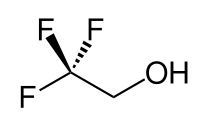
2,2,2-trifluoroethanol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 3 F 3 O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a characteristic odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 100.04 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
12.4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, soluble in alcohols , ketones , esters , ethers , miscible with lower aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons , with chloroform and 1,1,1-trichloroethane |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.2907 (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
24 (based on 100 years) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol (Trifluoroethanol, TFE) is an organofluorine compound with the constitutional formula CF 3 -CH 2 OH. The high electronegativity of the trifluoromethyl group is responsible for the compared to ethanol more pronounced acid character of trifluoroethanol, which in many reactions phenol-like behavior. The electric dipole moment (2.03 Debye), the high value of the polarity parameter E T (30) of 250.2 kJ mol −1 and the pronounced tendency to form hydrogen bonds make TFE an excellent protic solvent for polar compounds.
presentation
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol can be relatively expensive by catalytic hydrogenation of trifluoroacetic acid and its derivatives, such as. B. trifluoroacetyl chloride , or 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl trifluoroacetate can be obtained.
The route starting from 2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane, an intermediate product of the halothane synthesis, is of industrial interest . The process can either be discontinuous or in two stages via the formation of a TFE ester
or continuously and in one stage in the presence of water to give the 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol.
In the continuous process in a loop reactor , 2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane (by addition of hydrogen fluoride to trichloroethene in the gas phase) is treated with aqueous potassium acetate solution under pressure at temperatures above 250 ° C. and residence times of about one hour hydrolyzed to TFE at 77 percent conversion with a yield of up to 95%.
In one process variant, 2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane is reacted with the potassium salt of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (from γ-butyrolactone and potassium hydroxide solution ) in γ-butyrolactone as a solvent to form potassium chloride and γ-butyrolactone.
The process should be characterized by extreme product purity, mild reaction conditions and a lack of production waste (the KCl can be used as fertilizer).
properties
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol is a clear, colorless liquid with an ethanol-like odor that can be mixed with water and many polar solvents in all proportions. Its density is higher than that of dichloromethane . Trifluoroethanol is thermally stable up to 315 ° C and splits off hydrogen fluoride above the decomposition temperature . With its flash point of 33 ° C, TFE is classified as a flammable liquid, not readily biodegradable and can cause serious eye and fertility damage.
use
TFE is an excellent solvent for a variety of organic compounds, due to its low global warming potential as a cleaning fluid, e.g. B. for electronic components as a substitute for chlorofluorocarbons , as an eluent in HPLC , and as a working medium in the so-called Organic Rankine Cycle to recover waste heat.
Because of its high ionization energy and low specific conductivity , TFE is used as a solvent for ionic reactions and conductometric titrations .
The extraordinarily high dissolving power of TFE for polar polymers , such as. B. polyamides (nylon), polymethyl methacrylate , polyvinyl acetate , polyacrylonitrile and cellulose acetate , where nylon concentrations of up to 10% can be achieved and the TFE solutions can be used to determine the molecular weight distribution. The good solubility of polyamides in TFE can also be used to join solid nylon surfaces or to produce nylon-reinforced adhesives.
Like polyamides, TFE also dissolves peptides and proteins, often with denaturation .
TFE is also suitable as a solvent for polymerizations that z. B. be catalyzed by palladium or ruthenium complexes.
Of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol 2,2,2-trifluoroacetaldehyde is by electrochemical oxidation as trifluoroethyl hemiacetal or by gas phase oxidation in the presence of water to vanadium - molybdenum -Mischkontakten at 260 ° C as acetal accessible.
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol provides the molecular building blocks CF 3 CH 2 (trifluoroethyl group) and CF 3 CH 2 O (trifluoroethoxy group) for chemical syntheses, e.g. B. the halogen atoms in dihalosubstituted benzoic acids can be substituted by trifluoroethoxy radicals in a kind of Ullmann reaction .
The resulting 2,5-bis (2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy) benzoic acid is a building block for the antiarrhythmic flecainide .
The proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole contains a trifluoroethoxy group in the pyridine moiety which z. B. by replacing a nitro group in the intermediate 2-cyano-3-methyl-4-nitropyridine.
The herbicide triflusulfuron-methyl also contains a trifluoroethoxy group introduced via TFE.
When the polymer-analogous exchange of the chlorine atoms in the polydichlorophosphazene by TFE (as sodium salt) produced poly [bis (trifluoroethoxy) phosphazene], a standard polyphosphazene that as the hydrophobic elastomer forming films, fibers and membranes.
The esters of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol with acrylic acid or methacrylic acid are monomers which can be copolymerized with a large number of other monomers and make the resulting copolymers water-repellent, oxygen-permeable and highly transparent. These properties are used in the manufacture of soft contact lenses .
The most important application for 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol is the production of the inhalation anesthetic isoflurane and its derivative desflurane .
In a more recent process variant, isoflurane is obtained in two stages using chlorodifluoromethane (Freon 22, R22), which is largely forbidden as a refrigerant .
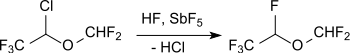
Desflurane is produced by replacing the chlorine atom with fluorine with hydrogen fluoride in the presence of antimony pentafluoride on activated carbon at 135 ° C.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 7, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol for synthesis (PDF) from Merck , accessed on December 15, 2015.
- ↑ a b c d Rhodia: 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol ( Memento from September 24, 2015 in the Internet Archive ), GPS Safety Summary
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 93rd Edition . CRC Press, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4398-8049-4 ( books.google.de ).
- ↑ a b c d e f g Halocarbon: Trifluoroethanol CAS No. 75-89-8
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Patent US4396784 : Hydrogenation of fluoroacids with rhenium-fluorided alumina Catalyst. Filed on March 4, 1982 , published on August 2, 1983 , Applicant: Phillips Petroleum Co., Inventor: MM Johnson, GP Nowack, PS Hudson, BH Ashe, Jr
- ↑ a b D. Lee, SI Cho, G.-J. Kim, H. Kim, I.-M. Lee: Efficient and selective hydrogenation of carboxylic acids catalyzed by Ni or Pd on ZSM-5 . In: Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry . tape 13 , no. 7 , 2007, p. 1067-1075 ( online ( memento from September 25, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) [PDF]).
- ↑ Patent US3970710 : Process for making trifluoroethanol. Filed April 9, 1975 , published July 20, 1976 , applicant: Abbott Laboratories, inventor: S. Wolownik.
- ↑ Patent US3356746 : Preparation of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol by catalytic hydrogenation. Filed September 30, 1964 , published December 5, 1967 , Applicant: Allied Chemical Corp., Inventor: LG Anello, WJ Cunningham.
- ↑ Patent US4434297 : Process for the preparation of trifluoroethanol. Filed August 30, 1982 , published February 28, 1984 , applicant: Halocarbon Products Corp., inventor: GW Astrologes.
- ↑ Patent EP0171248 : Process for the preparation of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol. Applied July 29, 1985 , published October 16, 1991 , Applicant: Anaquest, Inc., Inventor: PW Townsend, GG Vernice, C. Huang.
- ↑ a b c Tosoh F-Tech, Inc .: 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol (TFEA), Its production process and various applications
- ↑ Patent EP1426351 : Process for preparation of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol. Filed September 13, 2002 , published June 9, 2004 , Applicants: Tosoh F-Tech, Inc., Inventors: N. Nagasaki, T. Kawamura, K. Nukui, S. Arai.
- ↑ a b Solvay fluorine and derivatives: 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE)
- ↑ Patent US4232525 : Working fluid for the Rankine Cycle. Applied on January 23, 1979 , published on November 11, 1980 , applicant: Daikin Kogyo Co. Ltd., inventor: N. Enjo, H. Aomi.
- ↑ PJ Wang, RJ Rivard: Characterization of nylons by gel permeation chromatography and low angle laser light scattering in 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol . In: J. Liq. Chromatogr. tape 10 , no. 14 , 1987, pp. 3059-3071 , doi : 10.1080 / 01483918708068297 .
- ^ A. Kundu, N. Kishore: Interaction of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol with proteins: calorimetric, densimetric and surface tension approach . In: Biophys. Chem. Band 109 , no. 3 , 2004, p. 427-442 , doi : 10.1016 / j.bpc.2003.12.009 .
- ↑ A. Scarel et al .: trifluoroethanol: key solvent for palladium-catalyzed polymerization reactions . In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry . tape 690 , 2005, pp. 2106-2120 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jorganchem.2005.01.004 .
- ↑ DA Rankin, SJ P'Pool, H.-J. Schanz, AB Lowe: The controlled homogeneous organic solution polymerization of new hydrophilic cationic exo-7-oxanorbornenes via ROMP with RuCl 2 (PCy 3 ) 2 CHPh in a novel 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol / methylenechloride solvent mixture . In: Journal of Polymer Science A: Polymer Chemistry . tape 45 , no. 11 , 2007, p. 2113-2128 , doi : 10.1002 / pola.21976 .
- ↑ K. Shirai, O. Onomura, T. Maki, Y. Matsumura: Electrochemical oxidation of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol to trifluoroacetaldehyde 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl hemiacetal . In: Tetrahedron Letters . tape 41 , no. 31 , 2000, pp. 5873-5876 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4039 (00) 00880-7 .
- ↑ Patent EP1832343 : Catalyst for oxidizing 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol and method for producing trifluoroacetaldehyde. Filed November 29, 2005 , published September 12, 2007 , Applicants: Tosoh F-Tech, Inc., Inventors: H. Mimura, A. Watanabe, N. Nagasaki, K. Kawada.
- ↑ patent WO0190062 : Method for production of trifluoroethoxy-substituiertem benzoic acid. Applied on May 23, 2001 , published on November 29, 2001 , Applicant: Merck Patent GmbH, Inventor: K. Fabian, S. Enke, H. Tilly.
- ↑ K.-H. Ahn et al .: A new synthesis process of Lanzoprazole . In: B. Korean Chem. Soc. tape 23 , no. 4 , 2002, p. 626-628 .
- ^ HR Allcock, RL Kugel, KJ Valan: Phosphonitrilic Compounds. VI. High Molecular Weight Poly (alkoxy- and aryloxyphosphazenes) . In: Inorganic Chemistry . tape 5 , no. 10 , 1966, pp. 1709-1715 , doi : 10.1021 / ic50044a016 .
- ^ BD Ratner, AS Hoffman, FJ Schoen, JE Lemons (Eds.): Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine . 3. Edition. Academic Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-374626-9 , pp. 912 .
- ^ A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Syntheses, Patents and Applications of the most relevant APIs, 5th Edition . Thieme, 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-179275-4 .
- ↑ Patent US3637477 : Method of preparing of CF 3 CH = CHF 2 . Applied on February 20, 1970 , published January 25, 1972 , applicant: Air Reduction Co., Inc., inventor: LS Croix.
- ↑ H. Sivaramakrishnan, AA Upare, D. Satagopan, OR Chambers: The Preparation of Desflurane by the Vapor-Phase Fluorination of Isoflurane . In: Organic Process Research & Development . tape 15 , no. 3 , 2011, p. 585-592 , doi : 10.1021 / op100318b .