Nauen plate
| Nauen plate | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Foothills of the Nauener Platte to the Havel near Berlin-Gatow |
||
| Highest peak | Schwarzer Berg ( 89.3 m above sea level ) | |
| location | Berlin and District Havelland and District Potsdam-Mittelmark , Brandenburg an der Havel and Potsdam in Brandenburg ( Germany ) | |
|
|
||
| Coordinates | 52 ° 33 ' N , 12 ° 48' E | |
| Type | Ground and terminal moraine | |
| rock | Boulder clay , boulder clay , sand and gravel | |
| Age of the rock | Vistula Ice Age (until about 15,000 years ago) | |
|
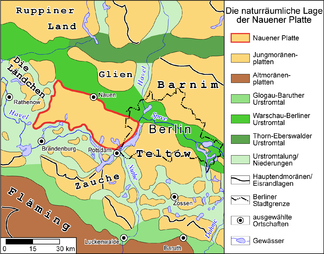
Natural location of the Nauener Platte |
||
The Brandenburg - Berlin Nauener Platte , which rises an average of 15 meters above its surrounding area, is a largely closed plateau that was formed in the Saale Ice Age and the last Ice Age . Basal moraine areas predominate , some of which are overlaid by flat, wavy terminal moraine formations. While the adjacent Zauche in the south of Teltow in the southeast and the Barnim simultaneously in the north-east of the geological formation adjacent to the landscape formation denote carrying culture landscape on the plate Nauener the name Havel country . The Havelland river landscape extends beyond the plate and includes in particular the Havelniederung and other lowlands.
location
The Nauener Platte is located in the Middle Mark and in the extreme west of Berlin. The northern border is formed by the Berlin glacial valley with the Havelländischer Luch , which is part of the Westhavelland nature park , and the Zehdenick-Spandau Havel lowlands . To the north of the lynx, there is the Ländchen Glien, a small ridge . The eastern border is formed by the Berlin-Potsdam chain of Havel lakes, which separates the Nauener Platte from the Teltow plateau to the east. After it bends to the west at Templiner See , the Havel lowlands between Potsdam and Brandenburg an der Havel also delimit the plate to the south and separate it from the Zauche.
The western border also forms the Havel lowlands in the first part, after the course of the river at Plauer See changes direction again and turns north. Between Pritzerbe , part of the city Havelsee and Paulinenaue the more western end of the Nauen plate runs west of Garlitzer Heide and Ribbecker Heide and east of protected and protected area for Great Bustards .
The total area covers about 90,000 hectares . The west-east extension is around 45 kilometers, the north-south extension around 20 kilometers.
Places and parts of the landscape
Like the big cities of Berlin and Potsdam, the eponymous city of Nauen is located on the edge of the Platte, on the northern edge. Other larger places on the plateau are Wustermark , Brieselang , Dallgow-Döberitz and Ketzin . The towns, villages and communities on the plateau mostly belong to the two districts of Potsdam-Mittelmark and Havelland .
The state government designated the Nauener Platte as a wind suitability area; therefore the Ketzin wind farm could be built here . It comprised eight 2.3 MW N90 turbines with a total output of 18.4 MW. The wind farm with 100 meter high tubular towers went online in June 2005. Additional systems were installed in the following years. In July 2012, the Ketzin and Ketzin II wind farms comprised a total of 26 systems with a total output of 48,500 kW. By April 2013, around 160 wind turbines had been installed on the Nauener Platte.
Also worth mentioning are:
- The Döberitzer Heide with the rare type of vegetation sand-dry grass flora . It is located on the area of the former Döberitz military training area and covers around 5000 hectares in addition to the nature reserve of the same name and the Ferbitzer Busch nature reserve .
- The nature reserve Windmühlenberg on the eastern slope of the Platte zur Havel in the Gatow district of the Berlin district of Spandau , also with sand-dry grass flora.
Geostructure
The ground moraine and terminal moraine formations of the Nauener Platte are partly overlaid by marls and decking sands that were left behind by the water from the thawing glaciers around 15,000 years ago at the end of the Vistula Ice Age. The glacial character of the relief led to an alternation of boulder clay , boulder clay , sand and gravel in a very small space . In the slope areas of the plateau to the Havelniederung near Groß Glienicke , Kladow and Gatow, up to ten meters thick plateau sands appear close to the surface and in large areas, such as on Gatower Windmühlenberg, in Gatower Heide or at Karolinenhöhe . The nutrient-poor and dry sand creates ideal conditions for the extreme site conditions of the dry grass.
The remaining soils in the surface relief of the Young Pleistocene landscape are characterized on the one hand by rust-brown soils , which, with good ventilation and deep rooting, form dry and nutrient-poor locations similar to the sands. Secondly, determine Parabraunerden soils, with their higher humus - and clay content as in the conservation area of Gatower Feldflur best conditions for agriculture offer.
Surveys
- The Black Mountain in the municipality of Beetzsee, north of the city of Brandenburg, reaches a height of 89.3 meters.
- The Gallberg in the city of Havelsee is 68.2 meters high. One of the most extensive urn grave fields of the first centuries AD was excavated on it.
- The Marienberg in the city of Brandenburg an der Havel is 67.7 meters high.
- The Fohrder Berg in the town of Havelsee is 67.6 meters high. There are several mining areas on it. Gravel and sand are extracted in open-cast mines.
- The Mosesberg in the municipality of Beetzseeheide is 62.9 meters high. A prehistoric urn grave cemetery with grave goods was found on it.
- The Hasselberg in the Beetzsee municipality, north of the city of Brandenburg, is 58.8 meters high. An extensive prehistoric urn cemetery was discovered on it.
- The Windmühlenberg in the Gatow district of Berlin is 52 meters high.
literature
- Potsdam and the surrounding area. Guide to the Geology of Berlin and Brandenburg No. 4 , Ed .: Johannes H. Schroeder, self-published Geoscientists in Berlin and Brandenburg eV, Berlin 2001, 2nd ext. Edition, ISBN 3-928651-09-9
- R. Weisse , The Potsdamer Glaziallandschaft - glacial sediments and glacial architectural styles , In: Brandenburgische Geoscientific Contributions , Ed .: State Office for Mining, Geology and Raw Materials Brandenburg, Kleinmachnow Issue 1 1995, pp. 13-26, ISSN 0947-1995
- Walter Behrmann, The environment of Berlin considered according to morphological groups of forms , In: Die Erde , Volume 1 1949/1950, pp. 93-122, Society for Geography in Berlin, ISSN 0013-9998
Web links
- Digital Environmental Atlas Berlin , see individual chapters under "Subject areas"
- Ketzin wind farm
Individual evidence
- ^ Press release from the manufacturer Nordex SE dated June 27, 2005
- ↑ List of wind farms, accessed August 2012