Hexachlorobenzene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hexachlorobenzene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 Cl 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 284.76 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.049 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
231 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
323-326 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
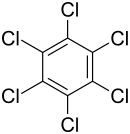
Hexachlorobenzene (HCB) is an aromatic compound . The molecule as benzene constructed, except that all the hydrogen atoms by chlorine atoms have been replaced. It is a colorless, crystalline powder that is largely resistant to acids and bases .
Representation and occurrence
HCB can be prepared by chlorination of benzene in the presence of catalysts such as iron (III) chloride (FeCl 3 ) are obtained at about 230 ° C in the liquid or the gas phase. It is also formed during the thermal decomposition of HCH ( hexachlorocyclohexane , see lindane ) in the presence of chlorine.
The chemical was widely used, for example in the EC in 1979 to the extent of 3500 tons. Large amounts were thus released into the environment. Even after the use of HCB has been banned, there are still releases. Sources for this are chlorinated pesticides , incomplete incineration processes, leaching from landfills, unsuitable manufacturing processes or unsuitable waste disposal of chlorinated compounds such as solvents, aromatic compounds or pesticides.
use
Hexachlorobenzene is a fungicide that was discovered in 1945. In the past it was used as a drying agent against fungal diseases such as dwarf stone fire in grain, as a disinfectant in grain storage, and also added to wood preservatives .
It also has a flame-retardant effect and was used until the 1950s for the impregnation of timber and for chimney linings , also for plastics, electrical insulation and paper. It is also used in pyrotechnic smoke products, the volatilizing HCB makes white smoke more intense, at high temperatures ( e.g. in tracer ammunition ) it also emits chloride ions when it decays .
In process technology, it is used as a starting product for various organic compounds such as pentachlorophenol (PCP) and pentachlorothiophenol .
Other applications include plasticizers for PVC , peptizers in tire production , stabilizers in the paint and plastics industries, as a means of controlling porosity in the manufacture of electrodes , as a flow agent in aluminum smelting .
Biological importance
In the body of warm-blooded animals HCB will Pentachlorobenzene , tetrachlorethylene, benzene and pentachlorophenol metabolized . With continuous intake, accumulations in adipose tissue , damage to the liver and reproductive organs , porphyria with photosensitivity and porphyrinuria were observed. In animal experiments, the occurrence of tumors was found in hamsters and mice . The permitted daily intake ( Acceptable Daily Intake , ADI value) is 0.6 μg kg −1 .
Legal status
Hexachlorobenzene has not been approved as a crop protection agent in Germany since 1981 . A ban in Austria has been in place since 1992. Since 2004, the Stockholm Convention has been subject to an almost worldwide restriction or prohibition of use.
No plant protection products containing this active ingredient are permitted in the EU or Switzerland .
Hexachlorobenzene is one of the so-called " dirty dozen ".
Analytical evidence
The chemical-analytical detection in environmental samples, food and animal feed is carried out after suitable sample preparation to separate the matrix and gas chromatographic separation of minor components by high-resolution mass spectrometry techniques such as flight mass spectrometry (Time-Of-Flight mass spectrometry).
Hexachlorobenzene in the environment
Because of its persistence , hexachlorobenzene accumulates in the environment. Its bioaccumulation leads to uptake by biota and into the food chain . It can also be transported over long distances via the troposphere before it enters the water and soil. In the air, HCB is slowly broken down photochemically ; Microbial decomposition takes place in the soil . The octanol-water partition coefficient (log K OW ) is around 5.3.
Diseases in Eastern Turkey
Porphyria cutanea tarda developed in around 4,000 people in eastern Turkey at the end of the 1950s after eating bread made from seeds . The so-called Pembe Yara or Pink Disease also occurred there, which had a mortality rate of 95% in small children and began with diarrhea , fever and skin- to pink-colored papules on the back of the hand, upper side of the finger and wrist, sometimes also on the feet and legs. As a result, developed subcutaneous abscesses , pulmonary infiltrates, enlargement of the liver and a hypochromic anemia . In the case of recovery, the duration of the illness was a good one to two months.
Carinthia - Görtschitztal
In March 2014, the Agency for Health and Food Safety in foods from the Görtschitztal in Carinthia found that the HCB limit values were exceeded . Knowledge of this became public in November 2014.
literature
- Substance report hexachlorobenzene (HCB) . In: Handbook of contaminated sites and groundwater damage cases ; published by the State Institute for Environmental Protection Baden-Württemberg, 1st edition, Karlsruhe 1995 ( texts and reports on contaminated sites 18/95; pdf, on lubw.baden-wuerttemberg.de).
Web links
- Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) for Hexachlorobenzene
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on hexachlorobenzene. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on hexachlorobenzene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 14, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Hexachlorobenzene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Substance report hexachlorobenzene (HCB) . In: Handbook of contaminated sites and groundwater damage cases ; published by the State Institute for Environmental Protection Baden-Württemberg, 1st edition, Karlsruhe 1995 ( texts and reports on contaminated sites 18/95; pdf, on lubw.baden-wuerttemberg.de), Chapter 2.4 Consumed quantities , p. 16 ff, especially table 4: Some data on HCB consumption .
- ↑ a b Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) for Hexachlorobenzene , accessed November 29, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e Report on Hexachlorobenzene (HCB) . In: Handbook of contaminated sites and groundwater damage cases ; published by the State Institute for Environmental Protection Baden-Württemberg, 1st edition, Karlsruhe 1995 ( texts and reports on contaminated sites 18/95; pdf, on lubw.baden-wuerttemberg.de), Chapter 2.3 Areas of application , p. 15 f.
- ↑ Concon: Food Toxicology, Part B, p 1145, New York: Marcel Dekker 1988th
- ↑ Hexachlorobenzene: One of the most dangerous substances .
- ↑ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on hexachlorobenzene in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 26, 2016.
- ↑ Eric J. Reiner, Adrienne R. Boden, Tony Chen, Karen A. MacPherson and Alina M. Muscalu: Advances in the Analysis of Persistent Halogenated Organic Compounds . In: LC GC Europe . 23 (2010), pp. 60-70.
- ^ Poisons Information Monograph (PIM) for Hexachlorobenzene , accessed November 29, 2014.
- ↑ HCB: limit value exceeded since March known orf.at
- ^ Environmental scandal HCB: A chronology .

