Boric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Boric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 3 BO 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White dust |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 61.83 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.49 g cm −3 (23 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
171 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (49.2 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
of particular concern : toxic for reproduction ( CMR ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 10 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust / aerosol fraction) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1094.3 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Boric acid (also: orthoboric acid , Acidum boricum ), H 3 BO 3 , is the simplest oxygen acid of boron . Their salts are called borates .
Occurrence and extraction
Free boric acid is found in the water vapor sources ( fumaroles ) of central Italy in Tuscany ; The acid can be obtained from these sources by evaporation into shiny platelets. Boric acid is also found in Tuscany as the mineral sassolin . However, alkali and alkaline earth salts such as the mineral kernite Na 2 [B 4 O 6 (OH) 2 ] · 3 H 2 O are of great importance . A similar, rarer mineral is borax , which contains 8 or 10 equivalents of crystal water . Nowadays, however, it is mainly extracted from kernite. By treating borax with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid , boric acid can be released.
properties
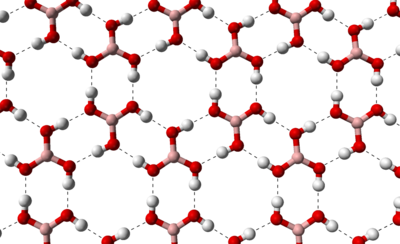
Pure boric acid forms flaky, colorless, shiny crystals that have a melting point of 171 ° C when heated quickly in a closed system. These form a layer structure in which hydrogen bonds are formed between the individual boric acid molecules . The distance between two layers is 318 picometers (pm) .
Initially it is difficult to dissolve in water , but this process accelerates as the concentration increases. The solution is weakly acidic. When the orthoboric acid is heated, water is split off, and the metaboric acid HBO 2 , which occurs in several modifications, and finally diboron trioxide (B 2 O 3 ), with further elimination of water, are formed .
Despite its three hydrogen atoms , boric acid reacts in water like a monoprotonic acid and reacts to form the tetrahydroxoborate ion, B (OH) 4 - . It does not behave like a Brønsted acid as a proton donor, but like a Lewis acid as an electron pair acceptor with the formation of an adduct with a hydroxide ion:
Boric acid is a very weak acid (pK s = 9.25). By reacting with polyhydric alcohols such as mannitol , the acid strength can be increased considerably. This is due to a shift in the equilibrium to the right towards a tetraoxoborate derivative as a result of an esterification :
This reaction is used for the alkalimetric titration of boric acid.
proof
Boric acid and its salts, the borates, form the volatile boric acid trimethyl ester with methanol and the dehydrating concentrated sulfuric acid , which burns with a green flame and is used for qualitative detection.
use
Boric acid is an intermediate product for the production of borosilicate glass , porcelain , enamel . The world annual production of boric acid is over 2,000,000 tons .
In medicine, boric acid as an aqueous solution ( boric acid solution ), and ointment ( boric ) as a mild disinfectant used. Since the recall of drugs containing boric acid in 1984 by the Federal Health Office at that time, boric acid and its esters and salts have only been approved for buffering and isotonicizing eye drops and for use in homeopathic dilutions.
3% boric acid solution (boron water) can be used for caustic burns. It is not corrosive itself and can neutralize alkalis.
In the food industry, boric acid is used as a preservative with the designation E 284.
Boric acid is used in disinfectants , as a bleaching agent in washing-up liquids, and as a fungicide and insecticide (e.g. to control fleas and cockroaches ).
In the construction sector, boric acid as well as borax and other borates (boron salts) are used for preventive wood protection , in stains and as flame retardants and to prevent mold and pest infestation in organic insulation materials. For example, an 8% additive was common for cellulose insulation materials, but this has to be limited to 5.5% due to more recent guidelines.
In pressurized water nuclear reactors , dissolved boric acid is used as a neutron absorber to regulate the chain reaction. It is based on the large absorption cross-section of the isotope 10 B for thermal neutrons, which is 20% contained in natural boron . This is where the nuclear reaction takes place
- .
Boric acid is used to calculate the carbon dioxide content in geological times. When the pH value changes to alkaline , the boric acid turns into borate, the salt of boric acid. This leads to an isotope , since 10 boron preferably is incorporated into the borate. Since foraminifera (fossil as well as recent unicellular organisms) and other shellfish need borate to build their shell, the isotope ratio can be used to determine which pH value was present in this area at which point in the history of the earth. Since the shells of such unicellular organisms as well as mussels etc. make up the main part of the marine sediment, sediment cores can simply be removed from there and examined in the laboratory for the two boron isotopes. Such results correlate well with the air bubbles trapped in ice cores.
When trimethyl borate is burned , a green flame is produced, while the boric acid esters of other alcohols show a green flame line when burned. This property is used to identify methanol (school experiment) and in pyrotechnics , for example, to color the flames of fire sticks, poi or fire bowls.
Up to 1.3% boric acid was detected in slime sold as a toy . The viscosity of the slimy mass increases with the boric acid content. During production, a constant low content must be ensured, since a daily intake of 0.57 mg / kg body weight must be expected to be harmful to health.
Hazardous substance lists
In June 2010 boric acid was added to the candidate list for SVHC ( substance of very high concern ) by the ECHA . After the CLP regulation and the REACH amendment regulation 790/2009 / EC came into force, boric acid was labeled as toxic to reproduction . Mixtures that contain free boric acid in a concentration of 5.5% or more must also be labeled as toxic to reproduction according to the GHS regulation.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on BORIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 26, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet boric acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on boric acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b entry on boric acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 19, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on boric acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 16, 2014.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 10043-35-3 or boric acid ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-6.
- ↑ Gerhart Jander , Ewald Blasius, Joachim Straehle, Eberhard Schweda: Textbook of analytical and preparative inorganic chemistry . 16th edition. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 2006, ISBN 978-3-7776-1388-8 , p. 368 .
- ↑ a b BMG Engineering AG: Study of January 22, 2013 on the handling of boron in the assessment of contaminated sites on behalf of the Canton of Aargau, Switzerland; accessed in September 2016
- ^ Bassermann; in: The new large colored lexicon ; 1988, ISBN 3-8094-0002-5 , p. 640.
- ^ Opinion of the Drugs Commission of German Pharmacists from November 23, 1999, accessed on November 22, 2010.
- ↑ The Biochemische Taschenbuch , 1956 by HM Rauen, recommends blowing a mixture of 10% pyrethrum , 40% boric acid and 50% kaolin into all cracks where cockroaches might be, Springer-Verlag, 2013.
- ↑ Chiara Noli, Fabia Scarampella, Stefano Toma - Practical Dermatology in Dogs and Cats: Clinic - Diagnosis - Therapy ... : "Boric acid and its salty compounds lead to holes in the parasite sheaths and thus to death through dehydration", Schlütersche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH , 2014
- ↑ Data sheet 1 and data sheet 2 ( Memento from September 13, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Isofloc cellulose insulation
- ^ Focus on chemistry, introductory phase , p. 22, Cornelsen-Verlag 2010.
- ^ Opinion of the BfR (formerly BgVV) of March 3, 1995: Boric acid content in Slime too high (PDF; 27 kB). As of October 8, 2008.
- ↑ BfR (formerly BgVV): Boric acid in jumping clay (PDF; 50 kB) - Health assessment No. 014/2005 of the BfR of October 27, 2004. As of October 8, 2008.



![\ mathrm {B (OH) _3 + H_2O \ rightleftharpoons [B (OH) _4] ^ - + H ^ +}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1703eb751568c898ed6f47c018dbd82447549669)




