB program for short ), launched in 1970 - in which 150 countries are now involved - emerged from the IBP.
1972–2004: The Limits to Growth

The study “The Limits to Growth - A Report for the Club of Rome on the State of Humanity” , published in 1972, was the prelude to numerous scientifically based prognoses on the future development of the world with regard to the consequences of human activities ( global economy , technology , politics ) entire system earth.
Various factors that show exponential growth were examined . The interactions and control loops became the basis for the computer simulation " World3 ". The result of the simulation was worrying:
“If the current increase in world population , industrialization, environmental pollution, food production and the exploitation of natural resources continue unchanged, the absolute limits of growth on earth will be reached over the next hundred years. [...] Technical solutions alone cannot lead us out of this diabolical control loop. "
This prognosis has long and heavily criticized for various reasons.
However, a CSIRO study from 2008 came to the conclusion that the actual development from 1970 to 2000 largely coincided with the predictions of the standard scenario from the “Limits to Growth”. The model assumes a global collapse for the middle of the 21st century.
Since 1972, the models have been checked, revised and expanded three times on the basis of accumulated data. Despite more extensive initial data and more powerful computers, the results were essentially unchanged. The 40-year forecast up to 2052 from 2012 comes in most of the calculated scenarios for exceeding growth limits with subsequent collapse (“overshoot and collapse”) by 2100 at the latest . In contrast to the first study, it is no longer possible to avert this scenario ; even with an extremely ambitious mixture of restricting consumption , controlling population growth, reducing pollutant emissions and numerous other measures. If the development of the last 30 years is continued unchanged, the collapse will occur as early as 2030, according to the forecast.
1980: Global 2000
The Global 2000 study was commissioned by US President Jimmy Carter in 1977 . It should identify fundamental developments in environmental conditions and their likely effects by the year 2000. The much broader and more progressive study than the “Limits to Growth” forecast both disproportionate population growth and growing environmental problems and already saw clear signs of climate change.
1995 and 2010: Factors four and five
Ernst Ulrich von Weizsäcker , Amory Lovins and Hunter Lovins also wrote reports for the Club of Rome: In 1995 “ Factor Four ” - Double Prosperity - Halved Consumption of Nature and 2010 “Factor Five” appeared. With the help of a technologically increased resource productivity , energy efficiency , eco-taxes and a conscious change from the standard of living to the quality of life , the authors try to achieve scenarios that manage without collapse.
2005: Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment study was initiated by the United Nations . The aim was a systematic overview of the global status of 24 key ecosystem services .
The results showed that the earth is in a state of degradation . 60% or 15 out of 24 ecosystem services examined had been in a state of advanced and / or sustained destruction since the middle of the 20th century. This leads to a decline in the functionality of the ecosystems. This process has accelerated increasingly due to increasing consumer needs. The plans of the UN to abolish hunger and to combat epidemics worldwide cannot be achieved with such pronounced environmental damage. The study shows solutions for many of the problems identified, but sees a lack of institutional and financial prerequisites for this.
2009: Planetary Boundaries

An international group of researchers led by Johan Rockström from the Stockholm Resilience Center published the study Planetary Boundaries in the journal Nature in 2009 . They determined the most important environmentally relevant parameters of planet earth and their critical limit values. The aim of this definition is to clearly simplify the highly complex interrelationships of the biosphere in this way in order to make risks visible quickly and clearly using a few key parameters. According to this study, mankind must manage to stay below 100% for all parameters in the long term in order not to endanger the environment - and thus our livelihoods - in an unpredictable manner:
-
Values that were over 100% in 2009 :
- Loss of biological diversity :> 1,000%
- Sulfur emissions : 346%
- Carbon dioxide in the earth's atmosphere : 111%
-
Values close to 100% :
- Thinning of the ozone layer : 98%
- Ocean acidification : 95%
-
Values well below 100% :
- Phosphorus loss from the seas: 82%
- Land areas influenced by settlement and agriculture: 78%
- Fresh water resources : 65%
1992, 2017 and 2019: Warnings to humanity
On November 13, 2017, 15,372 scientists from 184 countries published a “second warning to humanity”. They referred to a "first warning" issued in 1992 by 1,575 scientists from the American Union of Concerned Scientists .
“We, the undersigned - senior members of the world's scientific community - hereby warn all of humanity of the future. A major change in the way we deal with the earth and its living beings is necessary if threatening misery is to be avoided and our global home on this planet is not to be irrevocably mutilated. "
25 years later, the forecast at that time was compared with the actual developments. Since 1992, with the exception of stabilization of the stratospheric ozone layer and overfishing, humankind has not made sufficient progress in improving key global environmental features (see graphs at the beginning of this article) . On the contrary, the negative trend is unchanged. Of particular concern is the ongoing development of a potentially catastrophic climate change in connection with deforestation and agricultural production targets (especially the factory farming of cattle for meat consumption and the destruction of habitat ). In addition, the loss of species caused by humans is rated as the sixth “mass extinction event” in around 540 million years. Other negative trends concern the so-called dead zones in the world's oceans.
2018: Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene
An international team of scientists published a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on August 6, 2018 , according to which there remains a serious risk that global warming will not stay at 1.5 ° C to 2 ° in the long term C could be stopping. Even if the plans set out in the Paris Agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are implemented, there is still a risk that various feedback processes will cause the planet to end up in a state that researchers call “Hothouse Earth”. Such a hot period would be characterized in the long term by temperatures around 4 ° C to 5 ° C higher and a sea level rise of 10 m to 60 m, according to the publication. The transition to an emission-free world economy must therefore be accelerated significantly, argue the authors.
“These tilting elements could act like a series of dominoes. If one of them is tilted, this element pushes the earth towards another tipping point. It could be very difficult or even impossible to keep the whole row of dominoes from tipping over. Some places on earth could become uninhabitable if the "hot season" became a reality. "
2019: Scientists declare "climate emergency"
In November, more than 11,000 researchers from 153 countries warned of a global climate emergency . In the appeal published in the journal Bioscience , the researchers wrote that "unspeakable human suffering" can no longer be prevented unless human behavior changes, which lead to the emission of greenhouse gases and other factors that favor climate change. Scientists have "a moral obligation to warn humanity of any catastrophic threat and 'say what it is like.'" The data clearly showed that humanity was facing a climate emergency. Six decisive changes are necessary: switch to renewable energies , reduce pollutant emissions such as B. methane and soot, improved protection of ecosystems such as forests and moors, a change in diet to more plant-based and less animal products, sustainable change in the world economy and curbing global population growth .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Uta Kirschten: Sustainable personnel management: current concepts, innovations and corporate development. UVK, Konstanz / Munich 2017, ISBN 978-3-8252-8669-9 , p. 29.
- ^ Paul J. Crutzen: Geology of mankind. ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF). In: Nature. 415, 2002, p. 23; and newer: W. Steffen, PJ Crutzen, JR McNeill: The Anthropocene: Are Humans Now Overwhelming the Great Forces of Nature? In: Ambio. 36, 2007, pp. 614-621. doi : 10.1579 / 0044-7447 (2007) 36 [614: TAAHNO] 2.0.CO; 2
- ^ Joshua P. Howe: Behind the Curve: Science and the Politics of Global Warming. University of Washington Press, Seattle 2014, ISBN 978-0-295-99368-3 .
- ↑ GN Plass: The Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climatic Change. In: Tellus. 8, 1956, pp. 140-154. ( tellusb.net , PDF -and- American Scientist Feature Article: Carbon Dioxide and the Climate americanscientist.org ( Memento of the original from April 23, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original - and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this note. )
- ^ Spencer Weart: The Discovery of Global Warming: Basic Radiation Calculations . Center of History at the American Institute of Physics , aip.org
- ^ World Climate Program (WCP), historical background
- ↑ Spencer Weart: The Discovery of Global Warming: Biosphere: How Life Alters Climate . Center of History at the American Institute of Physics , aip.org
- ^ Susan L. Hautala, Evan A. Solomon, H. Paul Johnson, Robert N. Harris, Una K. Miller: Dissociation of Cascadia margin gas hydrates in response to contemporary ocean warming . In: Geophysical Research Letters . tape 41 , no. December 23 , 2014, p. 8486–8494 , doi : 10.1002 / 2014GL061606 (English, washington.edu [PDF]).
- ↑ James Lawrence Powell: The Inquisition of Climate Science . New York 2012, p. 178.
- ^ Riley Dunlap, Aaron M. McCright: Challenging Climate Change. The Denial Countermovement. In: Riley Dunlap, Robert J. Brulle (Eds.): Climate Change and Society. Sociological Perspectives. Report of the American Sociological Association's Task Force on Sociology and Global Climate Change . Oxford University Press, 2015, pp. 308f.
- ↑ Josef Settele , Robert Scholes a. a .: 4 Terrestrial and inland water systems . In: Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects . Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2014, 4.2 A Dynamic and Inclusive View of Ecosystems, p. 280–282 ( ipcc.ch [PDF; 10.4 MB ]).
- ↑ Jay Wright Forrester: The Infernal Control Loop. Can humanity survive? Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, 1972, ISBN 3-421-02632-7 .
- ^ St. Gallen Symposium: Past Symposia
- ↑ Dennis Meadows among others: The limits of growth. Translation by Hans-Dieter Heck. 14th edition. Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Stuttgart 1987, ISBN 3-421-02633-5 , pp. 17, 172.
- ^ Ugo Bardi: The Limits to Growth Revisited. 2011, ISBN 978-1-4419-9415-8 , p. 90 ff.
- ^ Graham Turner: A Comparison of The Limits to Growth with Thirty Years of Reality. In: Socio-Economics and the Environment in Discussion (SEED). CSIRO Working Paper Series Number 2008-09. June 2008, ISSN 1834-5638 ( Archived PDF; 706 KB ( Memento from December 14, 2011 on WebCite )) -and- Jeff Hecht: Prophesy of economic collapse "coming true" . In: New Scientist . November 17, 2008.
- ^ Club of Rome: The count-up to 2052: An overarching framework for action
- ↑ wdr.de: Global 2000 study . WDR deadline - 25 years ago. July 23, 2005 -and- Franz-Josef Brüggemeier : Chernobyl, April 26, 1986: The ecological challenge. P. 226.
- ↑ Ernst U. von Weizsäcker, Amory B. Lovins, LH Lovins: factor four. Twice the prosperity - halve the consumption of nature. ISBN 3-426-26877-9 .
-
^ Homepage of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ;
Processing of the main results in the network by greenfacts.org ;
Preparation of the biodiversity report in German by greenfacts.org ;
Study on the relevance of the MA for Germany - ^ Johan Rockström et al: A safe operating space for humanity. In: Nature . 461, 2009, pp. 472-475. doi: 10.1038 / 461472a
- ↑ Researchers define boundaries for the earth that humanity should not cross. on klimaktiv.de
- ↑ Stockholm Resilience Center: "Planetary Boundaries ( Memento of the original from January 11, 2016) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this note. "
- ^ Union of Concerned Scientists: 1992 World Scientists' Warning to Humanity .
- ↑ William J. Ripple, Christopher Wolf, Thomas M. Newsome, Mauro Galetti, Mohammed Alamgir, Eileen Crist, Mahmoud I. Mahmoud, William F. Laurance and 15,364 life scientists from 184 countries: World Scientists' Warning to Humanity: A Second Notice . In: BioScience . tape 67 , no. 12 , 2017, p. 1026-1028 , doi : 10.1093 / biosci / bix125 .
- ^ Will Steffen et al .: Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene . In: pnas.org PNAS , Washington DC, August 6, 2018, accessed August 8, 2018.
- ↑ On the way to the "hot time"? Planet could exceed critical threshold . In: pik-potsdam.de Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research , Potsdam, August 6, 2018, accessed on August 8, 2018.
- ^ William J. Ripple et al .: World Scientists' Warning of a Climate Emergency . In: BioScience . 2019, doi : 10.1093 / biosci / biz088 .
- ^ Süddeutsche Zeitung: More than 11,000 scientists declare a "climate emergency". Retrieved November 5, 2019 .