South Cotabato
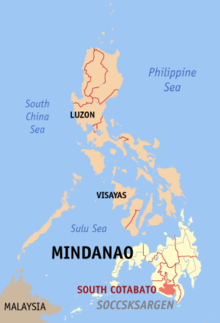
South Cotabato is a province of the Philippines . It is located in the south of the main land mass of Mindanao Island .
Politically the province belongs to the district number XII, also called SOCCSKSARGEN .
The capital of the province is Koronadal City , the governor is Daisy P. Fuentes.
geography
South Cotabato is located in the south of the central region of Mindanao Island . The province is surrounded by Sultan Kudarat Province to the north and west, Sarangani to the south and Davao del Sur to the east. In the southeast is the Bay of Sarangani , part of the Celebes Sea .
The town of General Santos City, on the coast of Sarangani Bay , is the largest and most important town of South Cotabato and the province's main seaport.
Sarangani Province was originally part of South Cotabato until it became an independent province itself in 1992.
The Mount Matutum in the town of Polomolok is 2,286 meters the highest mountain in the province. The second highest mountain is Mount Parker (1,828 m) whose crater is Lake Holon (formerly known as Lake Maughan).
The longest river is the Allah River, it has its source in the western part of the Daguma Mountains . There are also many different smaller and larger rivers, such as the Buayan , Marbel and Taplan Rivers. The largest lakes in the province are Sebu Lake , Lahit Lake, Siloton Lake and Holon Lake.
The total area of the province is 4,429 km².
Demographics and language
According to the 2007 census, South Cotabato has 767,254 people, excluding General Santos City residents . The province ranks 21st in the Philippines' population statistics. The population density is 173.23 people per km². This means 30th place in the demographic statistics.
Most of the residents of South Cotabato are Roman Catholic (64.66%), followed by Protestants (22.52%). Islam is only the third strongest religion in the province with 4.316%.
The people of South Cotabato are multilingual and speak Hiligaynon , Tagalog , Cebuano and English . In contrast, a number of other indigenous dialects are represented among the indigenous peoples.
Today's inhabitants of the province are of different origins. The Ilonggos come from the islands of Panay and Negros in the Visayas . Hiligaynon is thus the main dialect spoken in the province. In contrast, the Ilocano ethnic group from Luzon speaks the Ilocano dialect. Cebuano is again mostly used in Koronadal City and General Santos City.
The Maguindanao determine the predominantly Muslim ethnic groups in the province. Many still wear the traditional costumes and live according to the original guidelines of their culture. Others orient themselves towards the more liberal lifestyles of their Christian neighbors and wear shorts and sleeveless shirts, refuse to wear headscarves and take part in modern events.
The indigenous groups of the T'boli and B'laan are known for their brass work, their beadwork and their weaving skills. The costumes of this ethnic group are colorful and usually richly embroidered with pearls.
economy
The province is an agriculturally dominated region. The main crops are pineapple , asparagus ( vegetable asparagus ), coconut , grain , papaya , bananas and rice ; but cattle breeding is also widespread in the province. It is currently on the way to becoming the country's bread basket.
In the coastal regions, but also on the lakes of the province, fishing determines the livelihood of the inhabitants. The rich fishing grounds of the Celebes Sea are a source of food and income for thousands of families. In addition, Lake Siloton, Lake Sebu and Lake Lahit offer an abundance of freshwater fish.
For the indigenous peoples, the craftsmanship in bead, brass and textile processing is a factor worth mentioning.
Administrative division
South Cotabato is divided into ten independently administered parishes and two cities. The communities are in turn subdivided into a total of 225 barangays (districts).
The province is also divided into two congressional districts.
Cities
- General Santos City (Dadiangas)
- Coronadal City
Communities
climate
South Cotabato has an average high probability of precipitation throughout the year. The number of rainy days in 2004 was z. B. between 122 and 180 days, mainly spread over the months of May to October. The average rainfall is 1,637 to 2,500 mm per year, the humidity fluctuates between 72% and 80%.
The driest months are expected between February and April, the coolest are December and January.
Temperatures can range from 23 ° C to 38 ° C, with the hottest period being between January and April.
history
The majority of the residents are immigrants. The first were the B'laans, the Manobos, the Tagabilis and other ethical groups, some of which settled in Mindanao before the birth of Christ. Most of these groups are of Malay origin and are similar in their languages and cultures.
In the 15th century, Shariff Kabunsuan from Johor, Malay, reached the Cotabato area and brought Islam to the province. As the first sultan of the Sultanate of Maguindanao , he made Islam the dominant religion in Mindanao .
At the end of the 17th century, the Spaniards reached the southern part of the island and founded a fort in what is now Cotabato City . This served as the starting point for the subsequent planned subjugation of the Muslim population. But the residents of the area successfully defended themselves against the Spanish colonial power for years until the Spaniards withdrew from the area in 1889. The only thing they left behind was ultimately a fort and a small village called Cotabato.
Already at the beginning of the 20th century, many immigrants from Luzon and the Visayas came to settle the open and fertile land of South Cotabato. The first Christian settlers reached the province around 1914. During the Second World War the wave of immigration stopped, but increased again in 1950.
At that time the region belonged to a single large province of Cotabato . Since the residents felt underrepresented in the existing provincial government, the separation of the area from the mother province was demanded in the early 1960s. With Republic Act No. 4849, this separation was approved on July 18, 1966 and South Cotabato declared an independent province. The new province then consisted of 11 municipalities with the municipality of Koronadal as the seat of the provincial government.
In 1992 there was the next chapter in political history, when the southern coastal area with 7 parishes separated from South Cotabato as part of the new Sarangani province .
On October 12, 1990, Executive Order No. 429 signed by President Corazon Aquino reorganized all Mindanao counties. As a result of this reorganization, Koronadal became the seat of the district government of the entire region XII.
Cultural heritage
The indigenous Maguindanaon and other indigenous groups possess a remarkable and fascinating culture that revolves around kulintang music, a special kind of gong music that has its roots in both Muslim and non-Muslim populations of the southern Philippines. A set of gongs is embedded in a horizontally erected board, which are then played with two wooden mallets.
Attractions
- The Lonon Falls (or Seven Falls) in Lake Sebu
- The mountain caves on Lake Sebu in Lake Sebu Parish
- Lake Sebu in the municipality of the same name
- The Saravia Falls in Koronadal
- Lake Maughan in T'boli
- Mt Parker in T'boli
- Mt. Matutum in Polomolok
Web links
- Official website of the South Cotabato Province
- WOW - Philippines South Cotabato
- Information about South Cotabato
Coordinates: 6 ° 20 ' N , 124 ° 57' E