Baltimore-Washington International Airport
| Baltimore-Washington International Airport |
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Characteristics | |
| ICAO code | KBWI |
| IATA code | BWI |
| Coordinates | |
| Height above MSL | 45 m (148 ft ) |
| Transport links | |
| Distance from the city center | 8 miles south of Baltimore , 27 miles northeast of Washington, DC |
| Street | I-97 / I-195 / MD 162 / MD 170 |
| train |
Amtrak MARC Train |
| Local transport |
Bus rail : Baltimore Light Rail |
| Basic data | |
| opening | 1950 |
| operator | Maryland Aviation Administration (MAA) |
| surface | 1455 ha |
| Terminals | 1 with 5 concourses |
| Passengers | 27,145,831 (2018) |
| Air freight | 199,546 t (2018) |
| Flight movements |
266,569 (2018) |
| Employees | 24,211 (2017) |
| Runways | |
| 10/28 | 3201 m × 61 m asphalt |
| 15R / 33L | 2896 m × 46 m asphalt |
| 15L / 33R | 1524 m × 30 m asphalt |
The Baltimore-Washington International Airport is the international airport of the US city of Baltimore . It is located in Anne Arundel County , Maryland near the town of Glen Burnie . It opened in 1950 as the Friendship International Airport .
The Baltimore-Washington International Airport is mainly used by low-cost airlines and serves them as an alternative to the two Washington airports Dulles International and Reagan National . It is currently the largest airport in the Baltimore – Washington Metropolitan Area in terms of passenger volume .
Location and transport links
The airport is eight miles south of Baltimore and 27 miles northeast of Washington, DC The main terminal is at the southern end of Interstate 195 . A few miles north of the airport, I-195 crosses Interstate 95 , which connects Baltimore with Washington, DC. The General Aviation Terminal is located at the northeast end of the airport on Maryland State Route 162 .
The airport is integrated into local public transport by bus and train . A total of four different bus companies and three different railway companies serve the airport. The Baltimore Light Rail line ends in the basement of the passenger terminal. The station on the Northeast Corridor is two kilometers northwest of the passenger terminal. This is controlled by Amtrak and the Maryland Rail Commuter Service (MARC) . Shuttles run between the terminal and the train station.
history
prehistory
The history of aviation in the US state of Maryland began in 1906 with the commissioning of College Park Airport , which is now the oldest airport still in operation in the United States . It is located 44 kilometers southwest of downtown Baltimore . In 1921, the first commercial airport in Maryland went into operation, Logan Field , in Dundalk , a suburb of Baltimore. In 1929, Baltimore was connected to the airmail network, and construction of the Baltimore Municipal Airport began in the same year . From 1930, Eastern Air Lines operated scheduled passenger flights in Baltimore. During the Second World War , Logan Field was converted into a purely military airfield . After World War II, the airport was no longer reopened as a civil airport, instead it was completely replaced by the Baltimore Municipal Airport.
Construction of the major airport
In 1946, the Baltimore Aviation Commission began planning a new airport. For this purpose, an area was purchased near the Friendship Church, from which the airport's initial name, Friendship International Airport , was derived. Construction began the following year. The then US President Harry S. Truman opened the airport on June 24, 1950, and the first scheduled flights did not take place until a month later.
expansion
In 1972, the city of Baltimore sold the airport for 36 million US dollars to the Ministry of Transport of Maryland (Maryland Department of Transportation). Since then, the airport has been operated by the Maryland Aviation Administration . With the purchase of the airport, MAA grew from three to more than 200 employees. The following year, the Maryland Secretary of Transportation announced plans to expand and modernize the airport. First the name was changed to Baltimore / Washington International Airport . In 1974 the first phase of the expansion was completed. This cost 30 million USD and included, among other things, the renovation of the runway system, an improvement of the instrument landing system and the construction of three freight terminals. The $ 70 million renovation of the passenger terminal was completed five years later. This measure doubled the area of the terminal and increased the number of passenger boarding bridges from 20 to 27.
In 1980 the airport got its own train station on the Northeast Corridor . This made the BWI the first airport in the United States to be directly connected to a long-distance railway line. In 1983 the FAA moved into a new control tower , which was accompanied by a further improvement in the safety equipment. Piedmont Airlines also selected the airport as the location for a hub . A further 12 passenger boarding bridges were built for this purpose. For reasons of space, a new terminal for general aviation was built east of the passenger terminal in the same year, and the runway 15L / 33R was also built between the terminals . In 1984 the international area of the passenger terminal was expanded in order to cope with the increased number of passengers on international connections. At the same time improvements were made to the taxiways .
In 1986 a comprehensive development plan was drawn up which recommended that the airport be expanded significantly again. In that year, the lighting of the runways and taxiways was also improved. From the following year, runway 10/28 was used again. A commuter terminal was opened in 1988 and the gate of Piedmont Airlines, which has now been taken over by US Airways , was expanded. In addition, the use of the 15L / 33R runway was resumed. A year later, the runway was extended to its present length. In August 1989, for the first time, more than a million passengers were handled within a month. In 1990 the airport was given a direct connection to Interstate 95 with Interstate 195 .
In 1991 a new parking garage was built opposite the main terminal for $ 29 million. Two years later, Southwest Airlines established its first hub on the US east coast in Baltimore . In 1994, Pier C, used for domestic flights, was expanded to include new passenger boarding bridges for US $ 27.6 million. In order to expand the capacity for international flight connections, the extension of runway 10/28 was completed in the same year. Construction also began on a US $ 140 million international terminal. The first de-icing system was completed in 1995 , which was initially able to de-ice five aircraft at the same time. Furthermore, a viewing terrace was completed and a viewing point at the southern end of runway 15R / 33L was expanded.
In 1996 new parking garages were built, in the same year a second de-icing system, costing around USD 2.5 million, was put into operation, but this can only be used by smaller aircraft. In 1997 the international terminal was completed. This was named after William Donald Schaefer , a former governor of Maryland. The terminal connected the airport to the Baltimore Light Rail network and an additional fire station was set up. The next year, Southwest Airlines set up a pilot base. In 1999, a third de-icing system, costing around US $ 7.4 million, was completed. Another freight terminal was built and the renovation of Piers A and B began. The renovation cost around USD 85.2 million.
Development after 2000
In 2001 an automatic control system was installed in the parking garages. In addition, in July 2001 the number of 2 million passengers within a month was exceeded for the first time. The groundbreaking ceremony for the largest expansion of the airport to date also took place this year. It spent $ 1.8 billion on the five-year work. The strong growth in the 90s had made it one of the largest employers in Maryland by 2001. A total of around 85,000 people were employed at the airport in 2001, and sales of all companies were USD 6.5 billion. In the following year, Pier A was demolished and replaced by a $ 3 million new building.
In 2003, all car rentals were moved to a central building, which cost around $ 134.8 million. Furthermore, one worked from 2003 with the US Department of Defense . The airport offered people who were used for long periods in the Iraq war a 15-day vacation in Europe or the United States with free flights. Two years later, the number of passenger boarding bridges was again increased significantly through construction work at the main terminal. Southwest Airlines has been assigned most of the new boarding bridges. That same year, the airport was named after Thurgood Marshall , the first African-American judge on the United States Supreme Court . Since October 1, 2005, the full name of the airport is Baltimore / Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport .
At the beginning of the Lebanon War in 2006, the airport was used as the primary destination for evacuation flights. The American civilians were first brought to Cyprus from Lebanon , from where flights to the United States started. In 2010 a program to improve the airport's energy efficiency was launched. A year later, charging stations were also set up in several parking garages . In 2012, photovoltaic systems were installed on the roof of a parking garage.
Airlines and Destinations
In 2017, the passenger volume at Baltimore-Washington International Airport was largely due to the five airlines Southwest Airlines , Spirit Airlines , Delta Air Lines , American Airlines and United Airlines . Southwest Airlines has operated a hub in Baltimore since 1993 and is by far the largest airline at the airport with a share of around 67 percent of the passenger volume.
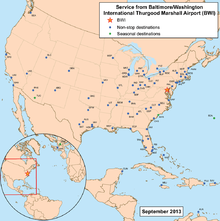
Baltimore Airport mainly serves destinations within the United States. The average number of these in 2017 was 79. The airport offers a total of 13 international destinations, but three of these destinations are only offered seasonally. One of two destinations in Europe is London , which is served by British Airways . Frankfurt am Main was added in the summer of 2012, although it is only served by Condor during the summer flight schedule.
Airline market shares
| airline | 2010 | 2018 | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| AirTran Airways | 16.22% | 0.00% | Integrated into Southwest in 2014 |
| Alaska Airlines | 1.52% | ||
| American Airlines | 4.19% | 6.31% | |
| Continental Airlines | 2.73% | 0.00% | 2011 merger with United Airlines |
| Delta Air Lines | 9.44% | 7.77% | |
| Jetblue Airways | 1.79% | ||
| Southwest Airlines | 53.53% | 66.57% | |
| Spirit Airlines | 9.35% | ||
| United Airlines | 5.08% | 3.99% | |
| US Airways | 6.02% | 0.00% | 2013 merger with American Airlines, brand abandoned in 2015 |
| Others | 2.78% | 2.70% |
Traffic figures
In 2016, Baltimore-Washington International Airport was ranked 22nd among the largest US airports in terms of passenger volume and 79th worldwide. In terms of air freight volume, including airmail , the airport was 32nd nationally and 122nd worldwide.If you look at the number of flight movements, it was 34th in a national comparison and 74th in the world.



| Baltimore-Washington International Airport traffic figures 1951–2018 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | Passenger volume | Air freight ( tons ) | Airmail (tons) | Aircraft movements (with military) |
|||
| National | International | Others | total | ||||
| 2018 | - | - | - | 27,145,831 | 194.279 | 5,267 | 266,569 |
| 2017 | 25.207.725 | 1,163,442 | 66,934 | 26.438.101 | 162,586 | 5,287 | 261,707 |
| 2016 | 23,889,185 | 1,233,466 | 72,375 | 25.195.026 | 113,698 | 4,376 | 248,585 |
| 2015 | 22,683,388 | 1,140,144 | 78,768 | 23.902.300 | 111.115 | 5,579 | 246.464 |
| 2014 | 21,448,107 | 864,569 | 52,692 | 22,365,368 | 100.506 | 4,665 | 245.121 |
| 2013 | 21,654,879 | 836.467 | 48,688 | 22,540,034 | 104.192 | 4,804 | 259.793 |
| 2012 | 21,975,916 | 703.971 | 54,187 | 22,734,074 | 106,764 | 4,986 | 268.186 |
| 2011 | 21,808,464 | 583,321 | 58,297 | 22,450,082 | 102,668 | 5,091 | 276.133 |
| 2010 | 21,411,843 | 524,618 | 65,585 | 22,001,946 | 96,969 | 5,410 | 276.457 |
| 2009 | 20,503,786 | 449,829 | 77.121 | 21,030,736 | 94,229 | 6.152 | 268.005 |
| 2008 | 19,995,068 | 493.813 | 504.838 | 20,993,719 | 94,529 | 7,654 | 277,662 |
| 2007 | 20,419,305 | 625.039 | 517.192 | 21,044,384 | 108,951 | 6,470 | 296,872 |
| 2006 | - | - | - | 20,698,967 | 113,545 | 10,430 | 305.630 |
| 2005 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2004 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2003 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2002 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1999 | - | - | - | 17,437,663 | 184,218 | - | 303.283 |
| 1998 | - | - | - | 15,003,819 | 190,823 | - | 291.093 |
| 1997 | - | - | - | 14.094.305 | 160,616 | - | 266.060 |
| 1996 | - | - | - | 13,431,922 | 125,486 | - | 268,655 |
| 1995 | - | - | - | 13.163.017 | 105,426 | - | 289,664 |
| 1994 | - | - | - | 12,817,192 | 105.264 | - | 295,413 |
| 1993 | - | - | - | 9,438,729 | 103.043 | - | 212,900 |
| 1992 | - | - | - | 8,845,598 | 108,327 | - | 264.165 |
| 1991 | - | - | - | 9,885,615 | 111.276 | - | 275.903 |
| 1990 | - | - | - | 10.210.568 | 115,821 | - | 302.248 |
| 1989 | - | - | - | 10,356,548 | 110.025 | - | 303,800 |
| 1988 | - | - | - | 9,857,790 | 108,295 | - | 307.879 |
| 1987 | - | - | - | 9,146,286 | 114,634 | - | 293,702 |
| 1986 | - | - | - | 8,670,506 | 108,561 | - | 285.012 |
| 1985 | - | - | - | 7,830,404 | 90.064 | - | 283.024 |
| 1984 | - | - | - | 6,675,156 | 89,851 | - | 281.181 |
| 1983 | - | - | - | 5,197,075 | 83.117 | - | 249,726 |
| 1982 | - | - | - | 4,552,683 | 59,156 | - | 219.119 |
| 1981 | - | - | - | 3,787,951 | 64,220 | - | 207.272 |
| 1980 | - | - | - | 3,764,123 | 49,659 | - | 219.916 |
| 1979 | - | - | - | 3,771,219 | 61.151 | - | 220.227 |
| 1978 | - | - | - | 3,557,139 | 67,421 | - | 222.108 |
| 1977 | - | - | - | 3,160,074 | 59,369 | - | 240,658 |
| 1976 | - | - | - | 2,975,778 | 43,900 | - | 232.846 |
| 1975 | - | - | - | 2,773,418 | 37,458 | - | 219.190 |
| 1974 | - | - | - | 2,797,839 | 37.173 | - | 219,897 |
| 1973 | - | - | - | 2,895,191 | 44,394 | - | 229,399 |
| 1972 | - | - | - | 2,894,392 | 46,646 | - | 218,404 |
| 1971 | - | - | - | 2,807,293 | 39,375 | - | 223,656 |
| 1970 | - | - | - | 3,019,581 | 42,062 | - | 230.343 |
| 1969 | - | - | - | 3,070,555 | 37,968 | - | 241.732 |
| 1968 | - | - | - | 2,910,158 | 36,301 | - | 226,576 |
| 1967 | - | - | - | 2,469,731 | 28,375 | - | 208.145 |
| 1966 | - | - | - | 2,001,765 | 25,437 | - | 187,640 |
| 1965 | - | - | - | 1,793,314 | 17,649 | - | 173.840 |
| 1964 | - | - | - | 1,459,302 | 11,554 | - | 160.266 |
| 1963 | - | - | - | 1,146,677 | 9,441 | - | 160.401 |
| 1962 | - | - | - | 1,436,361 | 13,172 | - | 159,612 |
| 1961 | - | - | - | 1,136,001 | 8,387 | - | 167.351 |
| 1960 | - | - | - | 746.690 | 5,852 | - | 188,447 |
| 1959 | - | - | - | 540,683 | 4,366 | - | 175.123 |
| 1958 | - | - | - | 388.282 | 3,541 | - | 160,560 |
| 1957 | - | - | - | 400.097 | 5,525 | - | 189,924 |
| 1956 | - | - | - | 343,855 | 4.025 | - | 164.165 |
| 1955 | - | - | - | 327,601 | 3,095 | - | 132,280 |
| 1954 | - | - | - | 305,542 | 2.127 | - | 115,446 |
| 1953 | - | - | - | 280,849 | 2,039 | - | 121.104 |
| 1952 | - | - | - | 234,597 | 1,864 | - | 98,304 |
| 1951 | - | - | - | 211,236 | 1,484 | - | 69,954 |
- ↑ The other passenger volume includes passengers on general aviation flights until 2017 and transit passengers until 2008 . From 2009, transit passengers were no longer taken into account.
- ^ Up to 1999, the total number of passengers only includes passengers on commercial flights.
comparison
| Airport | Distance to BWI (in km ) |
year | Passenger volume | Freight ( tons ) (by airmail) |
Flight movements | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BWI | - | 2018 | 27,145,831 |
+ 23.4%
|
199,546 |
+ 94.9%
|
266,569 |
-0.5%
|
||
| 2010 | 22,001,946 | 102,378 | 268.005 | |||||||
| DCA | 49 | 2018 | 23,464,618 |
+ 29.5%
|
2,336 |
-64.5%
|
293,827 |
+ 8.4%
|
||
| 2010 | 18,118,713 | 6,580 | 271.097 | |||||||
| IAD | 73 | 2018 | 24.060.709 |
+ 2.0%
|
300,936 |
-9.4%
|
274.281 |
-18.5%
|
||
| 2010 | 23,597,226 | 332.275 | 336,531 | |||||||
| PHL | 145 | 2018 | 31,691,956 |
+ 3.0%
|
503.784 |
+ 20.0%
|
379,665 |
-17.6%
|
||
| 2010 | 30,775,961 | 419,789 | 460,779 | |||||||
| Swell: | ||||||||||
Busiest routes
| rank | city | Passengers | Airlines |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atlanta , Georgia | 874.640 | Delta , Southwest , Spirit |
| 2 | Fort Lauderdale , Florida | 660.100 | JetBlue , Southwest, Spirit |
| 3 | Orlando , Florida | 606.070 | JetBlue, Southwest, Spirit |
| 4th | Boston , Massachusetts | 582.170 | JetBlue, Southwest, Spirit |
| 5 | Charlotte , North Carolina | 427.930 | American , Southwest |
| 6th | Denver , Colorado | 385,530 | Southwest, Spirit, United |
| 7th | Detroit , Michigan | 358.880 | Delta, Southwest, Spirit |
| 8th | Tampa , Florida | 343.980 | Southwest, Spirit |
| 9 | Chicago-O'Hare , Illinois | 341,470 | American, Spirit, United |
| 10 | Las Vegas , Nevada | 327.380 | Southwest, Spirit |
Incidents
- On 22 February 1974 three people died at the airport Baltimore during an attempted hijacking . On the morning of the day, gun-armed Samuel Byck entered the passenger terminal. His aim was to hijack an airplane in order to steer it into the White House and kill the then US President Richard Nixon . First he shot a policeman in the terminal. He then stormed a Douglas DC-9 of Delta Air Lines , which was just preparing for Delta Air Lines flight 523 to Atlanta . When the pilots of the plane told him they could not take off while the wheels were still locked, he shot both of them, grabbed one of the passengers and asked her to fly. Only one of the pilots survived his injuries. Eventually Byck was hit by two bullets that were fired at him by a police officer through the window of the aircraft door. Before the police could get on the plane, Byck killed himself with a shot in the head.
Web links
- The airport's website (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b BWI timeline. BWIAirport.com, accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c Facts & Figures. BWIAirport.com, accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Statistics. BWIAirport.com, accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ^ Ground Transportation. BWIAirport.com, accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ^ North America Airport Rankings. ACI-NA.org , accessed February 19, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c BWI Stats 1951 to 1999. BWIAirport.com, accessed on April 18, 2019 (English).
- ^ Reagan Air Traffic Statistics. MWAA.com, accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ^ Dulles Air Traffic Statistics. MWAA.com, accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ↑ Activity Reports. PHL.org, accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ^ Baltimore / Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport. Transtats.BTS.gov , accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ^ BWI route map. BWIAirport.com, accessed April 18, 2019 .
- ^ Delta Air Lines Flight 523. In: Aviation-Safety.net. Retrieved October 7, 2016 .