NGC 6890
| Galaxy NGC 6890 |
|
|---|---|
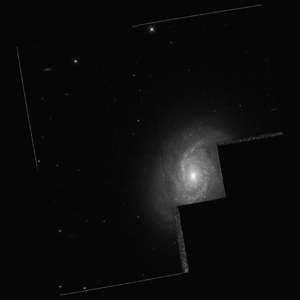
|
|
| Photo from the Hubble Space Telescope | |
| AladinLite | |
| Constellation | Sagittarius |
|
Position equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|
| Right ascension | 20 h 18 m 18.1 s |
| declination | -44 ° 48 ′ 24 ″ |
| Appearance | |
| Morphological type | (R ') SA (r:) ab / Sy2 |
| Brightness (visual) | 12.2 mag |
| Brightness (B-band) | 13.0 likes |
| Angular expansion | 1.6 ′ × 1.3 ′ |
| Position angle | 152 ° |
| Surface brightness | 12.8 mag / arcmin² |
| Physical data | |
| Redshift | 0.008069 ± 0.000083 |
| Radial velocity | 2419 ± 25 km / s |
|
Stroke distance v rad / H 0 |
(108 ± 8) x 10 6 ly (33.0 ± 2.3) Mpc |
| history | |
| discovery | John Herschel |
| Discovery date | July 1, 1834 |
| Catalog names | |
| NGC 6890 • PGC 64446 • ESO 284-G054 • MCG -07-41-023 • IRAS 20148-4457 • 2MASX J20181815-4448252 • GC 4563 • h 3824 • LDCE 1394 NED001 | |
NGC 6890 is a spiral galaxy of the Hubble-type (R ') SA (r:) ab in the constellation Sagittarius in the northern sky . It is estimated that 108 million light-years from the Milky Way away and is called Seyfert 2 galaxy classified
The object was discovered on July 1, 1834 by the astronomer John Herschel with his 18.7-inch reflecting telescope and was later included in his New General Catalog by Johan Dreyer .
