Regions of Japan
Japan is often divided into eight regions ( Japanese 地方 , chihō ).
meaning
The regions are not administrative units like the 47 prefectures of Japan . Only Hokkaidō is also a prefecture.
The regional division can be found in economic life (company structures, broadcasting areas, etc.), summarizes geographically and culturally related areas and is also taught in geography in schools. It is largely based on historical backgrounds.
list
The regions are classified from north to south:
- Hokkaidō : the island of Hokkaidō and surrounding smaller islands,
- Tōhoku : the northern Honshū ,
- Kantō : the eastern Honshū,
-
Chūbu , the central Honshū, often divided into:
- Hokuriku : the northern Chūbu,
- Chūō-kōchi or Tōsan: the central Chūbu,
- Tōkai : the southern Chūbu,
- Kinki : West-Central Honshu,
- Chūgoku : the western Honshū,
- Shikoku : the island of Shikoku in the southeast and
- Kyūshū - Okinawa : the island of Kyūshū in the southwest and the south adjoining Nansei Islands
To be added to the Kyūshū region, the Nansei Islands between Kyūshū and Taiwan include parts of Kagoshima Prefecture and the entire Okinawa Prefecture . Okinawa is the main island of the former independent empire of the Ryūkyū Islands and mostly also describes the region. The islands have only been part of Japan since 1879 ( occupied by the USA in 1945 , returned to Japan in 1972 ).
table
| region | location | map | Prefectures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hokkaidō ( 北海道 ) |

|

|
|
The island of Hokkaidō (roughly translated: Northern Sea District ) is the second largest island in Japan and, together with several surrounding small islands, forms the northernmost prefecture of the country. The region is also congruent with the prefecture. |
|
Tōhoku ( 東北 ) |

|

|
The Tōhoku region (translated: northeast) occupies the northern part of the island of Honshū . Tōhoku is relatively sparsely populated and has only a few large cities. |
|
|
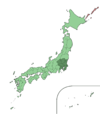
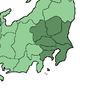
Kantō ( 関 東 ) |
|
|
The Kantō region occupies the eastern part of central Honshū. The name Kantō comes from the fact that the region is east ( 東 , tō) of the border station ( 関 所 ) Hakone . Together with Yokohama and Kawasaki, Tokyo forms the largest metropolitan area in the world with over 36 million inhabitants. |
|
|
Chūbu ( 中部 ) |

|

|
|
As the Japanese name ( middle part ) suggests, the Chūbu region occupies the central Honshū. Often it is also divided into:
Further subdivisions are: Shin'etsu (Nagano and Niigata), Kōshin'etsu (+ Yamanashi), Hokuriku-Shin'etsu (Hokuriku and Shin'etsu). |
|
Kinki ( 近畿 ) |

|

|
The Kinki region occupies the western part of the island of Honshu. The name Kinki (German: near the capital ) comes from the fact that all Japanese capitals were in this region until the Meiji Restoration. |
|
|
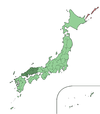
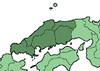
Chūgoku ( 中国 ) |
|
|
The Chūgoku region occupies the western and southern end of the island of Honshū. Since Chūgoku (German: Land der Mitte ) is also the name for China in Japanese, the Chūgoku region is now provided with the addition -chihō (地方) to avoid confusion. |
|
|
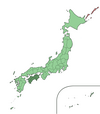
Shikoku ( 四 国 ) |
|

|
The Shikoku region is identical to the Shikoku Island in southeastern Japan. Shikoku (German: four countries ) is the smallest of the four main islands. The island is named Four Lands due to the fact that it used to consist of four provinces. Today there are four prefectures. |
|
|
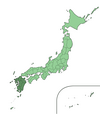
Kyushu - Okinawa ( 九州 ・ 沖 縄 ) |
|
 |
|
The region includes Kyūshū, the southernmost main island of Japan, and the Nansei Islands , of which Okinawa is the largest and most important island. The name Kyūshū (German: nine provinces) comes from the original division of the island into nine provinces. |
Other classifications
Different institutions use different regional divisions. Examples are:
The national weather service, the Kishō-chō (English Japan Meteorological Agency ), uses the following classification for weather reports:
- Hokkaidō and Tōhoku as above
- Kantō-Kōshin: Tochigi, Gunma, Ibaraki, Tokyo, Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Nagano, Yamanashi prefectures
- Hokuriku: Niigata, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui Prefectures
- Tōkai: Aichi, Gifu, Mie, Shizuoka prefectures
- Kinki: Kyōto, Hyōgo, Shiga, Nara, Wakayama, Osaka prefectures
- Chūgoku: Okayama, Hiroshima, Tottori, Shimane Prefectures
- Shikoku as above
- North Kyushu: Yamaguchi, Fukuoka, Ōita, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto Prefectures
- South Kyushu Amami: Miyazaki Prefectures, Kagoshima
- Okinawa: Okinawa Prefecture
The regions Hokkaidō and Tōhoku are grouped as Northern Japan , Kantō-Kōshin, Hokuriku and Tōkai as Eastern Japan and Kinki, Chūgoku, Shikoku, North and South Kōshū as Western Japan .
The regional lead prefecture studios of the public radio station NHK , which z. For example, the regional windows broadcast on national television and radio news are shared by Japan as follows:
- Hokkaidō and Tōhoku as above
- Kantō-Kōshin'etsu: Tokyo, Kanagawa, Saitama, Chiba, Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Yamanashi, Nagano, Niigata prefectures
- Tōkai-Hokuriku: Aichi, Gifu, Mie, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui, Shizuoka prefectures
- Kinki: Osaka, Shiga, Kyōto, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama prefectures
- Chūgoku, Shikoku and Kyūshū as above
The regional electoral blocks for the 1996 proportional representation in elections to Shūgiin , the lower house of the national parliament, use an eleven-part division in which Kantō (including Yamanashi, excluding Tokyo) is divided into north and south, Tokyo prefecture forms a separate region and Chūbu in Hokuriku-Shin'etsu and Tōkai (including Mie) is divided, see list of constituencies for Shūgiin .
The higher courts divide Japan into eight regional jurisdictions that differ from the above structure.
The national police authority also uses a regional structure that differs from the classic eight-region classification above: Hokkaidō and Tokyo are separate, the remaining 45 prefectures are grouped into seven regions (see Japanese police ).
Some regional governors ' conferences also use a different classification, see Zenkoku Chijikai # Regional Governors' Conferences .
Plans for the dōshūsei , which has been discussed for decades and planned by the central government especially since the early 2000s , a system of larger, financially more capable and more autonomous states, which are to be placed above the prefectures or to replace them entirely, see different divisions into 9, 11 or 13 states before.
The quarterly regional economic report of the Japanese central bank (Sakura report) uses a nine-part division into: Hokkaidō, Tōhoku, Hokuriku, Kantōkōshin'etsu, Tōkai, Kinki, Chūgoku, Shikoku, Kyūshū-Okinawa.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ 地 域名
- ↑ 全 般 気 象 情報 (日本)
- ↑ 全国 の NHK
- ↑ 放送 局 の ち か ら
- ↑ Sōmushō : Dōshūsei , 「道 州 制 の あ り 方 に 関 す る 答 申」 イ メ ー ジ (PDF; 674 kB), p. 4
- ↑ Nippon Ginkō : 地域 経 済 報告 (さ く ら レ ポ ー ト) (Japanese, English summaries )


