Staff Sergeant

The staff sergeant is a rank of the Bundeswehr . In the armed forces , the term is a collective term for higher NCO ranks.
armed forces
| Staff Sergeant | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Rank group | NCOs without portepee |
| NATO rank code | OR-5 |
| Rank Army / Air Force | Staff Sergeant |
| Marine rank | Chief mate |
| Abbreviation (in lists) | StUffz (SU) |
| Grade | A 6-7 according to BBesO |
The rank of staff sergeant is determined by the Federal President with the order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers on the basis of the Soldiers Act .
Authority to command and positions
In the armed forces, the Stabsunteroffizier a corporal rank , that according to the central service provision (ZDv) 1420 A-/ 24 "ranks and rank groups" to the rank group of NCOs without Portepee counts. Because they belong to the rank group of NCOs without porterage, staff NCOs can issue orders to soldiers of the rank group of men within the limits set there on the basis of § 4 ("Superiors relationship based on the rank") of the Superiors Ordinance.
Staff sergeants are used, for example, as group and squad leaders , as trainers or in lower staff posts . On the basis of their position in the service, non-commissioned officers can issue orders to all soldiers who are officially or professionally subordinate in the cases listed in the Supervisor Ordinance.
Appointment and remuneration
The decisive legal basis for the appointment as a staff sergeant is contained in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance (SLV) and in addition the Central Service Regulations (ZDv) 20/7. To rank Staff Sergeant to regular soldiers and ordered reservists are appointed. The prerequisite for being appointed to the rank of staff sergeant is membership of one of the career paths of the career group of sergeants . With a secondary school certificate , usable vocational training and two years of professional experience , soldiers can be hired directly with the rank of sergeant. Most staff sergeants, however, first go through the rank of sergeant. In this case, the rank can be achieved at the earliest one year after appointment as a sergeant .
Rod NCOs are after Bundesbesoldungsgesetz order (BBesO) with A 6 or A 7 remunerated .
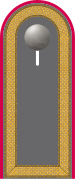
Rank badge
The rank badge for staff sergeants shows a closed braid as a shoulder badge .
history
In the Bundeswehr the staff sergeant in 1955 replaced the old rank designations Unterfeldwebel or Unterwachtmeister , which were used from 1921 to 1945 by the Reichswehr and Wehrmacht (and until 1990 by the East German NVA ). The sergeant in the army of the German Reich was the forerunner of the sergeant .
The rank designations Oberjäger and Stabsoberjäger for the ranks of sergeants and staff sergeants were partly used until the beginning of the 1960s based on the model of the ranks of the Wehrmacht in the hunter and paratrooper troops . However, there was no legal basis for this informal and widespread practice in the form of a corresponding order from the Federal President .
Equivalent, subordinate and superior ranks
Only Army and Air Force uniforms bear the rank of staff sergeant . Navy uniform wearers of the same rank hold the rank of chief mate . In the armed forces of NATO , the staff sergeant is equivalent to all ranks with the NATO rank code OR-5.
In the sergeant's careers , the staff sergeant is in accordance with No. 127 f. ZDv 20/7 between the lower rank NCO or Maat and the higher-ranking Sergeant or Bootsmann arranged. Lower-ranking officer candidates lead the ranks of Fahnenjunker or Naval Cadet . Senior officer candidates lead the ranks of ensign or ensign at sea . (First rank designation for army and air force uniforms; second rank designation for naval uniforms.)
|
|
||
| Lower rank | Higher rank | |
|
Sergeant Maat Fahnenjunker midshipman |
Staff Sergeant Obermaat |
Sergeant Boatswain Ensign Ensign at sea |
|
Rank group : Teams-NCOs-NCO-NCOs-Lieutenant-Captains-Staff officers-Generals |
||
Federal Army
In the Austrian Armed Forces the higher non-commissioned officers are referred to as staff non-commissioned officers. The application group M ZUO 1 (non-commissioned officers on time 1) comprises the staff sergeant , the chief staff sergeant and the officer’s deputy , the application group M BUO 1 (professional sergeants 1) also includes the highest sergeant grade vice lieutenant .
Staff sergeants' training was reformed in 1995 and introduced into the armed forces in 2000. First of all, professional NCOs should benefit from this training - especially those who already have a job in the M BUO 1 employment group. 150 participants are admitted annually. Prerequisites are at least four years in the rank of non-commissioned officer (from sergeant upwards) and very good knowledge of English.
After a positive admission test, the applicants attend the staff sergeant's course (new) at the Army Sergeant Academy (HUAk) in Enns . The one-year training is divided into two sections: a six-month course at the HUAk and a further six months at the respective military or technical school. The successful graduates of the staff sergeant's course can be used as platoon leaders and in staff duty.
See also: Ranks of the Austrian Armed Forces
Web links
Remarks
- ↑ Left: Rank badge on the shoulder flap of the jacket of the service suit for army uniforms of the armored forces . Right: Rank badge on the shoulder flap of the jacket of the service suit for Air Force uniform wearers.
- ↑ Unofficially, the non-commissioned officers without portepee are also simply summarized as non-commissioned officers , while the rank group of non-commissioned officers with portepee is referred to as sergeant ranks . However, according to the order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers , the group of NCOs includes both the rank group of NCOs without porters and the rank group of NCOs with porters .
- ↑ ZDv 20/7 on the basis of Section 44 of the Soldiers ' Career Ordinance ( Ordinance on the Careers of Soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002, Section 44 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Newly drafted by Bek. V. 19 August 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2 Paragraph 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730). )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Hartmut Bagger , Command Staff of the Armed Forces I 3, Federal Ministry of Defense (Ed.): ZDv 37/10. Suit regulations for soldiers in the Bundeswehr . July 1996. Reprint from October 2008. Bonn July 16, 2008, 4 labels, p. 539 ( digital version (PDF; 3.5 MB) - reprint October 2008 replaces first edition from July 1996). Digitized version ( memento of the original from September 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Law) ).
- ↑ a b Agreed English texts. STANAG 2116 . NATO standardization agreement (STANAG) . NATO codes for grades of military personnel. 5th edition. 1992 ( NATO Rank Codes - 1992 [accessed March 25, 2014] English).
- ↑ a b c d e The Federal President (Ed.): Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of the soldiers . BPresUnifAnO. July 14, 1978 ( PDF - Order of the Federal President on the rank designations and uniforms of soldiers from July 14, 1978 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 1067 ), last amended by Article 1 of the order of May 31, 1996 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 746 ) has been changed).
- ^ Federal Minister of Defense ; Command Staff of the Armed Forces IV 1 (Ed.): Abbreviations for use in the Bundeswehr - German Abbreviations - ZDv 64/10 . Bonn January 19, 1979 ( PDF - as of September 17, 1999).
- ↑ a b Appendix I (to § 20, paragraph 2, sentence 1) Bundesbesoldungsgesetz orders of A and B . ( Online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Federal salary regulations (BBesO) only apply to professional and temporary soldiers and are an annex to the Federal Salary Act (BBesG)).
- ↑ The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): Law on the legal status of soldiers (Soldiers Act - SG) . Bonn March 19, 1956, § 4 Paragraph 3 (2) - ( PDF [accessed on March 25, 2014] Revised by notice of May 30, 2005 I 1482. Last amended by Art. 1 G of April 8 2013 I 730).
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, amendment status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, The Superiors Ordinance, p. A 12 1 (Not to be confused with the Ordinance on the Regulation of Military Superiors (Superiors Ordinance - VorgV) ).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956, § 4 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] Last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ↑ Federal Minister of Defense (Ed.): Ordinance on the regulation of the military superior relationship (Superior Ordinance - VorgV) . June 4, 1956 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] last amended by Art. 1 No. 2 V of October 7, 1981 I 1129).
- ^ Ordinance on the career paths of soldiers (Soldiers' Career Ordinance - SLV) . March 19, 2002 ( online [accessed on March 25, 2014] revised by notice of August 19, 2011 I 1813. Last amended by Art. 2 Par. 5 G of April 8, 2013 I 730).
- ↑ Note also: Annex (to § 3). Allocation of the career paths of the soldiers to the career groups of the men and women, the NCOs and the officers
- ↑ a b The Federal Minister of Defense ; Personnel, Social and Central Affairs Department (Ed.): ZDv 20/7. Provisions for the transport and for the recruitment, acceptance and admission of soldiers . Bonn March 27, 2002, Art. 635 ( PDF ( memento of October 26, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) [accessed on March 26, 2014] DSK AP210100187, reprint January 2008). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ cf. Iller disaster . The death of Kempten . In: Der Spiegel . No. 24 , 1957 ( online ).
- ↑ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Second order of the Federal President on the rank designations, the appointment and dismissal as well as the uniform of the volunteer soldiers from February 1, 1956 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1956 , 4 of February 2, 1956. Bonn July 23, 1956, p. 63 ff . ( Online [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ Federal President Theodor Heuss et al .: Second order of the Federal President on the rank designations and the uniform of soldiers from July 26, 1957 . In: Federal Law Gazette Part 1 . tape 1957 , 39 of August 7, 1957. Bonn July 26, 1957, p. 1056 ( online [PDF; accessed May 12, 2015]).
- ↑ a b The equivalent, higher and lower ranks are given in accordance with ZDv 14/5 B 185, cf. The Federal Minister of Defense (ed.): ZDv 14/5. Soldiers Act . DSK AV110100174, change status July 17, 2008. Bonn August 21, 1978, rank designations in the Bundeswehr, p. B 185 (Not to be confused with the Law on the Legal Status of Soldiers (Soldiers Act) . The order of the ranks shown in the info box does not necessarily correspond to one of the regular rank sequences provided for in the Soldiers' Career Ordinance , nor does it necessarily correspond to the rank hierarchy described in the Superiors Ordinance a managerial relationship ).