Operation Plowshare
Operation Plowshare (also Project Plowshare or German " Operation Ploughshare " ) was the term used in the United States for the development of techniques for harnessing nuclear explosions for civil construction projects.
The term was coined in 1961 and is based on the book Micha ( Mi 4,3 LUT : "They will turn their swords into plowshares and their skewers into sickles." ). The Soviet Union was running a similar project under the name of Atomic Explosions for the National Economy , which was announced in 1949 by the Soviet Andrei Januaryevich Vyshinsky , diplomat at the UN.
The project manager in Livermore was Wilmot N. Hess from 1959 to 1961 .
Discussed areas of application
Among other things, it was proposed to widen the Panama Canal by means of nuclear explosions or to create a new waterway through Nicaragua, the Nicaragua Canal . A breakthrough through mountain ranges for the construction of highways or the creation of caverns to store water, oil or gases would also be conceivable .
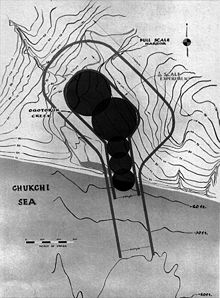
The planning for Operation Chariot was well advanced . An artificial harbor at Cape Thompson in Alaska was to be created with several hydrogen bombs . Ultimately, the plan failed due to the short ice-free time there and concerns about possible nuclear contamination of the area.
Test explosions
On May 7, 1960, President Eisenhower announced new seismic research “for the discovery of nuclear tests”. With one of the research and development director of the US Defense Department, Herbert York , as well as the "father of the hydrogen bomb " Edward Teller developed so-called Ditchdigger ( grave digger ) wanted to using thermonuclear produce blasting artificial ditches or channels.
The first test explosion as part of Operation Plowshare took place near Carlsbad , New Mexico , in late 1961 . A bomb with an explosive force of three kilotons of TNT equivalent was detonated. This happened in a rock salt area 360 meters below the surface, creating a round 52-meter-wide and 25-meter-high cavity.
Six months later, the Sedan nuclear weapon test was carried out as part of Operation Storax , during which around 12 million tons of earth were moved. This 104 kiloton bomb, like most of the 25 subsequent explosions, was carried out at the Nevada Test Site . Overall, the operation lasted until May 1973.
The following table contains all the attempts that have been made so far:
| Test name | Date / Time ( GMT ) |
place | Explosive power | Test series |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gnomes | December 10, 1961 , 7:00 p.m. | Carlsbad , New Mexico | 3 kT | Operation nougat |
| Sedan | July 6, 1962 , 5:00 p.m. | Nevada Test Site , Area 10h | 104 kT | Operation Storax |
| Anacostia | November 27, 1962 , 6:00 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 9i | 5.2 kT | Operation Storax |
| Kaweah | February 21, 1963 , 7:47 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 9ab | 3 kT | Operation Storax |
| Tornillo | October 11, 1963 , 9:00 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 9aq | 0.38 kT | Operation Niblick |
| Click quote | February 20, 1964 , 3:30 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 10e | 70 kT | Operation Niblick |
| Ace | June 11, 1964 , 4:45 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2n | 3 kT | Operation Niblick |
| You b | June 30, 1964 , 1:33 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 10a | 11.7 kT | Operation Niblick |
| par | October 9, 1964 , 2 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2p | 38 kT | Operation Whetstone |
| Handcar | November 5, 1964 , 3 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 10b | 12 kT | Operation Whetstone |
| Sulky | December 18, 1964 , 7:35 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 18d | 0.9 kT | Operation Whetstone |
| Palanquin | April 14, 1965 , 1:14 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 20k | 4.3 kT | Operation Whetstone |
| Templar | March 24, 1966 , 2:55 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 9bt | 0.37 kT | Operation Flintlock |
| Vulcan | June 25, 1966 , 5:13 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2bd | 25 kT | Operation Flintlock |
| Saxon | July 11, 1966 , 3:33 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2cc | 1.2 kT | Operation latchkey |
| Simms | November 6, 1966 , 2:45 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 10w | 2.3 kT | Operation latchkey |
| Switch | June 22, 1967 , 1:10 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 9bv | 3.1 kT | Operation latchkey |
| Marvel | September 21, 1967 , 8:45 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 10ds1 | 2.2 kT | Operation crosstie |
| Gas buggy | December 10, 1967 , 7:30 p.m. | Farmington , New Mexico | 29 kT | Operation crosstie |
| Cabriolet | January 26, 1968 , 4:00 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 20l | 2.3 kT | Operation crosstie |
| buggy | March 12, 1968 , 5:04 pm | Nevada Test Site, Area 30a-e | 5 × 1.08 kT | Operation crosstie |
| Stoddard | September 17, 1968 , 2 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2cms | 31 kT | Operation Bowline |
| Schooner | December 8, 1968 , 4 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 20u | 30 kT | Operation Bowline |
| Rulison | September 10, 1969 , 9:00 p.m. | Grand Valley , Colorado | 43 kT | Operation mandrel |
| Flask | May 26, 1970 , 3 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2az | 105 kT | Operation mandrel |
| Miniata | July 8, 1971 , 2 p.m. | Nevada Test Site, Area 2bu | 83 kT | Operation Grommet |
| Rio Blanco | May 17, 1973 , 4:00 p.m. | Rifle , Colorado | 3 × 33 kT | Operation toggle |
Negative consequences
There were several negative effects of Operation Plowshare's 27 nuclear explosions:
“The Gnome project blew radioactive steam over the press stand. The press had been invited to confirm the safety of the technology. The next explosion, a 104 kiloton bomb on the Nevada test site, moved twelve million tons of earth. A radioactive cloud rose 12,000 feet and fell over the Mississippi River . Other consequences have included land destroyed, resettled communities, tritium-contaminated water, radioactivity and fallout from debris thrown into the atmosphere. Those in charge ignored the problems and played them down until the program was discontinued in 1977, also in response to public pressure. "
Operation Plowshare shows how something that was supposed to improve national security can inadvertently do just the opposite if the social, political and environmental consequences are not considered. But it also shows that public resistance and opposition can stop projects like this one.
result
Ultimately, none of the possible uses was actually implemented. Even the advocacy of prominent scientists like Edward Teller could not change the result. In addition to the potential environmental pollution from radioactive contamination, the cost factor was also an enormous obstacle.
On May 16, 1960, a nuclear test moratorium was agreed in Paris between the great powers USA, Russia and France. Only in May 1977 by the UN a convention on a ban on "military or otherwise hostile operations of environmental modifications" adopted which aims at artificially induced interference with the weather patterns or provoked geological reactions such as earthquakes.
See also
Web links
- Radio reports on the peaceful use of atomic explosions in the archive of the Austrian Media Library
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Deutschlandfunk , Dossier , September 2, 2011, Gaby Weber , deutschlandfunk.de: Die nukleare Pflugschar - US test attempts despite the moratorium (September 3, 2011, January 30, 2015), accompanying manuscript
- ^ A b c Benjamin K. Sovacool, 2011: Contesting the Future of Nuclear Power: A Critical Global Assessment of Atomic Energy , World Scientific , pp. 171-172.


