Southern ocean

The to 5805 meters deep Southern Ocean , who is also the Southern Ocean , Southern Arctic , Antarctic Ocean or Antarctica is called, is with 20,327,000 square kilometers after the Arctic Ocean (Arctic Ocean) is the second smallest ocean of the earth . Together with the land mass Antarctica , it forms the world region of Antarctica .
geography
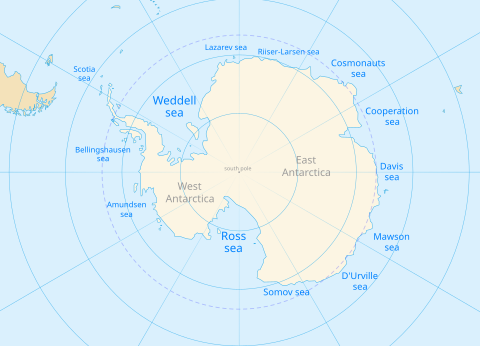
The Southern Ocean comprises the ocean area south of the 60th parallel or south of the Antarctic convergence . This summarizes the marine areas that surround the continent of Antarctica (the actual land mass of Antarctica ). To the north, it merges into the Atlantic , Indian and Pacific .
The designation Southern Ocean was officially decided by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) in the spring of 2000 . Until then, the Antarctic marine areas were known as the Southern Arctic Ocean , consisting of the southern areas of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. These marine areas are now known as the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Sectors of the Southern Ocean. The definition follows the legal stipulation of the Antarctic Treaty . The natural boundary is formed by the Antarctic convergence. This is the zone where the cold water masses of the Southern Ocean meet the warm water masses of the North. It runs between the 40th and 60th degree of latitude and fluctuates both in course and seasonally.
An amazing ecosystem has developed in the Southern Ocean , the key figure of which is krill . Large parts of it freeze over in winter. These areas are then called pack ice . Table icebergs that arise from fragments of the ice shelf are typical of the Southern Ocean . It is considered by seafarers to be the stormiest of all oceans .
In the Southern Ocean there is a complex current system, which is essentially composed of three main currents: the Antarctic surface water , the Antarctic bottom water and the circumpolar deep water . The Antarctic bottom water arises particularly in the coastal area of the Antarctic and is the coldest and densest water mass in the world, which transports cold water from the area of the Antarctic, whereby it could be detected even north of the equator in the Atlantic . The Antarctic surface water arises as a result of the thawing of the ice masses in the Antarctic and has a very low salinity and a correspondingly low density. Between the heavy Antarctic bottom water and the light Antarctic surface water, both of which carry cold water away from the Antarctic, lies the layer of warmer circumpolar deep water, which is pushed upwards by the topography of the seabed and the sinking Antarctic bottom water as it gets closer to the Antarctic continent . This creates a zone of strong upwelling, the Antarctic divergence .
Data
The Southern Ocean has an extension of around 20.327 million km². In the Atlantic-Indian-South Polar Basin it is up to 5805 m deep; this deep point is approximately 61 ° 0 '0 " S , 44 ° 0' 0" O . A greatest depth of 7235 meters is reached in the southernmost extension of the South Sandwich Gully , at 61 ° 0 ′ 0 ″ S , 24 ° 0 ′ 0 ″ W , about 180 km southeast of the Southern Thule Islands - the greater part of this deep sea channel and theirs The deepest point, however, is north of 60 ° south latitude and is therefore part of the Atlantic Ocean .
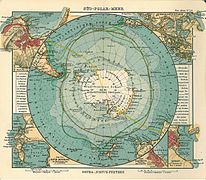
Historical map of the South Polar Sea ( Justus Perthes , Gotha 1906: Seeatlas , sheet 24)
Earth's gravitational field in the Southern Ocean
"Cigar ice cream", broken off from the shore ice of an island in the northwestern Weddell Sea (October 2016)
Seabed
Within the Southern Ocean or on its sea floor there are thresholds , deep-sea basins and a deep-sea channel .
In the Southern Ocean are the foothills of these thresholds or ridges , which merge towards the north into the Indic or Pacific : the southeastern extension of the Kerguelen-Gaußberg Ridge and the southwest part of the South Pacific Ridge . The three large deep-sea basins, of which at least the southern areas extend into the Southern Ocean , are the Atlantic-Indian-South Polar Basin up to 5872 m deep , the Indian South Polar Basin up to 5455 m deep and the Pacific South Polar Basin up to 5399 m deep ; these merge to the north in the Atlantic , Indic and Pacific . This also includes the South Antilles Basin , which merges north into the Atlantic . The deep-sea channel is the extreme southern branch of the South Sandwich Channel , which merges into the Atlantic in the north and is up to 8264 m deep there.
In some cases, on the bottom of the Southern Ocean, there is sediment in the form of fine gray mud in meter thickness: an excellent natural “ climate archive ” from the last Ice Age . Dead microorganisms belonging to the plankton make it possible to reconstruct the history of the climate over many millennia.
Tributaries
Like the rest of the oceans, the southern ocean has a number of important minor seas (order clockwise ):
|
- The Bransfield Strait separates the Antarctic Peninsula with its coastal islands from the South Shetland Islands
- The Scotia Sea is primarily a marginal sea of the Atlantic. In the south, however, it extends to the South Orkney Islands and the South Shetland Islands and thus nominally includes part of the Southern Ocean, the northern limit of which is 60 ° S latitude.
Island world

In the Southern Ocean or off the coast of Antarctica , for example, the following islands and archipelagos are located : Alexander I Island , Balleny Islands , Berkner Island , Ross Island , Scott Island , South Orkney Islands and South Shetland Islands .
Salinity
According to calculations by scientists, the freshwater input from glacier ice into the Southern Ocean increased by up to 20% between 1982 and 2008. This could explain the measurably decreasing salt content of the seawater there for years .
Influence on the earth's climate
The Southern Ocean, kept in motion by storms (see “ Roaring Forties ”) stores large amounts of carbon dioxide and heat: Persistent westerly winds and differences in water density move the strongest ocean current worldwide, the ring-shaped “ Antarctic Circumpolar Current ”. An important part of the global thermohaline or north-south overturning circulation, the North Atlantic Current carries relatively warm water on the surface from the tropics to the North Atlantic , where it cools and sinks, in the Southern Ocean it reappears at the end of the circulation. Despite the roughly constant temperature here, the Southern Ocean absorbs more than two thirds of the additional heat generated by the greenhouse effect : it drifts northward on the surface, while cooler water rises locally.
The Antarctic Ocean probably stored huge amounts of carbon dioxide by means of plankton circulation during the last ice age and in this way withdrew it from the earth's atmosphere : Plankton absorbs CO 2 on the surface, it sinks into the depths after it dies; Bacteria, in turn, quickly break down the plankton. The CO 2 is released again, but it remains in dissolved form in the deep ocean layers. Up until the end of the last ice age, the CO 2 content of the earth's atmosphere was probably around a third lower than it is today.
See also
- List of Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic Islands , List of Uninhabited Islands and Archipelagos (Southern Ocean)
- Roaring Forties
- PALAOA ( PerenniAL Acoustic Observatory in the Antarctic Ocean , "year-round acoustic observatory in the Antarctic Ocean")
literature
- Hans-Günter Gierloff-Emden: On the relief of the seabed in the south polar region . In: Geoswissenschaften in our time , 1, 2, 1983, pp. 46–50; doi: 10.2312 / geosciences.1983.1.46 .
- Jan Erik Arndt et al .: The International Bathymetric Chart of the Southern Ocean Version 1.0 - A new bathymetric compilation covering circum-Antarctic waters . In: Geophysical Research Letters , 40 (9), 2013, pp. 1-7; doi: 10.1002 / grl.50413 .
Web links
- CIA World Factbook: Southern Ocean (English)
- Sophia Wagner: The Sound of the South Polar Sea . deutschlandfunk.de , Research News , February 27, 2017
- Information about the Southern Ocean
- Map with the marginal seas of the southern ocean (Russian)
- Geography: lakes, rivers, volcanoes (Southern Ocean) (Russian)
Individual evidence
- ^ A New Ocean is Born: The fifth "Southern Ocean" . gdrc.org
- ↑ a b c How the Southern Ocean influences the Earth's climate . badische-zeitung.de , Education & Knowledge , December 24, 2016; Retrieved December 25, 2016
- ↑ Oceanology: Sea ice makes the Southern Ocean less salty . deutschlandfunk.de , Current Research , Reports; Retrieved December 25, 2016