Wiesel (military tracked vehicle)
| Weasel | |
|---|---|

Wiesel 1A1 MK |
|
| General properties | |
| crew | 2 (driver commander / gunner) or 3 (driver, commander, gunner) |
| length | 3.31–3.55 m (Wiesel 1) 4.11–4.78 m (Wiesel 2) |
| width | 1.82 m (Wiesel 1) 1.82–1.87 m (Wiesel 2) |
| height | 1.83–1.89 m (Wiesel 1) 1.83–2.17 m (Wiesel 2) |
| Dimensions | 2.75–3.30 t (Wiesel 1) 4.1–4.78 t (Wiesel 2) |
| Armor and armament | |
| Armor | Armor steel |
| Main armament | 20 mm automatic cannon MK 20 Rh 202 , TOW -2 launch system, 120 mm mortar, Stinger anti-aircraft missiles |
| Secondary armament | Smoke throwing system , MG3 |
| agility | |
| drive | Turbodiesel 64 kW (87 PS) (Wiesel 1) 81 kW (110 PS) (Wiesel 2) |
| suspension | Torsion bar |
| Top speed | over 70 km / h |
| Power / weight | 23–17 kW / t (23–31 hp / t) |
| Range | Road: 286 km Terrain: 200 km |
The Wiesel is a light armored tracked vehicle platform and exists in different variants for reconnaissance, command, effect and support purposes. In addition to the different vehicle variants, a basic distinction is made between the smaller Wiesel 1 and the larger Wiesel 2. The tracked vehicle manufactured by Rheinmetall Landsysteme GmbH - a subsidiary of Rheinmetall AG - is only used by the Bundeswehr in the infantry units as a fire support vehicle and as a robotic test vehicle in a small edition of seven vehicles by the US Army . The small tank is known in Germany as a weapon carrier.
Development history
In 1977, the Bundeswehr developed a concept of a small, armored tracked vehicle to replace the Faun Kraka (power cart) used by the airborne troops .
The project envisaged a quickly and easily air-transportable vehicle with limited protection against small arms and artillery fragments. The origins of the concept go back to 1969 with the first ideas of the Federal Ministry of Defense and the Army Office. In 1970 the Porsche company investigated the feasibility of suitable vehicles. The concept studies at that time, however, had gross weights between 6 t and 7.5 t, which allowed transport only in a Transall C-160 and a Lockheed C-130 Hercules. The Tactical Requirements (TAF) were then revised and the following claims were made:
- Air transport also in the CH-53G transport helicopter , thus an upper weight limit of 6 t and limited external dimensions
- Parachute removability
- Armament with automatic cannon (MK) 20 mm, HOT anti-tank system and 120 mm mortar
With this list, Porsche examined the optimization of their concepts, but at the same time worked out a study on an armored weapon carrier with a total weight of 2.75 t. However, the advantages of transporting two weapon carriers with the same transport capacity led to a limitation of the dimensions to a total length of 3.30 m and a height of the hull of 1.30 m.
After the first presentation of the studies, the TAF was changed again. The TOW weapon system was developed with an ammunition supply of 14 missiles for anti-tank defense, a crew of three men, a combat weight of a maximum of 2.5 t, the possibility of air transport of two weapon carriers as an internal load and one weapon carrier as an external load and the possibility of lowering using a parachute elected. The demands for a version with a 20 mm automatic cannon and 120 mm mortar were dropped.
On July 5, 1973, the TAF for the Waffträger LL project was put into effect by the Army Office, and device development began. Porsche, Faun, Gesellschaft für Systemtechnik (GST), IBH and Rheinstahl decided to develop drafts and submitted their offers, which were evaluated by the Federal Office for Defense Technology and Procurement (BWB). With the exception of Faun, which took a different route with a wheeled vehicle, all of the products on offer were light tracked vehicles. The decision was made on April 18, 1974 in favor of the Porsche concept, which was supplemented by a model with a 20 mm MK, and the definition phase ended on June 27, 1974 with the conclusion of a contract between the BWB and Porsche, the general contractor.
The planned serial number was 270 vehicles, 170 of them with TOW and 100 with MK 20 , but this was increased by another 230 Wiesel with MK 20 in April 1975. The total number thus amounted to 500 weapon carriers.
On October 2, 1975, Porsche presented the first wooden model on a 1: 1 scale in collaboration with Keller and Knappich Augsburg (KUKA), while the first six prototypes were being produced. As early as October 1976, the first driving tests began in the Porsche development center in Weissach, followed by technical testing in the Wehrtechnischen Dienststelle 61 from February 1977 to May 1978. However , as early as 1977 at the school, Techdok and KUKA and the elaboration of the technical service regulations Technical Troop 1 in Aachen and at the air landing and air transport school Altenstadt (LL / LTS) with troop tests.
In the spring of 1978 the BWB and Porsche started the series production, but the project was discontinued in 1979 for cost reasons. In order to secure the development results, Porsche received an order in the same year for the remainder of the Waffträger MK 20 / TOW project.
However, only two years later it became clear that the replacement of the Kraka was inevitable. In June 1981 the BWB restarted the Waffträger MK 20 / TOW project and examined 19 further proposals from domestic and foreign companies. Since Porsche had two prototypes of the Wiesel available on loan, it was possible to present a functional model of the TOW vehicle on September 3, 1981 in Hammelburg on the occasion of the presentation of armored wheeled and tracked vehicles of the KTS 1 (combat troop school).
With the new tactical demands of March 11, 1983, a concept and definition phase for a weapon carrier MK 20 / TOW was initiated again. Based on the BWB's market analysis, the Wiesel and an armored wheeled vehicle based on the Mercedes G-Model were shortlisted. However, there was no decision to award the contract, which prompted the Army Office and the Federal Office for Defense Technology and Procurement to carry out the concept study in the official area with industry participation. The following requirements were defined with the aim of feasibility by the start of series production in 1989:
- Air loadability of two vehicles in the CH-53G
- Shooting the MK 20 in single fire, rapid single fire and short bursts of fire
- Off-road mobility in the area of the VW Iltis
- Use of standard gasoline or diesel engines
- Use of an automatic transmission
- The MK mount is equipped with a thermal imaging device and the option of changing ammunition to 25 mm
- Conversion to TOW 2
- Installation of the SEM 80 radio family
In May 1984 a model was presented under the designation MK 20 closed at the top , but this prototype was still too high. A second alternative solution with a weapon and aiming device side by side in the turret was favored, which brought significant advantages when loading and unloading in the CH-53G as well as better ballistic protection, better visibility and a larger elevation range for the MK 20. According to a decree, only diesel engines could be installed in combat vehicles. For this reason, a 2-liter 5-cylinder turbo diesel engine from Volkswagen and an automatic transmission from ZF Friedrichshafen (at that time Zahnradfabrik Friedrichshafen) were installed. However, these changes led to an enormous increase in weight, which was compensated for by lightweight construction and new armor steel.
After the Army Office, the BWB and the Material Office of the Army had completed their assessment, the Waffträger Wiesel concept was recommended for introduction to the airborne troops. The reasons given were:
- All-round ballistic protection
- Small dimensions and therefore low silhouette
- Low combat weight
- Low ground pressure
- Air loading capability as internal and external load
- Transport of two weasels on a 10 ton truck
- High mobility on and off-road
- Low noise development
- Standard chassis for both variants
- Commercially available construction components
After the phase document “Military-Technical-Economic Demand”, or MTWF for short, was issued and the budget was released in April 1985, the development contract was awarded to Porsche. In March 1986 a weapon system was handed over to WTD 91 (Wehrtechnische Dienststelle für Waffen und Munition) and WTD 41 ( Wehrtechnische Dienststelle für Kraftfahrzeuge und Panzer ) for testing or system testing . The chassis followed at the end of June 1986.
Due to the long development phase in the run-up, the tests ran without major problems, which enabled the on-time troop test tactics and logistics in autumn 1986 and thus the series maturity by September 1987. The procurement contract was signed on December 21, 1988.
Series production was carried out by Krupp and MaK (part of Rheinmetall Landsysteme GmbH since 1992), who had applied alongside Krauss-Maffei and Thyssen Henschel. The total number of vehicles was 343, of which 210 were TOW (including 24 driving school tanks ) and 133 were MK 20. The delivery took place in the years 1990 to 1992. Another seven vehicles were delivered to the USA .
As early as 1981, various concept studies by the Porsche company indicated the expansion of the Wiesel-1 platform. For example, the tub of the Wiesel 1 was considerably enlarged for a planned recovery vehicle.
At the beginning of the 1990s, the Bundeswehr also recognized the increasing importance of armored air-transportable vehicles. In order to meet this need, the MAK company developed the first prototype of the future Wiesel 2 under its own responsibility.
The prototype was developed as a team transport vehicle and provided an interior volume that was almost twice that of the Wiesel 1. As a result, the vehicle hull was lengthened and a fourth roller was added. Due to this change in vehicle dimensions, only one Wiesel 2 can be transported in the CH-53. Along with the increase in the total weight, the engine was changed (near-series 1.9-liter TDI engine from Volkswagen ), and a new gearbox was also used, which now enables turning around the vertical axis. The cabin is air-conditioned, so that it can be used in many climate zones. Moreover, it is NBC protection guaranteed.
This further development was approved by the consumer. The light air defense system was implemented on the new vehicle base and delivered to the customer in 2004. Further vehicle versions followed.
MrsKpfSys, which is currently being manufactured, represents the latest state of vehicle development. Due to a further increase in the maximum vehicle weight, the tub was extended again and a fifth roller was added. Due to the lower technological advancement compared to the development from Wiesel 1 to Wiesel 2, this vehicle variant continues to be counted as part of the Wiesel 2 platform.
Service life extension
On November 19, 2019, the Federal Office for Equipment, Information Technology and Use of the Federal Armed Forces (BAAINBw) commissioned the FFG Flensburger Fahrzeugbau Gesellschaft mbH (FFG) to extend the useful life of a total of 181 Wiesel 1, which will enable the vehicles to be used beyond 2030. The commissioned measures are aimed at improving the landing gear, improving protection against mines and ballistic threats as well as installing modern means of communication and a new weapon system. The following variants are affected: Wiesel 1 reconnaissance aircraft, Wiesel 1 automatic cannon and Wiesel 1 MELLS (here replacement of the TOW as the main armament and integration of the MELLS weapon system). In addition, the FFG supplies 15 conversion kits for driving school vehicles. The project will run until 2022.
Mission concept


The Wiesel 1 is a lightly armored, night-fighting and air-packable weapon carrier. It was developed primarily for the paratroopers, but also takes after the restructuring of the Bundeswehr use in the Jägertruppe and the mountain troops . The Wiesel is used in the anti-tank defense, for fire support of the hunter companies, for monitoring sections of terrain and objects, for observing and securing at checkpoints, for strengthening forces in object protection and, contrary to its concept, also as a convoy escort and protection.
The Wiesel 1 reaches a top speed of up to 80 km / h. The reason for this is the high specific power . For the Wiesel 1, this is around 23 kW / t, a value that can be described as very good for tracked vehicles. Thanks to a ground pressure of 3.5 N / cm², the weapon carrier has good off-road mobility even in the most unfavorable ground conditions, combined with a speed of approx. 50 km / h. Its small size makes it easier to use and makes it easier to get into covered positions. This can be seen as part of passive protection. As a rule, two weapon carriers always work together to secure each other.
A CH-53G can transport two Wiesel 1 (one Wiesel 2) as an internal load or one Wiesel as an external load. In the case of transport aircraft such as the C-160 Transall , the number rises to four, while the US Lockheed C-130 can accommodate three weapon carriers. Another way to land the weasel is to drop it with a parachute. However, this was discarded after four weapon carriers were damaged during testing and the tactical importance of this type of discharge sank.
The weasel was and is used by the German armed forces on many missions abroad ( UNOSOM II , IFOR , SFOR , KFOR , TFH , ISAF ).
construction
Due to the essential requirement to transport the Wiesel in a CH-53, great attention was paid to a lightweight construction for the Wiesel.
The weasel consists of a self-supporting tub made of armored steel sheets of various thicknesses. It offers the crew limited protection against fragments and infantry ammunition. Therefore, the Wiesel is not an armored vehicle, but a weapon carrier chain that uses its weapons against enemy forces from low positions. All Wieseln 1 lack the smoke throwing device that is otherwise common in armored vehicles, which offers protection from optronic reconnaissance equipment. In addition, due to its primary property of being easily air-relocated, the vehicle only offers space for two - in some versions three - crew members, which is why the commander is also a gunner; a disadvantage compared to other combat vehicles.
As with the Leopard family, the engine, the automatic transmission, the air filter system, the exhaust system and the range and steering gear are combined in one block. This engine block is located in the left front area of the vehicle. Thanks to quick disconnection points, the entire engine can be changed in ten minutes. The military driver sits to the right of the partitioned engine room. The crew and the corresponding conversion kit are located in the rear of the vehicle. Welded to the tub are so-called hot eyes for lashing to the helicopter or in the transport aircraft.
Like all components of the Wiesel, the drive is also made of lightweight construction. The drive takes place via the drive wheel at the front end of the vehicle. Depending on the type of vehicle, there are three (Wiesel 1) or four to five rollers with torsion bars (Wiesel 2). At the rear of the vehicle are the large pulleys, which both bear part of the vehicle's weight and are responsible for tensioning the chain. At the top of the drive, one (Wiesel 1) or two (Wiesel 2) support rollers ensure that the chain is returned to the drive wheel. The endless rubber chain from Kluth was unusual, but was later replaced by a classic steel end connector chain from Diehl.
variants
Weasel 1
MK 20
The MK Wiesel is used for fire support to the infantry and for fighting against soft targets, to a certain extent also against hard targets and slow and low-flying aircraft and especially helicopters. The main weapon of the Wiesel 1 consists of a 20 mm automatic cannon (MK) MK 20 Rh 202 from Rheinmetall. The MK was installed in a one-man tower E6-II-A1 from KUKA Wehrtechnik (part of Rheinmetall since 1999). The mechanical straightening drives enable a lateral straightening range of 110 ° and a vertical straightening range of −10 ° to + 45 °. On the side of the weapon and thus outside there are two ammunition boxes with 60 cartridges of armor-piercing hard core ammunition (AP) on the left and 100 cartridges of explosive ammunition (HE) on the right. A double belt feeder enables a quick change from AP to HE or vice versa. Thanks to the PERI Z-59 image intensifier , the MK Wiesel is capable of night combat.
As part of combat value increases , night combat capabilities were improved from February 2002. 76 weapon carriers with the new designation Wiesel 1A1 MK received the Autonomous Optronic Aiming System (AOZ 2000) from STN Atlas Elektronik with laser range finder, thermal imaging device and fire control computer.
Starting in 2006, a total of 53 vehicles under the identification Wiesel 1A2 MK were equipped with the PERI Z17 BM48 WBG target periscope (day vision channel with four and eight times magnification and third generation thermal imaging device). With the introduction of the command and information system Heer, the name of the converted Wiesel 1 changed to Wiesel 1 A3 MK (AOZ 2000 with FüInfoSys) and Wiesel 1 A4 MK (PERI Z17 with FüInfoSys).
In contrast to the Wiesel TOW, the crew consists of only two soldiers (commander / gunner and driver). The tasks of the commander include driving the tracked vehicle, observing the battlefield and fighting targets, as well as maintaining telecommunication connections on up to two radio circuits. As a result, the low crew size results in a limited use of the capabilities of the vehicle and only limited stamina on the battlefield.
Expansion stages
- Wiesel 1 A0 MK - production version with 20 mm on-board machine gun
- Wiesel 1 A1 MK - upgraded with an Autonomous Optronic Aiming System (AOZ 2000) for better night combat capabilities
- Wiesel 1 A2 MK - upgraded with the PERI Z17 BM48 WBG for better night fighting capabilities.
- Wiesel 1 A3 MK - Wiesel 1A1 with command and information system Heer (FüInfoSys Heer)
- Wiesel 1 A4 MK - Wiesel 1A2 with command and information system Heer (FüInfoSys Heer)
TOW
The TOW weapon system was mounted on a height-adjustable mount. It consists of the launch tube, the optics block and the AN / TAS 4 thermal imaging device designed for day and night vision . The directional range is 45 ° to the side and +/− 10 ° in height. The maximum stock of ammunition is officially six TOW 2, five of them in the vehicle and one outside on the rear wall. When a guided missile is stowed in the weapon system, this increases to seven. The vehicle commander controls the vehicle and the crew, maintains communications connections, observes the battlefield and is the gunner of the weapons system.
The TOW Wiesel also has a MG3 as secondary armament . Initially not equipped for this, the vehicles were converted by the troops' own construction and supplemented by a carriage mount at the loader’s place. With the standardized takeover, the designation changed to Wiesel 1A1 TOW and for weapon carriers with the command and information system for the army it changed to Wiesel 1A2 TOW
Expansion stages
- Wiesel 1 TOW - with wire-controlled ( T ube launched; O ptically tracked; W ire-guided missile) anti-tank guided missiles
- Wiesel 1 A1 TOW - Equipped with a MG3 as secondary armament
- Wiesel 1 A2 TOW - Wiesel 1 A1 with command and information system Heer (FüInfoSys Heer)
spotter
This is a modified Wiesel TOW that was procured for the airborne reconnaissance companies (LL AufklKp). The vehicle has undergone extensive changes. The weapon position was removed, the vehicle roof was raised and a hybrid navigation system, an autonomous optronic aiming system (AOZ 2000) with TV camera, IR camera and laser range finder and the FaKoM guidance, communication and information system were installed. The reconnaissance optics are located on a pan / tilt device that can be extended up to three meters with a lifting mast. The reconnaissance tank is equipped with the SEM 80/90 and HRM 7400 radios for communication . A MG3 mounted on an open-air gun is used as armament. In July 2001, Rheinmetall delivered the troop test model to the LL AufklKp 310. There are a total of 16 reconnaissance vehicles in the Bundeswehr.
Driving school tanks
Additional Wiesel 1 TOWs were modified for driving school training. For this purpose, all vehicle superstructures such as the carriage and rear hatches were removed. Instead, an air-conditioned cabin with large glass windows was mounted on the rear of the vehicle. This is where the driving instructor is located. Similar to civilian driving school vehicles, this can intervene in the driving process.
Concepts and prototypes
As with other German developments, the suitability of the weasel for various purposes was examined.
BTM 208
The Wiesel, designed as a reconnaissance tank, had a one-man turret from the SAMM company. He was armed with a 12.7 mm machine gun.
BTM-263 mortar carrier
This version also has a one-man tower from SAMM. It was modified to accommodate a 60mm mortar and an FN-Mag as armament.
Anti-aircraft tanks
As an anti-aircraft tank, it was equipped with an adjustable pedestal for launching the Mistral anti-aircraft missiles.
Ambulance
A troop medical armor. Similar to the concept of a mobile medical team
Armored recovery vehicles
The concept of an armored recovery vehicle had a rotating crane system and a cable winch.
Resupply tanks
Its concept envisaged its use as an ammunition transporter.
Tank destroyers
Equipped with the anti-tank weapon MILAN on a rotating twin mount.
Battlefield radar
Equipped with the Franco-German artillery radar RATAC (Radar de tir l'artillerie de campagne), it should be used for battlefield surveillance, target acquisition and target classification as well as for guiding artillery fire.
ATM HOT
It served as a universal weapon carrier for reconnaissance, anti-tank, surveillance and observation. It also has an extendable universal platform with thermal imaging device, goniometer with TV camera, laser range finder and surveillance camera for close range. He was armed with an M2HB and the HOT anti-tank weapon .
RMK 30
This test vehicle serves as proof of the possibility of mounting the low-recoil 30 mm automatic cannon RMK 30 as armament. It was presented in November 2004 in Hammelburg.
Detector vehicle
As part of the “Route Clearance System” for the reconnaissance of IEDs , Wiesel 1s remotely controlled from a fox and equipped with integrated ground penetration radar and metal detectors are used as detector vehicles.
DIOK
D emonstratorfahrzeug I nnovatives, O ptimiertes K ettenlaufwerk : test vehicle FFG for the testing of drive systems consisting of a cut apart and extended Wiesel 1 MK, in which the arrangement of the drive has been changed: instead of three rollers plus large combined Running / are guide roller it five rollers and an extra deflection roller as well as three support rollers instead of one, and another chain is used. The driving behavior should thus be better, and an additional electric drive can also be tested if necessary (pictures and description :).
LLX
A variant from 1996 with wheel hub motors (fully electric drive).
Weasel 2
Light air defense system (leFlaSys)
The Wiesel 2 LeFlaSys ( le ichtes Fl ug a bwehr- Sys tem) consists of the following vehicles:
- Battery guide and support vehicle (BF / UF)
- Reconnaissance and fire control vehicle (AFF)
- Waffträger Ozelot (FlaRaWaTrg)
A total of 67 vehicles were procured for the leFlaSys . After the dissolution of the anti-aircraft missile battery 100, light anti-aircraft missile training battery 610 and light anti-aircraft missile battery (8./JgRgt 1), these weapon systems were handed over to the air defense missile service area, anti- aircraft missile squadron 1 .
Medical Corps (SanTrp)
The Wiesel 2 (SanTrp) is intended for the rescue of injured people in difficult terrain and for first aid on site. For this, one wounded person can be lying down or two injured people can be seated and a paramedic can be transported. The crew consists of a military driver and a medic. 33 medical vehicles were delivered to the Bundeswehr.
Pioneer Reconnaissance Troop (PiErkTrp)
The PiErkTrp is equipped with an inflatable boat for water explorations. Material for blocking and blasting operations is also carried along. Eight PiErkTrp were delivered to the Bundeswehr.
Movable command post (bewBefSt)
The bewBefSt serves as a command vehicle for an army unit at company and battalion level. It is equipped with extensive radio equipment for this purpose. 32 bewBefSt were delivered to the Bundeswehr.
Mortar Combat System (MrsKpfSys)
The airborne reconnaissance, command and control network, mortar combat system consists of various vehicles based on Wiesel 2 in different designs and functions. In June 2009, a contract was signed with Rheinmetall AG for the delivery of the first eight Wiesel 2 lePzMrs, which were to be delivered to the German armed forces in 2011. In addition, two lead vehicles in the variant ZgTrp and FltTrp are supplied. The order has a total value of € 61.5 million. As part of the realignment of the Bundeswehr , the system will not be fully procured.
Light tank mortar (lePzMrs)
The lePzMrs forms the active component of the system network. Equipped with a return-mounted 120 mm muzzle-loading mortar, which is designed for both conventional ammunition with a range of 8000 m and for end-phase guided ammunition, the weapon system is operated and reloaded under ballistic and NBC protection. The automatic determination of direction, height and position as well as the fully automatic correction of the weapon position from shot to shot ensure rapid fire readiness and high precision. This allows the Wiesel 2 lePzMrs to be used for quick position changes (hide-hit-run-hide tactics). Due to a weight increase compared to the other Wiesel 2 variants, the series vehicles have five pairs of rollers. The prototypes are also equipped with four pairs of rollers.
Lead vehicles (FüFhz)
At the management level of MrsKpfSys, there are various functions that are met with specially adapted vehicle equipment. The platoon troop (ZgTrp) and fire control troop (FltTrp) lead a mortar train. Here reconnaissance data are analyzed, the further course of action of the train is determined and the corresponding target assignments with the fire control data are forwarded to the subordinate lePzMrs. The company command troop (KpFüTrp) leads the unit at company level. The Joint Fire Support Coordination Team (JFSCT) handles communication with higher command levels.
Reconnaissance vehicle JFST (Joint Fire Support Team)
The Joint Fire Support Team (JFST) represented the reconnaissance component in MrsKpfSys . It has retractable observation equipment with a high-resolution CCD camera, a 3rd generation thermal imaging camera, a laser pointer (only surface-to-air variant BL) and a laser range finder for combat - and mission reconnaissance. Clarified goals are made available via integrated command and fire control systems within the own system network as well as external forces.
Concepts and prototypes
Test vehicle 1 (VT01)
The VT01 is the first Wiesel 2 with four castors as a personnel carrier.
ATM HOT
This vehicle serves as a universal weapon carrier for reconnaissance, anti-tank, surveillance and observation. It also has an extendable universal platform with thermal imaging device, goniometer with TV camera, laser range finder and surveillance camera for close range. He was armed with an M2HB and the HOT anti-tank weapon .
Argus
The Argus is an observation and reconnaissance vehicle with elevatable observation equipment. For long observation missions, it was given an ergonomically designed interior, and innovative operating concepts were implemented.
SYRANO
The chassis of the Wiesel 2 is used as the basis for the experimental French SYRANO program ( Sy stème R obotisé d ' A cquisition pour la N eutralisation d' O bjectifs ). This program researches the use of unmanned automatic combat vehicles.
Test vehicle 2 (VT02)
The VT02 is the first Wiesel 2 with five castors as a test vehicle. A vehicle of the type movable command post served as the basis , the floor assembly of which was separated and replaced by an extended assembly with five pairs of rollers. The vehicle was used to demonstrate the suitability of the Wiesel-2 platform for five castors and a maximum total weight of 4.78 t.
Technical specifications
Weasel 1
| designation | Wiesel 1 MK | Weasel 1 TOW | Wiesel 1 scout | |
| Type: | airborne weapon carrier | |||
| Engine: | Audi 5-cylinder diesel with exhaust gas turbocharger | |||
| Displacement: | 1986 cc | |||
| Power: | 64 kW (87 PS) | |||
| Cooling: | Liquid cooling | |||
| Transmission: | 3HP-22 hydromechanical torque converter with three forward gears, one reverse gear | |||
| Landing gear: | Torsion bar sprung support roller drive with three rollers, one support roller and one deflection roller per side | |||
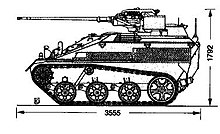
| Length over all: | 3545 mm | 3310 mm | 3550 mm | |
| Width over everything: | 1820 mm | |||
| Height above everything: | 1825 mm | 1897 mm | 1838 mm | |
| Ground clearance: | 302 mm | |||
| Wading ability: | 500 mm | |||
| Ability to exceed: | 1200 mm | |||
| Climbing ability: | 400 mm | |||
| Gradeability: | 60% | |||
| Bank slope: | 30% | |||
| Max. Total weight: | approx. 3000 kg | approx. 3300 kg | ||
| Top speed: | over 70 km / h (road), 50 km / h terrain | |||
| Fuel quantity: | 80 L | |||
| Fuel consumption: | Road: 28 L over 100 km, terrain: 40 L over 100 km | |||
| Driving range: | Road: 286 km, terrain: 200 km | |||
| Armament: | 1 automatic cannon 20 mm |
TOW-2 start system and MG3 (optional) |
MG3 | |
| Ammunition: | 400 rounds | 5-7 TOW 2 | ||
| Crew: | 2 | 3 | ||
Weasel 2
| designation | Wiesel 2 FlaRaWaTrg | Wiesel 2 BF / UF | Weasel 2 AFF | Wiesel 2 SanTrp | Wiesel 2 PiErk | Wiesel 2 bewBefSt | Wiesel 2 lePzMrs | Wiesel 2 FüFhz |
| Type: | airborne weapon carrier | |||||||
| Engine: | VW 4-cylinder TDI with exhaust gas turbocharger | |||||||
| Displacement: | 1896 cc | |||||||
| Power: | 81 kW (110 PS) | |||||||
| Cooling: | Liquid cooling | |||||||
| Transmission: | hydromechanical torque converter with four forward gears, one reverse gear | |||||||
| Landing gear: | Torsion bar-sprung support roller drive with four rollers, two support rollers, one idler per side | Torsion bar-sprung support roller drive with five rollers, two support rollers, one idler per side | ||||||
| Length over all: | 4505 mm | 4106 mm | 4150 mm | 4392 mm | 4258 mm | 4783 mm | 4258 mm | |
| Width over everything: | 1820 mm | 1870 mm | 1816 mm | 1870 mm | 1857 mm | |||
| Height above everything: | 1915 mm | 1885 mm | 2144 mm | 2168 mm | 1810 mm | 1810 mm | ||
| Ground clearance: | 302 mm | |||||||
| Wading ability: | 500 mm | |||||||
| Ability to exceed: | 1200 mm | |||||||
| Climbing ability: | 400 mm | |||||||
| Gradeability: | 60% | 40% | ||||||
| Bank slope: | 30% | |||||||
| Max. Total weight: | 4500 kg | approx. 4300 kg | approx. 4100 kg | approx. 4500 kg | approx. 4780 kg | |||
| Top speed: | over 70 km / h (road), 50 km / h terrain | |||||||
| Fuel quantity: | 80 l | |||||||
| Fuel consumption: | Road: 28 l per 100 km, terrain: 40 l per 100 km | |||||||
| Driving range: | Road: 286 km, terrain: 200 km | |||||||
| Crew: | 3 | 2 | 3 | |||||
literature
- Michael Scheibert: Waffträger Wiesel 1 - armored and air-packable. Waffen-Arsenal Volume 136, Podzun-Pallas Verlag, Friedberg / H.
- Karl Anweiler, Rainer Blank: The wheeled and tracked vehicles of the Bundeswehr, 1956 until today. Bechtermünz Verlag, Augsburg.
Web links
- Wiesel 1 & Wiesel 2 - Information from Rheinmetall DeTec AG
- Bundeswehr Classix: nimble, nimble Wiesel (1995) ( YouTube video of the Bundeswehr)
- 60 seconds Bundeswehr: Wiesel (YouTube video of the Bundeswehr, November 29, 2017)
- The Wiesel - Firepower for the paratroopers (Documentation from Welt on YouTube)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Army-Guide.com: Wiesel first
- ^ Military-Today.com: Wiesel 1. Airportable armored vehicle.
- ^ Bundeswehr commissions FFG to modernize the Wiesel 1 weapon carrier. In: https://esut.de/ . European Security and Technology, November 25, 2019, accessed November 25, 2019 .
- ↑ a b Waffträger Wiesel 1, Tankograd - Military Vehicles Special No. 5022
- ↑ s. Video nimble weasel . From youtube.com, accessed on May 4, 2016 (MP4; approx. 19.78 MB)
- ↑ Christian Dewitz: With high tech against maliciousness, in: bundeswehr-journal , St. Goar, mediakompakt http://www.bundeswehr-journal.de/2013/mit-hightech-gegen-heimtuecke/ , March 18, 2013, accessed on March 3, 2014
- ↑ Page no longer available , search in web archives: European Security and Technology Image and description of the DIOK
- ↑ Facebook several pictures of the DIOK
- ↑ Wiesel tracked vehicle - firepower for the paratroopers | Documentary. Retrieved on October 13, 2019 (German).
- ↑ Press release from June 25, 2009 on www.rheinmetall-defence.de ( Memento from September 13, 2012 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Page no longer available , search in web archives: Info-Brief Heer June 2012 (PDF; 1.2 MB), accessed on July 28, 2012.