United States Military History
The term United States Military History refers to the military history of the United States and the history of the United States Armed Forces . These evolved from a group of disorganized revolutionaries striving for independence from the British crown to the leading military apparatus on earth and, as such, to a pillar of the United States' ever-growing superpower prestige since 1917 .
chronology
prehistory
The time of the Protestant settlement was marked by the fear of the Indians and the ambivalent relationship with them. Initially, the settlements were inadequately guarded by relatives. Increasingly, these guards organized themselves into militias and troops to patrol the area . From this period dates the term Ranger , from the English word to range (too dt. "Rank", "extend", but "measured" as well).
Indian Wars 1607–1890
→ Main article: Indian wars
War of Independence
→ Main article: American Revolutionary War
The long-standing tension between the British Crown and the Thirteen Colonies turned into a tangible political crisis when the British declared martial law on the province of Massachusetts . While skirmishes developed at Concord and Lexington , George Washington was appointed commander in chief of the recently formed Continental Army, which was supplemented by militias throughout the war. Although the British were militarily superior to the Americans and Washington lost more battles than won, it won the war because of its strategy . Characteristic of his approach was to keep his troops together, to involve the enemy in a war of attrition and to avoid decisive battles , unless he could have taken advantage of the capital mistakes of the British.
The British lacked a central authority to coordinate the efforts of several deployed armies, as well as a clearly designed strategy. With the help of their world-leading navy, the Royal Navy , they ruled the American coastline , but they were unable to convert their ability to load the troops quickly into control of the interior of the country beyond the conquered cities . The British Saratoga campaign , which should have led to the separation of New England, ended in a military debacle and the surrender of the royal troops. On the American side, the instruction by the Prussian General von Steuben improved the training and discipline of the Continental Army from 1777 onwards . After the defeat at Saratoga, France and Spain entered the war on the American side as they competed for colonies with Great Britain in North America .
When the British shifted their attention to the southern colonies , they achieved several victories at first, but the tenacity of the American troops under General Nathanael Greene , which they also expressed in guerrilla warfare , disrupted and then prevented the success of the British strategy of a march through North. A French victory at sea in Chesapeake Bay in 1781 led to the British surrender at Yorktown . This battle led to the Paris Agreement of 1783, in which the British recognized the independence of the United States .
Since many Americans of the revolutionary generation had an aversion to standing armies , the Continental Army was disbanded shortly after the end of the war. General Washington, who had repeatedly postponed the payment of wages during the fighting, then submitted his resignation as commander, albeit not without the ulterior motive of evading a conspiracy against himself. With this step, he placed the military back under civilian control, which continues to this day.
American-Tripolitan War
→ Main article: American Tripolitan War
The piracy of the barbarian states in the Mediterranean against American ships led to the establishment of a naval force of the United States. The American-Tripolitan War (or First Barbarian War) is one of the most important roots of the United States Navy .
The background to the war was that the British Royal Navy no longer had protection for American ships after the United States became independent in 1783. First in 1784 it was decided that piracy should be countered by paying tribute. As early as 1785, the then American ambassador to France, Thomas Jefferson , refused to pay US $ 60,000, which the Bey of Algiers demanded as a ransom for two hijacked merchant ships and their crew. Nonetheless, the policy of paying tribute and ransom remained. In 1800 such payments finally amounted to 20% of the annual US state revenue. In 1801 Jefferson became president. In line with his previous position, the president rejected a tribute demand from the Pasha of Tripoli in the amount of US $ 225,000. Tripoli then declared war on the USA, and the other Babaresque states joined them. In 1802 the warships USS Constitution , USS Constellation , USS Philadelphia , USS Chesapeake , USS Argus , USS Syren and USS Intrepid were dispatched to the Mediterranean Sea under the command of Edward Prieble . Prieble began a blockade of the ports of the Babaresque states. On July 14, 1804, he attacked Tripoli directly. In April and May 1805 the Battle of Derna took place, in which American marines and Arab, Greek and Berber mercenaries took part on the American side. Finally, on June 10, 1805, an armistice was signed.
British-American War
→ Main article: British-American War
Second barbarian war
→ Main article: Second Barbarian War
Monroe Doctrine
→ Main article: Monroe Doctrine
Mexican-American War
→ Main article: Mexican-American War
Utah war
→ Main article: Utah War
Civil war
→ Main article: Civil War
Spanish-American War
→ Main article: Spanish-American War
Filipino-American War
→ Main article: Philippine-American War
Banana Wars
→ Main article: Banana Wars
First World War
→ Main article: First World War
When the United States entered World War I, it began to rise to become a superpower . The unrestricted submarine warfare of the German Reich endangered trade relations with the United Kingdom. As early as 1915, the sinking of the steamer “ Lusitania ” almost provoked the USA to enter the war. From a military point of view, the German strategy was a failure, not a single American soldier was killed by enemy fire while being transported to Europe.
The USA deployed more than one million soldiers in the American Expeditionary Forces and shifted the military balance decisively in favor of the Entente cordiale, also with regard to the urgently needed supplies . the small size of the Army of the United States enabled numerous officers to advance rapidly, so that the war ultimately turned the armed forces into a cadre army . They also benefited from industrial modernization. John J. Pershing became known as the commander of American troops in World War I.
Second World War
→ Main article: Second World War
During the interwar period , the size of the military was reduced again, but in a tense neutrality before the United States entered World War II, it was mobilized to an unprecedented level . World War II was the most costly war of all time for the United States, as it was for the rest of the world.
Initially, the population was against entering the war, the USA initially limited itself to delivering to the countries fighting against the Axis powers of the United Kingdom , the Soviet Union and the Republic of China . The attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese Empire on 7. December 1941 , however, caused an immediate shift in public opinion . President Franklin D. Roosevelt declared war on Japan the following day. On December 11, 1941, Italy and the German Empire declared war on the United States. The conflict had finally become global. The war against the German Reich was given priority in agreement with Winston Churchill.
The loss of eight warships and nearly 2,000 sailors forced the Navy to rely on its remaining aircraft carriers , which won the decisive battle for Midway just six months after the attack on Hawaii . The Navy and Marine Infantry accompanied the advance of the carrier groups in the Pacific War through the occupation of the shielded islands, which was known as " island hopping ". During 1942 and 1943 , the US armed forces dispatched millions of men and tons of material to the United Kingdom to prepare for an invasion of the European continent , which the Wehrmacht tried to prevent with the expansion of the Atlantic Wall to strengthen "Fortress Europe". Of the British Isles from the Allied air forces gained increasingly airspace over European airspace. Landings in North Africa , Sicily , Italy and Normandy , which were accompanied by the constant advance of the Red Army on the Eastern Front , brought the German Reich to unconditional surrender .
United States forces advanced relentlessly in the Pacific, but faced dogged resistance from Japanese forces, they sought ways to bring about Japanese surrender with fewer casualties. Therefore, they decided to drop the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki , which the Japanese leadership was supposed to give up when the Soviet Union invaded Manchuria .
Despite the devastating effects of the Great Depression , the US had been able to prepare quickly to enter the war, ultimately becoming the dominant military power on all fronts of the war, with the exception of Eastern Europe and East Asia. The industrial power of the United States of America is widely believed to be the most important factor in Allied victory.
At the beginning of the World War, the US army was considered too inexperienced, so that it was often seen as cannon fodder , whose fight against the more experienced German and Japanese troops was hopeless. However, as the conflict progressed, the military developed into a well-trained and equally experienced force. The tactical and strategic conclusions they drew from the course of the war, above all the indispensability of air sovereignty and the clout of carrier groups, determine their military strategy to this day.
World War II killed approximately 400,000 American soldiers, only exceeded by the Civil War . 16 million people served in the armed forces, which makes up 13% of the total population at the time. The USA still draws its military consciousness from its victory over several authoritarian systems.
Cold War
→ Main article: Cold War
The United States finally emerged from the Second World War as a superpower, on par with the Soviet Union. In this almost forty-year struggle about the ultimate supremacy and the respective containment policy of the other, they supported allies in proxy wars and provided them with economic and military aid. The United States was the main foreign power in both the Korean War and the Vietnam War. With ever larger arsenals of nuclear weapons, both superpowers maintained the balance of horror with which they threatened their mutual destruction, even after both had reached the level of overkill .
Korean War
→ Main article: Korean War
Vietnam War

→ Main article: Vietnam War
The Vietnam War marked the second major turning point in the American military in the 20th century . Due to the military invincibility of the Viet Cong , which led to the de facto defeat of the United States, the military initiated a series of reforms. While military renewal was deemed necessary, it required a great deal of outside pressure to impose social and political renewals. To date, the US military has hardly assumed responsibility for war crimes or violations of international law in Vietnam.
The most important measure carried out by the Vietnam War was the suspension of conscription . The lack of burst limitation and the inadequate propellant charge in the standard M-16 assault rifle , which were soon repaired, had proven to be militarily fatal . The strategy of air cavalry had proven to be useful in principle, but half-baked, and its armor and equipment were therefore continuously improved. The Special Forces had also proven to be powerful, so that they were made an increasingly central instrument of American warfare.
Late 20th century
Second Gulf War
Powell-Weinberger Doctrine
In the aftermath of the Second Gulf War of 1990, the Weinberger-Powell Doctrine or Powell Doctrine, named after Powell and Weinberger, was developed under the then American Defense Minister Caspar Weinberger and the then Chief of the United General Staff Colin Powell . This said that the use of the armed forces was the last resort. The mission was only justified if interests of paramount importance to the security and viability of the USA were at stake and, moreover, only if the mission was supported by a broader public in the United States. The war would then be conducted with superior means and with as few losses as possible. There must also be a strategy to withdraw after the conflict has ended. The Powell-Weinberger Doctrine is a processing of the experiences from the Vietnam War.
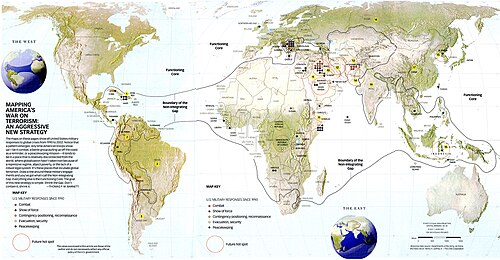
War on terrorism
→ Main article: War on Terrorism

After the terrorist attacks of September 11th, the US invoked its right to self-defense . Since they suspected Osama bin Laden and the core of al-Qaeda to be in Afghanistan , they intervened there. This took place within the framework of Operation Enduring Freedom ("Enterprise Long-Term Freedom"), which combines several operations under one strategy. Several ship associations, including foreign ones, patrol the sea routes around the Arabian Peninsula .
By February 10, 2007, the War on Terrorism cost 353 deaths in Afghanistan and 3,115 soldiers of the armed forces, according to official American figures. Of 24,646 wounds, 23,350 took place in Iraq.
Afghanistan war
→ Main article: War in Afghanistan
On October 7, 2001 , the United States began the war against al-Qaeda and its supporters, the Taliban . The Air Force captured Afghan airspace within fifteen minutes . The war ended de facto with the conquest of Kabul by the allied Northern Alliance , but the country was not pacified.
Iraq war

On March 20, 2003 , the United States invaded Iraq on a variety of controversial arguments. A decisive reason for war, the so-called smoking gun , did not materialize.
The strategic goal of the coalition campaign was the conquest of the outstanding capital of Iraq , Baghdad in all aspects . This goal was achieved within three weeks. The President of the United States , George W. Bush , declared the official fighting ended on May 1st on the aircraft carrier USS Abraham Lincoln . Similar to Afghanistan, the security situation remained unstable during the occupation . The coalition soldiers were just embroiled in an asymmetrical war with opponents of the occupation in Baghdad . From the mixture of different interests, which were mainly determined by ethnic and religious affiliations, conditions similar to civil war developed .
References
See also
- List of United States military operations
- Historical ranking of the highest officers in the United States
literature
Cold War
- Hans J. Schulz: On the way to nuclear war. US military strategy. 1986. - 128 pages - ISBN 3-88332-102-8 .
Web links
- Homepage of the United States Army Center of Military History
- United States Army Military History Institute website
- American Military History , text version, approx. 700 pages
- Well-known American military personalities of the USA, sorted by military epoch
- Website on the structure and combat operations of the American Expeditionary Force during World War I.
- Link collection of the National Museum of the US Army
- Link collection from an Air Force institute
- History of the US Army on European soil on GlobalSecurity.org
- Chronology of the Army in World War II
- The US Army in Vietnam, 16 chapters
- List of Congress of all military operations in the United States by 2006 (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ "In the fledgling years of Colonial America, the colonist found themselves in a strange new land that to them seemed vast, overwhelming, uncharted and unknown. These early Americans chose the bravest of their numbers to" Range "out into the new frontier and explore, map and report what they found. These were the first Rangers. " Quote from the American Association of Rangers. Date of discovery: March 4, 2007
- ↑ Detlev Quintern: To the shores of Tripoli. The USA in the Mediterranean around 1800 - The myth of the US Navy. In: Hartmut Roder (Ed.): Pirates. Adventure or Threat? Edition Temmen : Bremen 2002, ISBN 3-86108-785-5 , pp. 132-147
- ↑ Worldwide US Active Duty Military Personnel Casualties - Worldwide casualties (dead and wounded) of active personnel in the US armed forces in the fight against terrorism, listed by cause. Source: United States Department of Defense. Date of discovery: March 16, 2007 ( Memento of the original from March 7, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ "Commander in Chief lands on USS Lincoln". CNN report dated May 2, 2003. Accessed March 4, 2007