History of Spain

The history of Spain spans the period from pre-historic times, through the rise and fall of a global empire, to Spain's modern-day renaissance in the post-Franco era.
Modern humans landed on the Iberian Peninsula in the area of today's Spain some 35,000 years ago. Waves of invaders and colonizers followed over the millennia, including the Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians, and Greeks, and by about 200 B.C., the area was controlled by the Roman Empire. After the fading of the Roman Empire, the history of the modern nation of Spain has been viewed as beginning with the Christian Visigothic kingdom established during the 5th through early 8th centuries.[1] By 711, the first Muslim invaders arrived from North Africa, and within a few years, these invaders dominated a large portion of the Iberian Peninsula. During the next 750 years, independent Muslim states were established, and the entire area of Muslim control became known as Al-Andalus. This period is remembered in part for a flowering of philosophy and religious thought, and in part for continuing tensions between Christians and Muslims. What became known as the Reconquest (or Reconquista) of Spain by Christian forces began almost immediately in the 8th century with resistance efforts in northern Spain, and gradually rolled south over the centuries, culminating in the defeat of the last Muslim ruler of Granada in 1492. During this period of the re-taking of Spain, Christian kingdoms and principalities developed, including most importantly, the Kingdom of Castile and the Kingdom of Aragon. The union of these two kingdoms, through the marriage in 1469 of Queen Isabella I and King Ferdinand II, led to the creation of the Kingdom of Spain.

The year 1492 was also epochal as the year that Ferdinand and Isabella sent the Italian explorer, Christopher Columbus across the Atlantic Ocean in search of a new trade route to Asia. Columbus's arrival in the New World, and the development of the Spanish Empire ushered in an age of glory for Spain. The next several centuries saw Spain as a colonial power become the most important European nation on the global stage, and a central actor in European affairs and conflicts. Spanish literature and fine arts flourished during this time; the period was, however, marred by the expulsion of the Jews and Muslims, the Inquisition, and the treatment of Indigenous peoples during the colonization of the Americas. During these next three hundred years, Spain's colonial empire covered almost all of South America, large portions of North America, the Philippines in Asia, and portions of coastal Africa—it was one of the largest empires in the history of the world. Financed in major part by the riches pouring in from its colonies, Spain became embroiled in wars and intrigues in continental Europe, including, for example, obtaining and losing possessions in today's Netherlands and Italy, and engaging in wars with England (including the sea battle involving the famous Spanish Armada) and France. The dynastic family of the Hapsburgs took control of the Spanish throne, followed by the crown being worn by the Bourbon family. Spain's European adventures led, however, to successive bankruptcies, and reduced Spain to a second-tier European power by the end of the 18th century.

The 19th century saw monumental change across Europe, and Spain was no exception. The early part of the century saw the independence of almost all the Spanish colonies in the New World. The century was also marked by foreign intervention and internal conflicts. Napoleon placed his brother on the Spanish throne, but with the expulsion of the French, Spain entered into an extended period of unrest. Similar to events in other parts of Europe, much of the 19th century was series of struggles among elites, as well as struggles between elites and newly-empowered republican and liberal forces. Experiments in democracy alternated with returns to more authoritarian rule, and pressure grew in Spain's regions for increased autonomy. The arrival of the Industrial Revolution, late in the century, brought wealth to an expanding middle class in some major centres, however the Spanish-American War at the end of the 19th century led to the loss of almost all of Spain's remaining colonies.
Despite a rising standard of living and increasing integration with the rest of Europe, the first third of the 20th century continued the political turmoil. Spain remained neutral during the First World War, however, by 1936 Spain was plunged into a bloody civil war which by some accounts cost 1,000,000 lives. The war ended in a fascist dictatorship, led by Francisco Franco which controlled the Spanish government until 1975. Spain was officially neutral during the Second World War; the post-war decades were relatively stable (with the notable exception of an armed independence movement in the Basque Country), and though the country experienced an astonishingly rapid economic surge in the 1960s and early 1970s, it remained culturally and politically repressed. The death of Franco in 1975 began a remarkable transformation. While tensions remain (for example, with Muslim immigrants and in the Basque region), modern Spain has seen the development of a robust, modern democracy (a constitutional monarchy with popular King Juan Carlos), one of the fastest-growing standards of living in Europe, the flowering of an artistic community (particularly film makers), entry into the European Community, and the 1992 Summer Olympics. In 2005, Spain became the first nation in the world to grant full marriage and adoption rights to same-sex couples.
| History of Spain |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
Early history
The earliest record of hominids living in Europe has been found in the Spanish cave of Atapuerca which has become a key site for world palaeontology. Fossils found there are dated to roughly 1,000,000 years ago.
Modern humans in the form of Cro-Magnons began arriving in the Iberian Peninsula from north of the Pyrenees some 35,000 years ago. The most conspicuous sign of prehistoric human settlements are the famous paintings in the northern Spanish Altamira, which were done ca. 15,000 BCE and are regarded, along with those in Lascaux, France, as paramount instances of cave art.
The earliest urban culture documented is that of the semi-mythical southern city of Tartessos, pre-1100 BCE. The seafaring Phoenicians, Greeks and Carthaginians successively settled along the Mediterranean coast and founded trading colonies there over a period of several centuries.
Around 1100 BCE, Phoenician merchants founded the trading colony of Gadir or Gades (modern day Cádiz) near Tartessos. In the 9th century BCE the first Greek colonies, such as Emporion (modern Empúries), were founded along the Mediterranean coast on the East, leaving the south coast to the Phoenicians. The Greeks are responsible for the name Iberia, apparently after the river Iber (Ebro in Spanish). In the 6th century BCE the Carthaginians arrived in Iberia while struggling first with the Greeks and shortly after with the Romans for control of the Western Mediterranean. Their most important colony was Carthago Nova (Latin name of modern day Cartagena).
The native peoples whom the Romans met at the time of their invasion in what is now known as Spain were the Iberians, inhabiting from the Southwest part of the Peninsula through the Northeast part of it, and then the Celts, mostly inhabiting the north and northwest part of the Peninsula. In the inner part of the peninsula, where both groups were in contact, a mixed, distinctive, culture was present, the one known as Celtiberian.
Roman Spain

Roman Iberia was divided: Hispania Ulterior and Hispania Citerior during the late Roman Republic; and, during the Roman Empire, Hispania Taraconensis in the northeast, Hispania Baetica in the south (roughly corresponding to Andalucia), and Lusitania in the southwest (corresponding to modern Portugal).
Hispania supplied Rome with food, olive oil, wine and metal. The emperors Trajan, Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius and Theodosius I, the philosopher Seneca and the poets Martial, Quintilian and Lucan were born in Spain. The Spanish Bishops held the Council at Elvira in 306. The collapse of the Western Roman empire did not lead to the same wholesale destruction of Western classical society as happened in areas like Britain, Gaul and Germania Inferior during the Dark Ages, even if the institutions, infrastructure and economy did suffer considerable degradation. Spain's present languages, its religion, and the basis of its laws originate from this period. The centuries of uninterrupted Roman rule and settlement left a deep and enduring imprint upon the culture of Spain.
Visigothic Hispania (5th–8th centuries)
- See also: Kingdom of Toledo
After the decline of the Roman Empire, Germanic tribes invaded the former empire. Several turned sedentary and created successor-kingdoms to the Romans in various parts of Europe. Iberia was taken over by the Visigoths after 410.

In the Iberian peninsula, as elsewhere, the Empire fell not with a bang but with a whimper. Rather than there being any convenient date for the "fall of the Roman Empire" there was a progressive "de-Romanization" of the Western Roman Empire in Hispania and a weakening of central authority, throughout the 3rd, 4th and 5th centuries. At the same time, there was a process of "Romanization" of the Germanic and Hunnic tribes settled on both sides of the limes (the fortified frontier of the Empire along the Rhine and Danube rivers). The Visigoths, for example, were converted to Arian Christianity around 360, even before they were pushed into imperial territory by the expansion of the Huns. In the winter of 406, taking advantage of the frozen Rhine, the (Germanic) Vandals and Sueves, and the (Sarmatian) Alans invaded the empire in force. Three years later they crossed the Pyrenees into Iberia and divided the Western parts, roughly corresponding to modern Portugal and western Spain as far as Madrid, between them. The Visigoths meanwhile, having sacked Rome two years earlier, arrived in the region in 412 founding the Visigothic kingdom of Toulouse (in the south of modern France) and gradually expanded their influence into the Iberian peninsula at the expense of the Vandals and Alans, who moved on into North Africa without leaving much permanent mark on Hispanic culture. The Visigothic Kingdom shifted its capital to Toledo and reached a high point during the reign of Leovigild.
Importantly, Spain never saw a decline in interest in classical culture to the degree observable in Britain, Gaul, Lombardy and Germany. The Visigoths tended to maintain more of the old Roman institutions, and they had a unique respect for legal codes that resulted in continuous frameworks and historical records for most of the period between 415, when Visigothic rule in Spain began, and 711, when it is traditionally said to end. The proximity of the Visigothic kingdoms to the Mediterranean and the continuity of western Mediterranean trade, though in reduced quantity, supported Visigothic culture. Arian Visigothic nobility kept apart from the local Catholic population. The Visigothic ruling class looked to Constantinople for style and technology while the rivals of Visigothic power and culture were the Catholic bishops— and a brief incursion of Byzantine power in Cordoba.
The period of Visigothic rule saw the spread of Arianism briefly in Spain. In 587, Reccared, the Visigothic king at Toledo, having been converted to Catholicism put an end to dissension on the question of Arianism and launched a movement in Spain to unify the various religious doctrines that existed in the land. The Council of Lerida in 546 constrained the clergy and extended the power of law over them under the blessings of Rome.
The Visigoths inherited from Late Antiquity a sort of feudal system in Spain, based in the south on the Roman villa system and in the north drawing on their vassals to supply troops in exchange for protection. The bulk of the Visigothic army was composed of slaves, raised from the countryside. The loose council of nobles that advised Spain's Visigothic kings and legitimized their rule was responsible for raising the army, and only upon its consent was the king able to summon soldiers.
The impact of Visigothic rule was not widely felt on society at large, and certainly not compared to the vast bureaucracy of the Roman Empire; they tended to rule as barbarians of a mild sort, uninterested in the events of the nation and economy, working for personal benefit, and little literature remains to us from the period. They did not, until the period of Muslim rule, merge with the Spanish population, preferring to remain separate, and indeed the Visigothic language left only the faintest mark on the modern languages of Iberia. The most visible effect was the depopulation of the cities as they moved to the countryside. Even while the country enjoyed a degree of prosperity when compared to the famines of France and Germany in this period, the Visigoths felt little reason to contribute to the welfare, permanency, and infrastructure of their people and state. This contributed to their downfall, as they could not count on the loyalty of their subjects when the Moors arrived in the 8th century.
Muslim Occupation and Reconquista (8th–15th centuries)
By 711 Arabs and Berbers had converted to Islam, which by the 8th century dominated all the north of Africa. A raiding party led by Tariq ibn-Ziyad was sent to intervene in a civil war in the Visigothic kingdoms in Iberia. Crossing the Strait of Gibraltar, it won a decisive victory in the summer of 711 when the Visigothic king Roderic was defeated and killed on July 19 at the Battle of Guadalete. Tariq's commander, Musa bin Nusair quickly crossed with substantial reinforcements, and by 718 the Muslims dominated most of the peninsula. The advance into Europe was stopped by the Franks under Charles Martel at the Battle of Tours in 732.
The rulers of Al-Andalus were granted the rank of Emir by the Umayyad Caliph in Damascus. After the Umayyads were overthrown by the Abbasids, Abd-ar-rahman I declared Cordoba an independent emirate. Al-Andalus was rife with internal conflict between the Arab Umayyad rulers and the Visigoth-Roman Christian population.

In the 10th century Abd-ar-rahman III declared the Caliphate of Cordoba, effectively breaking all ties with the Egyptian and Syrian caliphs. The Caliphate was mostly concerned with maintaining its power base in North Africa, but these possessions eventually dwindled to the Ceuta province. Meanwhile, a slow but steady migration of Christian subjects to the northern kingdoms was slowly increasing the power of the northern kingdoms. Even so, Al-Andalus remained vastly superior to all the northern kingdoms combined in population, economy, culture and military might, and internal conflict between the Christian kingdoms contributed to keep them relatively harmless.
Muslim interest in the peninsula returned in force around the year 1000. Under Al-Mansur (also known as Almanzor), who sacked Barcelona (985), and subsequently his son, Christian cities were subjected to numerous raids. After his son's death, the caliphate plunged into a civil war and splintered into the so-called "Taifa Kingdoms". The Taifa kings competed against each other not only in war, but also in the protection of the arts, and culture enjoyed a brief upswing. The Taifa kingdoms lost ground to the Christian realms in the north and, after the loss of Toledo in 1085, the Muslim rulers reluctantly invited the Almoravides, who invaded Al-Andalus from North Africa and established an empire. In the 12th century the Almoravid empire broke up again, only to be taken over by the Almohad invasion, who were defeated in the decisive battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. By the mid-13th century Granada was the only independent Muslim realm in Spain, which would last until 1492.
Kingdom of Spain

As the Reconquista continued, Christian kingdoms and principalities developed. By the 15th century, the most important among these were the Kingdom of Castile (occupying a northern and central portion of the Iberian Peninsula) and the Kingdom of Aragon (occupying northeastern portions of the peninsula). The rulers of these two kingdoms were allied with dynastic families in Portugal, France, and other neighboring kingdoms. The death of Henry IV in 1474 set off a struggle for power between contenders for the throne of Castile, including Juana la Beltraneja, supported by Portugal and France, and Queen Isabella I, supported by the Kingdom of Aragon, and by the Castilian nobility. Following the War of the Castilian Succession, Isabella retained the throne, and ruled jointly with her husband, King Ferdinand II.
Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon were known as the "Catholic Monarchs" (Spanish: los Reyes Católicos), a title bestowed on them by Pope Alexander VI. They married in 1469 in Valladolid, uniting both crowns and effectively leading to the creation of the Kingdom of Spain, at the dawn of the modern era. They oversaw the final stages of the Reconquista of Iberian territory from the Moors with the conquest of Granada, conquered Canary Islands and expelled the Jews and Muslims from Spain under the Alhambra decree. They authorized the expedition of Christopher Columbus, who became the first European to reach the New World (since Leif Ericson) which led to an influx of wealth into Spain, funding the coffers of the new state that would prove to be a dominant power of Europe for the next two centuries.
Isabella ensured long-term political stability in Spain by arranging strategic marriages for each of her five children. Her firstborn, a daughter named Isabella, married Alfonso of Portugal, forging important ties between these two neighboring countries and hopefully ensuring peace and future alliance. Juana, Isabella’s second daughter, married Philip the Handsome, the son of the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I. This ensured alliance with the Holy Roman Empire, a powerful, far-reaching territory which assured Spain’s future political security. Isabella’s first and only son, Juan, married Margaret of Austria, maintaining ties with the Habsburg dynasty, on which Spain relied heavily. Her fourth child, Maria, married Manuel I of Portugal, strengthening the link forged by her older sister’s marriage. Her fifth child, Catherine, married Henry VIII, King of England and was mother to Queen Mary I.
Muslims, however, were not the only people persecuted during this time period. In the interest of creating a state unified under one religion, the Catholic Kings started to expel all of the Jews in their kingdoms. Jews of any age who lived within the kingdoms of 'los Reyes Católicos' were under persecution - being thrust into 'ghettos' and even being exiled. Their wealth was also taken. Units of money, called 'sueldos' and made of gold, were taken from the Jews - those responsible for money.
The Spanish language and universities
In the 13th century, there were many languages spoken in the Christian sections of what is now Spain, among them Castilian, Catalan, Basque, Galician, Aranese and Asturian-Leonese. But throughout the century, what is known today as the Spanish language gained more and more prominence in the Kingdom of Castile as the language of culture and communication. One example of this is the El Cid. In the last years of the reign of Ferdinand III of Castile, Castilian began to be used for certain types of documents, but it was during the reign of Alfonso X that it became the official language. Henceforth all public documents were written in Castilian, likewise all translations were made into Castilian instead of Latin.
Furthermore, in the 13th Century many universities were founded in Castile, some, like those of Salamanca and Palencia were among the earliest universities in Europe. In 1492, under the Catholic Monarchs, the first edition of the Grammar of the Castilian Language by Antonio de Nebrija was published.
Spanish Empire
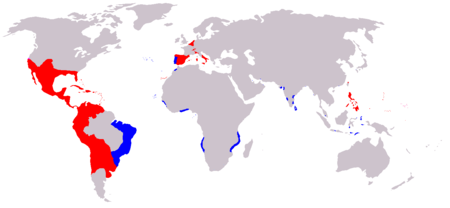
The Spanish Empire was the first modern global empire. It was also one of the largest empires in world history. In the 16th century Spain and Portugal were in the vanguard of European global exploration and colonial expansion and the opening of trade routes across the oceans, with trade flourishing across the Atlantic between Spain and the Americas and across the Pacific between East Asia and Mexico via the Philippines. Conquistadors toppled the Aztec, Inca and Maya civilizations and laid claim to vast stretches of land in North and South America. For a time, the Spanish Empire dominated the oceans with its experienced navy and ruled the European battlefield with its fearsome and well trained infantry, the famous tercios: in the words of the prominent French historian Pierre Vilar, "enacting the most extraordinary epic in human history". Spain enjoyed a cultural golden age in the 16th and 17th centuries.
From the middle of the 16th century silver and gold from the American mines increasingly financed the military capability of Habsburg Spain in its long series of European and North African wars. From the time beginning with the incorporation of the Portuguese empire in 1580 (lost in 1640) until the loss of its American colonies in the 19th century, Spain maintained the largest empire in the world even though it suffered fluctuating military and economic fortunes from the 1640s. Confronted by the new experiences, difficulties and suffering created by empire-building, Spanish thinkers formulated some of the first modern thoughts on natural law, sovereignty, international law, war, and economics; there were even questions about the legitimacy of imperialism — in related schools of thought referred to collectively as the School of Salamanca.
Spain under the Habsburgs (16th–17th centuries)
Spain's powerful world empire of the 16th and 17th centuries reached its height and declined under the Habsburgs. The Spanish Empire reached its maximum extent in Europe under Charles I of Spain, who was also (also known as Charles V) emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Charles V became king in 1516, and the history of Spain became even more firmly enmeshed with the dynastic struggles in Europe. During his reign, the Spanish economy was drastically reoriented by the beginnings of the influx of precious metals from America. The king was not often in Spain, and as he approached the end of his life he made provision for the division of the Habsburg inheritance into two parts: on the one hand Spain, and its possessions in the Mediterranean and overseas, and the Holy Roman Empire itself on the other. The Habsburg possessions in The Netherlands also remained with the Spanish crown.
This was to prove a difficulty for his successor Philip II of Spain, who became king on Charles V's abdication in 1556. Spain largely escaped the religious conflicts that were raging throughout the rest of Europe, and remained firmly Roman Catholic. Philip saw himself as a champion of Catholicism, both against the Turks and the heretics. In the 1560s, plans to consolidate control of the Netherlands led to unrest, which gradually led to the Calvinist leadership of the revolt and the Eighty Years' War. This conflict consumed much Spanish expenditure, and led to an attempt to conquer England – a cautious supporter of the Dutch – in the unsuccessful Spanish Armada, an early battle in the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) and war with France (1590–1598).
Despite these problems, the large inflow of American gold, the justified military reputation of the Spanish infantry and even the navy quickly recovering from its Armada disaster, made Spain the leading European power, a novel situation of which its citizens were only just becoming aware. The Iberian Union with Portugal in 1580 not only unified the peninsula, but added that country's worldwide resources to the Spanish crown. However, economic and administrative problems multiplied in Castile, and the weakness of the native economy became evident in the following century: rising inflation, the expulsion of the Jews and Moors from Spain, and the dependency of Spain on the gold and silver imports combined to cause multiple bankruptcies and economic crashes in Spain.
The coast villages of Spain and Balearic Islands were frequently attacked by Barbary pirates from North Africa, the Formentera was even temporarily left by its population and long stretches of the Spanish and Italian coasts were almost completely abandoned by their inhabitants. In 1514, 1515 and 1521 coasts of the Balearic Islands and the Spanish mainland were raided by infamous Turkish privateer and Ottoman admiral Hayreddin Barbarossa. According to Robert Davis between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by North African pirates and sold as slaves between the 16th and 19th century. These slaves were captured mainly from seaside villages in Spain, Italy and Portugal.
Philip II died in 1598, and was succeeded by his son Philip III, in whose reign a ten year truce with the Dutch was overshadowed in 1618 by Spain's involvement in the European-wide Thirty Years' War. Government policy was dominated by favorites, but it was also the reign in which the geniuses of Cervantes and El Greco flourished.
Philip III was succeeded in 1621 by his son Philip IV of Spain. Much of the policy was conducted by the minister Gaspar de Guzmán, Conde de Olivares. In 1640, with the war in central Europe having no clear winner except the French, both Portugal and Catalonia rebelled. Portugal was lost to the crown for good, Catalonia was suppressed. In the reign of Philip's son and successor Charles II, Spain was gradually being reduced to a second-rank power.
The Habsburg dynasty became extinct in Spain and the War of the Spanish Succession ensued in which the other European powers tried to assume control of the Spanish monarchy. King Louis XIV of France eventually "won" the War of Spanish Succession, and control of Spain passed to the Bourbon dynasty but the peace deals that followed included the relinquishing of the right to unite the French and Spanish thrones and the partitioning of Spain's European empire.
The Golden Age (Siglo de Oro)
The Spanish Golden Age (in Spanish, Siglo de Oro) was a period of flourishing arts and letters in the Spanish Empire (now Spain and the Spanish-speaking countries of Latin America), coinciding with the political decline and fall of the Habsburgs (Philip III, Philip IV and Charles II). The last great writer of the age, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, died in New Spain in 1695.
The Habsburgs, both in Spain and Austria, were great patrons of art in their countries. El Escorial, the great royal monastery built by King Philip II of Spain, invited the attention of some of Europe's greatest architects and painters. Diego Velázquez, regarded as one of the most influential painters of European history and a greatly respected artist in his own time, cultivated a relationship with King Philip IV and his chief minister, the Count-Duke of Olivares, leaving us several portraits that demonstrate his style and skill. El Greco, another respected Spanish artist from the period, infused Spanish art with the styles of the Italian renaissance and helped create a uniquely Spanish style of painting. Some of Spain's greatest music is regarded as having been written in the period. Such composers as Tomás Luis de Victoria, Luis de Milán and Alonso Lobo helped to shape Renaissance music and the styles of counterpoint and polychoral music, and their influence lasted far into the Baroque period.
Spanish literature blossomed as well, most famously demonstrated in the work of Miguel de Cervantes, the author of Don Quixote de la Mancha. Spain's most prolific playwright, Lope de Vega, wrote possibly as many as one thousand plays over his lifetime, over four hundred of which survive to the present day.
The Enlightenment: Spain under the Bourbons (18th century)
Philip V, the first Bourbon king, of French origin, signed the Decreto de Nueva Planta in 1715, a new law that revoked most of the historical rights and privileges of the different kingdoms that conformed the Spanish Crown, unifying them under the laws of Castile, where the Cortes had been more receptive to the royal wish. Spain became culturally and politically a follower of absolutist France. The rule of the Spanish Bourbons continued under Ferdinand VI and Charles III.
Under the rule of Charles III and his ministers, Leopoldo de Gregorio, Marquis of Esquilache and José Moñino, Count of Floridablanca, Spain embarked on a program of enlightened despotism that brought Spain a new prosperity in the middle of the eighteenth century. After losing alongside France against the United Kingdom in the Seven Years' War, Spain recouped most of her territorial losses in the American Revolutionary War. The reforming spirit of Charles III was extinguished in the reign of his son, Charles IV, seen by some as mentally handicapped. Dominated by his wife's lover, Manuel de Godoy, Charles IV embarked on policies that overturned much of Charles III's reforms. After briefly opposing Revolutionary France early in the French Revolutionary Wars, Spain soon allied with its northern neighbor, only to be blockaded by the British. The loss of commercial and political ties to its colonies and, more importantly, the occupation of Spain by Napoleon's forces, would lead to the independence of most of the Spanish Empire in the New World. Charles IV's vacillation as a French ally led Napoleon I, Emperor of the French, to invade Spain in 1808, beginning the Peninsular War.
During most of the eighteenth century Spain had made substantial progress since the dark days of the middle and latter 17th century. But it continued to seriously lag in the enlightenment and mercantile developments transforming other parts of Europe, most notably in the United Kingdom, France, the Low Countries and, in some respects, parts of the Holy Roman Empire. The chaos unleashed by the Napoleonic intervention would cause this gap to widen greatly.
Napoleonic Wars: War of Spanish Independence (1808–1814)
Spain initially sided against France in the Napoleonic Wars, but the defeat of her army early in the war led to Charles IV's pragmatic decision to align with the revolutionary French. A major Franco-Spanish fleet was annihilated, at the decisive Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, prompting the vacillating king of Spain to reconsider his alliance with France. Spain broke off from the Continental System temporarily, and Napoleon — aggravated with the Bourbon kings of Spain — invaded and deposed Charles. The Spanish people vigorously resisted the move and juntas were formed across Spain that pronounced themselves in favor of Charles's son Ferdinand.
Spain was put under a British blockade, and her colonies — for the first time separated from their colonial rulers — began to trade independently with Britain. The defeat of the British invasions of the River Plate in South America emboldened an independent attitude in Spain's American colonies. Initially, the juntas declared their support for Ferdinand, expecting greater autonomy from Madrid under the liberal constitution that the juntas had drafted. The Cortes took refuge at Cádiz. In 1812 the Cádiz Cortes created the first modern Spanish constitution, the Constitution of 1812 (informally named La Pepa).
The British, led by the Duke of Wellington, fought Napoleon's forces in the Peninsular War, with Joseph Bonaparte ruling as king at Madrid. The brutal war was one of the first guerrilla wars in modern Western history; French supply lines stretching across Spain were mauled repeatedly by Spanish guerrillas. The war in Iberia fluctuated repeatedly, with Wellington spending several years behind his fortresses in Portugal while launching occasional campaigns into Spain. The French were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vitoria in 1813, and the following year, Ferdinand was restored as King of Spain.
Spain in the nineteenth century (1814–1873)

Although the juntas that had forced the French to leave Spain had sworn by the liberal Constitution of 1812, Ferdinand VII openly believed that it was too liberal for the country. On his return to Spain, he refused to swear by it himself, and he continued to rule in the authoritarian fashion of his forebears.
Although Spain accepted the rejection of the Constitution, the policy was not warmly accepted in Spain's empire in the New World. Revolution broke out. Spain — nearly bankrupt from the war with France and the reconstruction of the country — was unable to pay her soldiers, and in 1820, an expedition intended for the colonies revolted in Cadiz. When armies throughout Spain pronounced themselves in sympathy with the revolters, led by Rafael del Riego, Ferdinand relented and was forced to accept the liberal Constitution of 1812. Ferdinand himself was placed under effective house arrest for the duration of the liberal experiment.
The three years of liberal rule that followed coincided with a civil war in Spain that would typify Spanish politics for the next century. The liberal government, which reminded European statesmen entirely too much of the governments of the French Revolution, was looked on with hostility by the Congress of Verona in 1822, and France was authorized to intervene. France crushed the liberal government with massive force, and Ferdinand was restored as absolute monarch. The American colonies, however, were completely lost; in 1824, the last Spanish army on the American mainland was defeated at the Battle of Ayacucho in southern Peru.
A period of uneasy peace followed in Spain for the next decade. Having borne only a female heir presumptive, it appeared that Ferdinand would be succeeded by his brother, Infante Carlos of Spain. While Ferdinand aligned with the conservatives, fearing another national insurrection, he did not view the reactionary policies of his brother as a viable option. Ferdinand — resisting the wishes of his brother — decreed the Pragmatic Sanction of 1830, enabling his daughter Isabella to become Queen. Carlos, who made known his intent to resist the sanction, fled to Portugal.
Ferdinand's death in 1833 and the accession of Isabella (only three years old at the time) as Queen of Spain sparked the First Carlist War. Carlos invaded Spain and attracted support from reactionaries and conservatives in Spain; Isabella's mother, Maria Cristina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, was named regent until her daughter came of age.
The insurrection seemed to have been crushed by the end of the year; Maria Cristina's armies, called "Cristino" forces, had driven the Carlist armies from most of the Basque country. Carlos then named the Basque general Tomás de Zumalacárregui his commander-in-chief. Zumalacárregui resuscitated the Carlist cause, and by 1835 had driven the Cristino armies to the Ebro River and transformed the Carlist army from a demoralized band into a professional army of 30,000 of quality superior to the government forces.
Zumalacárregui's death in 1835 changed the Carlists' fortunes. The Cristinos found a capable general in Baldomero Espartero. His victory at the Battle of Luchana (1836) turned the tide of the war, and in 1839, the Convention of Vergara put an end to the first Carlist insurrection.
Espartero, operating on his popularity as a war hero and his sobriquet "Pacifier of Spain", demanded liberal reforms from Maria Cristina. The Queen Regent, who resisted any such idea, preferred to resign and let Espartero become regent instead. Espartero's liberal reforms were opposed, then, by moderates; the former general's heavy-handedness caused a series of sporadic uprisings throughout the country from various quarters, all of which were bloodily suppressed. He was overthrown as regent in 1843 by Ramón María Narváez, a moderate, who was in turn perceived as too reactionary. Another Carlist uprising, the Matiners' War, was launched in 1846 in Catalonia, but it was poorly organized and suppressed by 1849.
Isabella took a more active role in government after she came of age, but she was immensely unpopular throughout her reign. She was viewed as beholden to whoever was closest to her at court, and that she cared little for the people of Spain. In 1856, she attempted to form a pan-national coalition, the Union Liberal, under the leadership of Leopoldo O'Donnell who had already marched on Madrid that year and deposed another Espartero ministry. Isabella's plan failed and cost Isabella more prestige and favor with the people. Isabella launched a successful war against Morocco, waged by generals O'Donnell and Juan Prim, in 1860 that stabilized her popularity in Spain. However, a campaign to reconquer Peru and Chile during the Chincha Islands War proved disastrous and Spain suffered defeat before the determined South American powers.
In 1866, a revolt led by Juan Prim was suppressed, but it was becoming increasingly clear that the people of Spain were upset with Isabella's approach to governance. In 1868, the Glorious Revolution broke out when the progresista generals Francisco Serrano and Juan Prim revolted against her, and defeated her moderado generals at the Battle of Alcolea. Isabella was driven into exile in Paris.
Revolution and anarchy broke out in Spain in the two years that followed; it was only in 1870 that the Cortes declared that Spain would have a king again. As it turned out, this decision, and therefore the Revolution, played an important role in European and thus world history, for a German prince's candidacy to the Spanish throne and French opposition to him served as the immediate motive for the (arguably inevitable) Franco-Prussian War. Amadeus of Savoy was selected, and he was duly crowned King of Spain early the following year.
Amadeus — a liberal who swore by the liberal constitution the Cortes promulgated — was faced immediately with the incredible task of bringing the disparate political ideologies of Spain to one table. He was plagued by internecine strife, not merely between Spaniards but within Spanish parties.
First Spanish Republic (1873–1874)
Following the Hidalgo affair, Amadeus famously declared the people of Spain to be ungovernable, and fled the country. In his absence, a government of radicals and Republicans was formed that declared Spain a republic.
The republic was immediately under siege from all quarters — the Carlists were the most immediate threat, launching a violent insurrection after their poor showing in the 1872 elections. There were calls for socialist revolution from the International Workingmen's Association, revolts and unrest in the autonomous regions of Navarre and Catalonia, and pressure from the Roman Catholic Church against the fledgling republic.
The Restoration (1874–1931)
Although the former queen, Isabella II was still alive, she recognized that she was too divisive as a leader, and abdicated in 1870 in favor of her son, Alfonso, who was duly crowned Alfonso XII of Spain. After the tumult of the First Spanish Republic, Spaniards were willing to accept a return to stability under Bourbon rule. The Republican armies in Spain — which were resisting a Carlist insurrection — pronounced their allegiance to Alfonso in the winter of 1874–1875, led by Brigadier General Martinez Campos. The Republic was dissolved and Antonio Canovas del Castillo, a trusted advisor to the king, was named Prime Minister on New Year's Eve, 1874. The Carlist insurrection was put down vigorously by the new king, who took an active role in the war and rapidly gained the support of most of his countrymen.
A system of turnos was established in Spain in which the liberals, led by Práxedes Mateo Sagasta and the conservatives, led by Antonio Canovas del Castillo, alternated in control of the government. A modicum of stability and economic progress was restored to Spain during Alfonso XII's rule. His death in 1885, followed by the assassination of Canovas del Castillo in 1897, destabilized the government.
Cuba rebelled against Spain in the Ten Years' War beginning in 1868, resulting in the abolition of slavery in Spain's colonies in the New World. American interests in the island, coupled with concerns for the people of Cuba, aggravated relations between the two countries. The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish-American War in 1898, in which Spain fared disastrously. Cuba gained its independence and Spain lost its remaining New World colony, Puerto Rico, which together with Guam and the Philippines it ceded to the United States for 20 million dollars. In 1899, Spain sold its remaining Pacific islands—the Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands and Palau—to Germany and Spanish colonial possessions were reduced to Spanish Morocco, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Guinea, all in Africa.
The "disaster" of 1898 created the "generation" of 1898, a generation of statesmen and intellectuals who demanded change from the new government. Anarchist and fascist movements were on the rise in Spain in the early twentieth century. A revolt in 1909 in Catalonia was bloodily suppressed.
Spain's neutrality in the First World War allowed it to become a supplier of material for both sides to its great advantage, prompting an economic boom in Spain. The outbreak of Spanish influenza in Spain and elsewhere, along with a major economic slowdown in the postwar period, hit Spain particularly hard, and the country went into debt. A major worker's strike was suppressed in 1919.
Mistreatment of the Moorish population in Spanish Morocco led to an uprising and the loss of this North African possession except for the enclaves of Ceuta and Melilla in 1921. (See Abd el-Krim, Annual). In order to avoid accountability, the king Alfonso XIII decided to support the dictatorship of General Miguel Primo de Rivera, ending the period of constitutional monarchy in Spain.
In joint action with France, the Moroccan territory was recovered (1925–1927), but in 1930 bankruptcy and massive unpopularity left the king no option but to force Primo de Rivera to resign. Disgusted with the king's involvement in his dictatorship, the urban population voted for republican parties in the municipal elections of April 1931. The king fled the country without abdicating and a republic was established.
Second Spanish Republic (1931–1939)
Under the Second Spanish Republic, women were allowed to vote in general elections for the first time. The Republic devolved substantial autonomy to the Basque Country and to Catalonia.
The first governments of the Republic, were center-left, headed by Niceto Alcalá-Zamora, and Manuel Azaña. Economic turmoil, substantial debt inherited from the Primo de Rivera regime, and fractious, rapidly changing governing coalitions led to serious political unrest. In 1933, the right-wing CEDA won power; an armed rising of workers of October 1934, which reached its greatest intensity in Asturias and Catalonia, was forcefully put down by the CEDA government. This in turn energized political movements across the spectrum in Spain, including a revived anarchist movement and new reactionary and fascist groups, including the Falange and a revived Carlist movement.
Spanish Civil War (1936–1939)
In the 1930s, Spanish politics were polarized at the left and right of the political spectrum. The left wing favoured class struggle, land reform, autonomy to the regions and reduction in church and monarchist power. The right-wing groups, the largest of which was CEDA, a right wing Roman Catholic coalition, held opposing views on most issues. In 1936, the left united in the Popular Front and was elected to power. However, this coalition, dominated by the centre-left, was undermined both by the revolutionary groups such as the anarchist CNT and FAI and by anti-democratic far-right groups such as the Falange and the Carlists. The political violence of previous years began to start again. There were gunfights over strikes, landless labourers began to seize land, church officials were killed and churches burnt. On the other side, right wing militias (such as the Falange) and gunmen hired by employers assassinated left wing activists. The Republican democracy never generated the consensus or mutual trust between the various political groups that it needed to function peacefully. As a result, the country slid into civil war. The right wing of the country and high ranking figures in the army began to plan a coup and when Falangist politician José Calvo-Sotelo was shot by Republican police, they used it as a signal to act.
On July 17, 1936, General Francisco Franco led the colonial army from Morocco to attack the mainland while another force from the north under General Sanjurjo moved south from Navarre. Military units were also mobilised elsewhere to take over government institutions. Franco's move was intended to seize power immediately, but successful resistance by Republicans in places such as Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, the Basque country and elsewhere meant that Spain faced a prolonged civil war. Before long, much of the south and west was under the control of the Nationalists, whose regular Army of Africa was the most professional force available to either side. Both sides received foreign military aid, the Nationalists, from Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy and Portugal, the Republic from the USSR and communist organised volunteers in the International Brigades.
The Siege of the Alcázar at Toledo early in the war was a turning point, the Nationalists winning after a long siege. The Republicans managed to hold out in Madrid, despite a Nationalist assault in November 1936 and frustrated subsequent offensives against the capital at Jarama and Guadalajara in 1937. Soon, though, the Nationalists began to erode their territory, starving Madrid and making inroads into the east. The north, including the Basque country fell in late 1937 and the Aragon front collapsed shortly afterwards. The bombing of Guernica was probably the most infamous event of the war and inspired Picasso's picture. It was used as a testing ground for the German Luftwaffe's Condor Legion. The Battle of the Ebro in July-November 1938 was the final desperate attempt by the Republicans to turn the tide. When this failed and Barcelona fell to the Nationalists in early 1939, it was clear the war was over. The remaining Republican fronts collapsed and Madrid fell in March 1939.
The war, which cost between 300,000 to 1,000,000 lives, ended with the destruction of the Republic and the accession of Francisco Franco as dictator of Spain. Franco amalgamated all the right wing parties into a reconstituted Falange and banned the left-wing and Republican parties and trade unions.
The conduct of the war was brutal on both sides, with massacres of civilians and prisoners being widespread. After the war, many thousands of Republicans were imprisoned and up to 150,000 were executed between 1939 and 1943. Many other Republicans remained in exile for the entire Franco period.
The dictatorship of Francisco Franco (1936–1975)
Spain remained officially neutral in World Wars I and II, but suffered through a devastating Civil War (1936–1939). During Franco's rule, Spain remained largely economically and culturally isolated from the outside world, but began to catch up economically with its European neighbors.
Under Franco, Spain actively sought the return of Gibraltar by the UK, and gained some support for its cause at the United Nations. During the 1960s, Spain began imposing restrictions on Gibraltar, culminating in the closure of the border in 1969. It was not fully reopened until 1985.
Spanish rule in Morocco ended in 1956. Though militarily victorious in the 1957–1958 Moroccan invasion of Spanish West Africa, Spain gradually relinquished its remaining African colonies. Spanish Guinea was granted independence as Equatorial Guinea in 1968, while the Moroccan enclave of Ifni had been ceded to Morocco in 1969.
The latter years of Franco's rule saw some economic and political liberalization, the Spanish Miracle, including the birth of a tourism industry. Francisco Franco ruled until his death on November 20 1975, when control was given to King Juan Carlos.
In the last few months before Franco's death, the Spanish state went into a paralysis. This was capitalized upon by King Hassan II of Morocco, who ordered the 'Green March' into Western Sahara, Spain's last colonial possession.
The transition to democracy (1975–1978)
The Spanish transition to democracy or new Bourbon restoration was the era when Spain moved from the dictatorship of Francisco Franco to a liberal democratic state. The transition is usually said to have begun with Franco’s death on November 20, 1975, while its completion is marked by the electoral victory of the socialist PSOE on October 28, 1982.
Along with political change came radical change in Spanish society. Spanish society had been extremely conservative under Franco, but the transition to democracy also began a liberalization of values and societal mores.
Spain since 1978
Spain 1978–1982: The Unión del Centro Democrático governments. 1981 The 23-F coup d'état attempt. On February 23 Antonio Tejero, with members of the Guardia Civil entered the Congress of Deputies, and stopped the session, where Leopoldo Calvo Sotelo was about to be named president of the government. Officially, the coup d'état failed thanks to the intervention of King Juan Carlos. Spain joined the NATO before Calvo-Sotelo left office.
Spain 1982–1996: Felipe González's social democratic governments. 1986 Spain joined the European Economic Community (EEC, now European Union). 1992 Barcelona Olympics, Expo '92 in Seville.
Spain 1996–2004: The Partido Popular governments of José María Aznar. On January 1, 1999 Spain exchanged the Peseta for the new Euro currency. On March 11 2004 a number of terrorist bombs exploded on busy commuter trains in Madrid during the morning rush-hour days before the general election, killing 191 persons and injuring thousands. Although José María Aznar and his ministers were quick to accuse ETA of the atrocity, soon afterwards it became apparent that the bombing was the work of an extremist Islamic group linked to Al-Qaeda. Many people believe that the fact that qualified commentators abroad were beginning to doubt the official Spanish version the very same day of the attacks while the government insisted on ETA's implication directly influenced the results of the election. Opinion polls at the time show that the difference between the two main contenders had been too close to make any accurate prediction as to the outcome of the elections.
Spain 2004—: José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero's socialdemocratic government.
On July 3, 2005, the country became the first country in the world to give full marriage and adoption rights to homosexual couples (Belgium allows same-sex marriage since 2003 and co-parenting since April 2006, and the Netherlands allows same-sex marriage since 2001 and has a law being prepared now to provide full adoption rights in equal conditions to opposite-sex marriages).
At present, Spain is a constitutional monarchy, and is comprised of 17 autonomous communities (Andalucía, Aragón, Asturias, Islas Baleares, Islas Canarias, Cantabria, Castile and León, Castile-La Mancha, Cataluña, Extremadura, Galicia, La Rioja, Community of Madrid, Region of Murcia, País Vasco, Comunidad Valenciana, Navarra) and 2 autonomous cities (Ceuta and Melilla).
Notes
- ^ Although it is debatable whether there is continuity between the Visigothic Kingdom and the Kingdom of Castile and Aragon after the 15th century, a discussion of modern Spain would be incomplete without a mention of the Visigothic Kingdom. Another early Christian kingdom is that of the Suebi or Suevi in northwestern Spain.
External links
- Henry Kamen. Spain. A Society of Conflict (3rd ed.) London and New York: Pearson Longman 2005. ISBN
- Spain Chronology World History Database
- Castilian Spanish and the History of Spanish language
- History of Spain: Primary Documents
- Stanley G. Payne The Seventeenth-Century Decline
- Henry Kamen, "The Decline of Spain: A Historical Myth?", Past and Present,) (Explains the complexities of this subject)
- Carmen Pereira-Muro. Culturas de España. Boston and New York: Houghton Mifflin Company 2003. ISBN
