Velen
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 54 ' N , 6 ° 59' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Muenster | |
| Circle : | Bark | |
| Height : | 57 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 70.75 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 13,107 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 185 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 46342 | |
| Area code : | 02863 | |
| License plate : | BOR, AH, BOH | |
| Community key : | 05 5 54 064 | |
| LOCODE : | DE VLN | |
| City structure: | 5 districts | |
City administration address : |
Ramsdorfer Str. 19 46342 Velen |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Dagmar Jeske (independent) | |
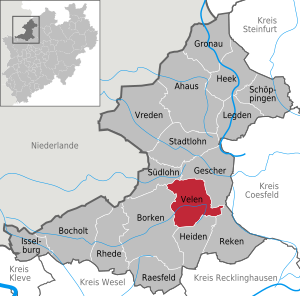
| Location of the city of Velen in the Borken district | ||
The city Velen is located in the western Münsterland in the northwest of the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia in the district of Borken in the administrative district of Münster . In 2003, Velen was awarded the title of State Recognized Resort from the District President in Münster. Since August 23, 2012, Velen has been called the City of Velen . Originally, today's city of Velen consists of the amalgamation of the municipalities of Ramsdorf and Velen.
geography
Spatial location
Velen is north of the mountain range Die Berge on the Bocholter Aa .
City structure
Velen is made up of the areas of the former municipalities of Velen and Ramsdorf. These are subdivided again so that 5 districts arise:
- Velen
Neighboring communities
| City of Südlohn | City of Gescher | |
|
Weseke (to the city of Borken ) |

|
Hochmoor (to the city of Gescher ) |
| City of Borken | Parish Heiden | Reken municipality |
history
The current districts are first mentioned in writing around 890 (Velen) and 1050 (Ramsdorf).
While Ramsdorf subsequently assumed the character of a town - albeit a small one - through the granting of town charter in 1319 and the construction of the castle in 1425, Velen has been under the dominant influence of the Lords of Velen since the Middle Ages. Although she Bishop of Münster since 1372 lehnspflichtig had succeeded the family of Velen to rise over the next few centuries into the top ranks of the Westphalian nobility. Hermann VII von Velen (1516–1595) established the close ties between Velen and the Emsland, which Dietrich von Velen (1591–1657) strengthened and expanded with the establishment of the city of Papenburg. Alexander von Velen zu Raesfeld (1599–1675) brought it to the imperial field marshal as military leader of the Catholic League in the Thirty Years' War and was referred to as the Westphalian Wallenstein .
Ramsdorf Castle was built in 1425 for Prince-Bishop Heinrich II of Moers from Münster . As early as 1451 in the Münster collegiate feud (1450-1457) it was destroyed and then partially rebuilt. It fell into disrepair again in the 17th century. The now existing rectangular brick building with ashlar structure was built in 1727 by the brothers Alexander and Anton Jungeblodt. Remnants of the complex from the 15th century, especially the round corner tower, have been preserved. The castle has housed the Ramsdorf Castle Museum since 1930. The exhibition, which was redesigned in 1993 according to the latest museum aspects, is divided into sections on regional prehistory and early history, urban and social history and natural history. The castle hall serves cultural purposes.
The three-aisled hall church of St. Walburga , which was originally built in 1410, refers to the long history of the parish of St. Walburga . The construction of the west tower and the two side aisles began in 1513. The eastward expansion through the transept and choir took place from 1912 to 1914.
Another important historical building is the Röllinghoff house. A wing from the early 16th century has been preserved on the farmhouse. On the main floor of this brick building is one of the oldest secular halls in western Münsterland that has been preserved in its original form.
The Velen with origins from the first half of the 15th century, learned particularly among the most significant Westphalian master builder, Johann Conrad Schlaun , in the mid-18th century, the transformation for future fairytale castle of Münsterland . After a devastating fire in 1931, the castle was rebuilt and initially housed a hospital, an old people's home and then a customs school . After extensive renovation and restoration measures, today's sports hotel was opened in 1988.
Meanwhile, the common people suffered from the recurring wars until the beginning of the 19th century. Last but not least, the enormous military costs and the constant billeting meant that Ramsdorf, despite its city rights, did not get beyond the status of a so-called wigbold, a city with lesser rights. When Prussia took control of the Westmünsterland in 1816, today's municipality (with the offices of Velen and Ramsdorf at that time) had 3780 inhabitants. The majority of the inhabitants lived from agriculture and operated mainly hand-weaving as a secondary and additional occupation. Even though poverty and hardship continued to be frequent guests in the houses of Velen and Ramsdorf and many people sought their fortune in emigrating to America, a change for the better slowly began. As early as 1848, both offices were headed by a bailiff in Velen. The expansion of the school system, the agricultural reforms and the local textile industry, which has been machine-operated since around 1870, gave both places important impulses. The noble house of Velen shaped Westphalian history beyond the community, primarily through Ignatz von Landsberg-Velen (1788–1863) and his grandson Maximilian (1847–1902). Despite this development, Ramsdorf in particular had retained the character of a farming town into the 20th century, and the number of inhabitants in both offices had hardly increased until 1900 (4,100).
For both offices, the years up to 1933 were characterized by changing economic conditions, an increase in the population and slow modernization. When Velen and Ramsdorf took stock of the twelve years of Nazi rule in 1945, the material damage caused by the World War was only of greater importance in Ramsdorf. In terms of personnel and morals, however, the losses were immeasurable, with more than 500 missing and fallen people as well as Jewish families fallen victim to the war.
Despite many difficulties in the first post-war years (e.g. refugee problems), the community developed very positively after 1945. In addition to a further improvement in the infrastructure, it was possible, above all, to increase economic strength by setting up new businesses. As part of the local reorganization, which led to a more effective administration, the municipalities of Ramsdorf-Stadt and Ramsdorf-Kirchspiel were merged to form the municipality of Ramsdorf in 1959. Ten years later, the three Velen municipalities, Velen-Dorf, Waldvelen and Nordvelen were merged. This development came to an end in 1975 with the formation of the bipolar municipality of Velen from the former municipalities of Velen and Ramsdorf.
Velen is the seat of the Regionale-2016 -Agentur , the central control point for the regional process in Westmünsterland.
Incorporations
On April 1, 1959, the parishes of the parish of Ramsdorf and the city of Ramsdorf were merged by state law to form the new municipality of Ramsdorf. On July 1, 1969, the three Velen municipalities Velen-Dorf, Waldvelen and Nordvelen were merged to form the new municipality of Velen. On January 1, 1975, Ramsdorf became a part of the municipality of Velen. In addition, a sub-area of the neighboring municipality of Heiden, which had around 150 inhabitants at that time, was incorporated.
politics
City council
After the local elections on May 25, 2014 , Velen's council was composed as follows:
mayor
From 2009 to 2015 Christian Schulze Pellengahr was mayor of the municipality of Velen, most recently he was re-elected in 2014. After he was elected District Administrator of the Coesfeld district in the 2015 municipal elections , the first deputy, Thomas Brüggemann, took over the official duties on a temporary basis. In the new election on February 28, 2016, Dagmar Jeske, who was not part of the party, clearly beat her competitor Thomas Kronenfeld (CDU) with 69.9% of the vote.
Coat of arms, banner and flag
The city of Velen bears the coat of arms, banner and official seal of the former office of Velen-Ramsdorf, as awarded by the Minister of the Interior with a decree of November 17, 1961, in the version as approved by the District President of Münster with a document of November 14, 1977 . On December 17, 2012, the city council of Velen also decided to introduce a flag that was approved by the district administrator of the Borken district - local authority - on December 28, 2012.
coat of arms
Blazon : "The coat of arms of the city of Velen shows in the enlarged yellow head of the shield three red merlettes arranged in bars, below in blue a yellow ram with a yellow cross."
Before the merging of the municipalities of Velen and Ramsdorf, Velen's coat of arms only showed the three red merlettes (the coat of arms of the von Velen family) on a gold background. The Merlette is a heraldic trimmed little, duck-like bird; his beak and feet are missing. Many heraldists see a mutilated blackbird in the merle. Ramsdorf showed the golden (yellow) ram with a cross in blue.
Banner and flag
Description of the banner: "In the yellow banner head in the lower part three red merlettes arranged in bars, below in blue in the upper half a yellow ram equipped with a yellow cross." The main statute gives no description of the banner.
Description of the flag: "The flag is blue and yellow in two stripes and shows the coat of arms in the middle." The official gazette of the city of Velen gives the following completely inadequate description: "The colors of the coat of arms are repeated in the colors of the hoisted flag."
Community partnerships
Culture and sights
Buildings
Worth seeing are the moated castle Velen , which has been used as a conference and sports hotel for several years, as well as the local Catholic parish churches and the mill on the Thesingbach. The Röllinghoff house is to the southwest. In summer, the artesian well on the municipal border with Heiden is a popular destination.
Parks
Velen is located on the northern edge of the Hohe Mark-Westmünsterland nature park , which is characterized by its wooded landscape.
The moated castle Velen is surrounded by a park with partly ancient trees. The castle's golf course is also located here. This is followed by the zoo to the south. This is a forest and park area, which in 2006 was again approximated to the historical shape, designed according to plans by Johann Conrad Schlaun.
Museums
- Museum Burg Ramsdorf in Ramsdorf
- Gut Ross sawmill museum in Velen
Sports
The most important sports club in Velen is TuS Velen 1925, which offers volleyball and popular sports in addition to football.
Velen is connected to some tourist bike routes, including a. to the 100 Castles Route , the Flamingo Route , the Aare Route, the Hohe Mark Route and the agri-cultura route.
Regular events
- Every year in October there is the Kolle Kaermes autumn festival with a flea market, dance and singing performances , raffles and attractions for children in Velen.
- Walburgismarkt in May: The Walburgismarkt in Ramsdorf takes place annually on the last Sunday in May.
- Ramsdorf shooting festival in July
- Shooting festival Velen in August
- Schützenfest Ostendorf in May
- Schützenfest Holthausen on Ascension Day
- Stag shooting festival Bleking-Holthausen on the first Saturday after the Ramsdorf shooting festival
- Schützenfest Nordvelen on Whitsun
Personalities
- Hendrickje Stoffels (* 1626 in Ramsdorf † 1663 in Amsterdam), partner of the Dutch baroque painter Rembrandt
- Joseph Niesert (born November 27, 1766 in Münster, † June 14, 1841 in Velen), Catholic priest, scholar of antiquity and author
- Max von Landsberg-Velen (born January 17, 1847 in Münster, † December 31, 1902 in Velen), Westphalian nobleman and Prussian agricultural politician
- Josef Tillmans (born July 4, 1876 in Ramsdorf; † 1935), food chemist
- Bernhard Laum (April 12, 1884 - October 22, 1974), classical scholar
- Frieda Terhoch (December 17, 1889 in Dingden - February 27, 1957 in Winnipeg ), a merchant, moved with her family to Canada in 1939 as a Jewish emigrant
- Hans Meis (born June 28, 1902 in Waldvelen; † December 8, 1984 in Dortmund), German politician (CDU)
- Elisabeth Enseling (born November 12, 1907; † January 5, 1998 in Bonn), German politician (CDU)
- Ludwig Averkamp (born February 16, 1927 - † July 29, 2013 in Hamburg), Archbishop of Hamburg
- Klaus Balkenhol (born December 6, 1939), German dressage rider
- Georg Veit (born January 20, 1956), teacher and writer
- Ludgera Selting (* 1964), judge
- Dirk Bernemann (* 1975), author
- Sören Storks (* 1986), soccer referee
Web links
- Website of the city of Velen
- Document registers from the general archive of Landsberg-Velen / digital Westphalian document database (DWUD)
- Link catalog on Velen at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
- Velen in the Westphalia Culture Atlas
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ↑ OFFICIAL SHEET for the municipality of Velen number / volume: 07/2012 from May 25, 2012
- ↑ Stephanie Reekers: The regional development of the districts and communities of Westphalia 1817-1967 . Aschendorff, Münster Westfalen 1977, ISBN 3-402-05875-8 , p. 274 .
- ↑ Martin Bünermann: The communities of the first reorganization program in North Rhine-Westphalia . Deutscher Gemeindeverlag, Cologne 1970, p. 78 .
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 312 f .
- ↑ https://kreis-borken.de/fileadmin/internet/downloads/fe15/wahlen/2014_Kommunalwahlen.pdf Results of the local elections on May 25, 2014
- ↑ Borkener Zeitung of February 29, 2016
- ↑ Main Statute of the City of Velen, § 2. (PDF; 121 kB) Retrieved on February 10, 2013 .
- ↑ Official Journal of the City of Velen of March 25, 2013, p. 29 (PDF; 167 kB) Accessed on June 23, 2013 .
- ↑ TuS Velen website. Retrieved June 25, 2017 .
- ^ Münsterland eV: Cycling in Velen | Münsterland eV Tourism. Retrieved June 22, 2017 .
- ^ Society for the Difussion of Useful Knowledge: The Penny Cyclopaedia of the Society for the Difussion of Useful Knowledge. Charles Knight , 1841, p. 383. limited preview in Google Book search
- ↑ Hendrikje Stoffels (PDF file)