Enns
|
Borough Enns
|
||
|---|---|---|
| coat of arms | Austria map | |
|
|
||
| Basic data | ||
| Country: | Austria | |
| State : | Upper Austria | |
| Political District : | Linz Land | |
| License plate : | LL | |
| Surface: | 33.04 km² | |
| Coordinates : | 48 ° 12 ' N , 14 ° 28' E | |
| Height : | 281 m above sea level A. | |
| Residents : | 11,940 (January 1, 2020) | |
| Postal code : | 4470 | |
| Area code : | 07223 | |
| Community code : | 4 10 05 | |
| NUTS region | AT312 | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Hauptplatz 11 4470 Enns |
|
| Website: | ||
| politics | ||
| Mayor : | Franz Stefan Karlinger ( SPÖ ) | |
|
Municipal Council : (2015) (37 members) |
||
| Location of Enns in the Linz-Land district | ||
 The main square of Enns with the city tower in the center |
||
| Source: Municipal data from Statistics Austria | ||
Enns is a city with 11,940 inhabitants (1 January 2020) in the district Linz-Land in Upper Austria . It lies on the Danube and the Enns River , which forms the border with Lower Austria here.
The city describes itself as the oldest city in Austria , but this is controversial. The town charter from 1212 can be viewed in the Enns Museum. Enns is the successor town of Lauriacum , which was elevated to town in 212. Enns was also the first Cittàslow city in Austria. The city's landmark is the 60 m high city tower.
geography
Enns lies at an altitude of approx. 240–300 m in the central region of Upper Austria . The community extends from the left (northern) bank of the Danube opposite Mauthausen on the left bank up the lowest Enns. The northern parts of the municipality belong to the largely flat Linzer Feld , the southeast to the Lower Ennstal , the southwest to the Traun-Enns-Platte . Another main body of water is the lowest Kristeiner Bach and its subsidiary brook, the Stallbach ( Moosbachl, Bleicherbach or Lorcherbach ) .
The extension of the municipality is 7.5 km from north to south and 8.6 km from west to east. The total area is 34.3 km². 12.8% of the area is forested, 64.1% is used for agriculture.
Neighboring communities
| Branches |
Langenstein district of Perg |
Mauthausen (Perg district) |
| St. Florian |

|
Ennsdorf ( Amstetten district , Lower Austria) |
| Hargelsberg | Kronstorf |
St. Valentin (Amstetten district, Lower Austria) |
Community structure
The municipal area comprises the following 14 localities (population in brackets as of January 1, 2020):
- Einsiedl (62)
- Enghagen (24)
- Enghagen am Tabor (0)
- Enns (9765, capital of the municipality)
- Ental (40)
- Alder Trench (16)
- Hiesendorf (791)
- Kottingrat (55)
- Kristein (819)
- Kronau (0)
- Lorch (199)
- Moss (3)
- Rabenberg (17)
- Volkersdorf (149)
The community consists of the cadastral communities Enns , Hiesendorf, Kristein, Lorch , Moos and Volkersdorf .
Counting areas are Enns-Zentrum-Nord, -Zentrum-Süd, -Süd, -West, -Nord for the city and the more direct peripheral areas, Kristein for the second larger town of the municipality, Severinusstrasse residential complex for the main settlement area of Lorch, as well Enns-Umgebung-Nord for the other places in Linzerfeld and Enns-Umgebung-Süd for the places in the south on the Enns and Moosbachl.
history
etymology
The name of the Enns is derived from the Celtic Ani . The Romans made the Latin name anisus out of it. In the 9th century the river was called Anesis or Enisa , from which the name Enns later developed.
Early history and development of the city
The first settlements in the confluence of the Enns can be found around 4000 years ago. Around 400 BC Celts populated the country. Their kingdom Noricum was annexed to the Roman Empire in 15 AD and raised to the Roman province of Noricum in 45. Before 205, the Romans built the Lauriacum military camp with up to 6400 soldiers for the second Italian Legion north of today's city center, near the Danube , which formed the imperial border and had to be defended against Germanic tribes . Lauriacum received 212 by Kaiser Caracalla the city law ; At that time, around 30,000 people lived here with the civil town located southwest of the fortified camp.
According to tradition, during the persecution of Christians at the time of Emperor Diocletian , Saint Florian was martyred on May 4, 304 by drowning in the Enns . Around the year 370 an early Christian basilica was built on the remains of previous Roman buildings (in 1344 the current basilica of St. Laurentius von Lorch was built over the foundation of the old church ).
During the time when Lauriacum was threatened by the Germanic tribes, the future Saint Severin von Noricum worked here, among other things. In 488 the Roman administration and many Roman settlers withdrew to Italy; the bishopric was also given up. Remnants of the Romanesque settlement remained, however, when Bavaria began to settle here from 530 . Around 700 the border town was devastated by the Avars , but later by the Bavarian Duke Tassilo III. brought back under his rule. Charlemagne used Lorch as a strategic base for his victorious Avar Wars.
If in Roman times the enemy was to be expected from the north, an attack now threatened from the east. Therefore, around 900 on the Georgenberg, near today's city center, the Enisiburg ('Ennsburg') was built to protect against the invasions of the Hungarians and in 976 handed over to the Passau bishopric . Ennsegg Castle later emerged from it. The surrounding settlement experienced a boom from the 12th century when Count Otakar II established a market; the former Roman Lorch was now just a village.
In 1186 the Georgenberg Handfeste , a succession contract between Otakar IV. (Ottokar IV.) Of Steyr (duke since 1180), who had no male heirs, and the Babenberg duke Leopold V of Austria was signed on the Georgenberg . After Otakar's death in 1192, Styria , which at that time was much larger than today's federal state and stretched from the Save in today's Slovenia to the Danube, fell to the Babenbergs.
With the granting of city rights by Leopold VI. Enns became a town in 1212, making it one of the oldest towns in Austria. The town charter from 1212 can be viewed in the Enns Museum.
After the death of the last male Babenberger, Friedrich the arguable , in the Peace of Ofen in 1254 - in addition to the County of Pitten - the Traungau and with it the city of Enns were separated from Styria, incorporated into the Duchy of Austria and thus the nucleus for the division of Austria in the two later archduchies of Upper Austria and Lower Austria . In 1319 the important customs post for the salt trade was relocated to Reintal , then in 1340 to Enghagen , where the Roman Danube fleet had probably already been located.
As part of the “ Wiener Geserah ” ordered by Duke Albrecht V in 1420/21 , the Jewish community in Enns and other princes of Austria was destroyed. The official reason for the annihilation, which began in 1420, was a host crime allegedly committed in Enns, where a sexton from the St. Laurenz Church is said to have stolen hosts and sold them to an Enns Jew named Israel ( Isserlein ) and his wife. Isserlein's wife committed suicide after being tortured in prison. On the orders of Duke Albrecht V, the last survivors of the Austrian Jewish communities were burned alive on March 12, 1421 on the so-called Gänseweide in Vienna-Erdberg in front of the population. On April 16, 1421, the Enns sacristan involved in the alleged host crime was burned in Vienna-Erdberg, presumably in the same place as the Jews before.
Enns was under discussion as the state capital, but fell under Friedrich III in 1490. the decision for Linz . Under Maximilian I, however, Enns temporarily became the seat of the regiment for the Lower Austrian states in 1501. Relocated to Linz in 1502, the regiment moved back to Vienna in 1510. Nevertheless, in 1501, Emperor Maximilian I allowed the Ennsern to build a bridge over the Danube. It was only the fourth Danube bridge in Austria after Vienna, Stein and Linz. The bridge was built in 1502 and lasted until 1662.
In the 16th century Enns became Protestant . In 1532 the Turks stood before Enns. The city tower , today's landmark of the city, was built from 1564 to 1568 under Maximilian II at the request of the Enns citizens by the master builder Hans von Matz as bells, watch and clock tower. In 1569/70 the old Enns Castle, which slowly fell apart, was converted into Ennsegg Castle and expanded. The princely castle, built around 1483, was also expanded during these years. The seals with red wax was the city of Enns from 1594 with the acquisition of the Rotsiegelprivilegs allowed.
The Enns had to suffer from the pressure of the Counter Reformation . The billeting of Churbayrian war people and tax burdens demanded great sacrifices from the citizens. In addition, there was the plague in 1625, which killed every 14th inhabitant. When the peasants besieged the city for 30 days in 1626, two thirds of the houses were badly damaged. During the war of succession that Archduchess Maria Theresa had to wage over her hereditary lands, Enns was occupied by Churbayrian and French troops for 16 weeks in 1741.
During the Napoleonic Wars in 1805 and 1809, French troops were quartered in Enns. After the battle of Ebelsberg , which lies a few kilometers west of Enns (and today belongs to the city of Linz ), there was fierce fighting on the Enns Bridge from May 4 to 6, 1809. Napoleon was quartered in Ennsegg Castle for three days.
After these times of war followed by the pre-March period to a period of prosperity. Since it was feared that the wagons could no longer get through, the city gates were demolished from 1845 to 1849, and then the curtain walls were also removed, which are still visible today. Since the Empress Elisabeth Railway from Vienna to Linz (extended to Salzburg and Munich in August 1860) with a station in Enns was opened on December 15, 1858 , the city has been connected to modern transport networks. The fountains on the main square were removed around 1900.
Contemporary history and community development
In 1938 the municipality of Lorch was incorporated together with all other present-day localities in the city. During the Second World War, there was a satellite camp of the Mauthausen concentration camp in Enns , in which around 2000 concentration camp prisoners were used for forced labor in the bunker construction.
Enns was in the US zone of occupation from 1945 to 1955 ; Lower Austria, neighboring to the east, was occupied by the Red Army . The Enns formed a zone boundary on which the Soviet soldiers carried out strict controls until 1954 and arrested many travelers. In 1945 displaced German Bohemians, especially from Gablonz (Jablonec nad Nisou), settled and founded the Neugablonz settlement .
In the 1960s the West Autobahn was built. It runs with one exit (Enns Ost) south of Enns city center. In October 2010 the B 309 junction Enns West / Steyr was opened. It connects the expressway ( B 309 to Steyr) with the West Autobahn (A 1) and the B 1 . In 2005, the high-speed route of the new Westbahn was built in the section around Enns; it has no station in Enns.
Population development

politics
The community is located in the judicial district of Steyr .
Community representation
The municipal council consists of 37 members and has been made up of mandates from the following parties since the 2015 municipal council election:
- 13 seats in the Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ)
- 10 mandates Austrian People's Party (ÖVP)
- 8 mandates for the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ)
- 8 mandates The Greens - The Green Alternative (GREEN)
- 1 mandate NEOS - The New Austria and Liberal Forum (NEOS)
- mayor
- since July 1, 1997 Franz Stefan Karlinger (SPÖ)
coat of arms
|
Blazon : “ Divided ; above in green a silver , red armed , growing panther ; divided below by silver and red. The community colors are green-white-red. " |
|
| Reasons for the coat of arms: The coat of arms reminds of the Georgenberger Handfeste , exhibited in Enns in 1186 , the inheritance contract between the Dukes Ottokar IV (Styria) and Leopold V (Austria) from the House of Babenberg that became effective in 1192 . The upper part of the coat of arms represents the upper half of the Styrian coat of arms (the Styrian panther ), the lower part the lower half of the Austrian red-white-red shield . |
Regional policy
- The city is a member of the Cittàslow movement .
Town twinning
-
 Zeltweg , Styria
Zeltweg , Styria -
 Dingolfing , Bavaria (D), since October 17, 1965
Dingolfing , Bavaria (D), since October 17, 1965 -
 Ennsdorf , Lower Austria, since 2012
Ennsdorf , Lower Austria, since 2012
Main town of the municipality: City of Enns
|
Enns ( district ) locality ( capital of the municipality ) Enns cadastral municipality |
|
|---|---|
| Basic data | |
| Pole. District , state | Linz-Land (LL), Upper Austria |
| Judicial district | Steyr |
| Pole. local community | Enns |
| Coordinates | 48 ° 12 ′ 43 " N , 14 ° 28 ′ 42" E |
| height | 281 m above sea level A. |
| Residents of the village | 9765 (January 1, 2020) |
| Area d. KG | 9.71 km² |
| Post Code | 4470 Enns |
| Statistical identification | |
| Locality code | 09816 |
| Cadastral parish number | 45102 |
| Counting district / district | Enns-Zentrum-Nord, Enns-Zentrum-Süd, Enns-Süd, Enns-West, Enns-Nord, residential complex Severinusstr (41005 X [000–005, 008]) |
 View over the main square to the south (Wiener Straße) |
|
| Severinusstraße belongs to KG Lorch Source: STAT : Ortsverzeichnis ; BEV : GEONAM ; DORIS ; |
|
The main town of the municipality is the city of Enns itself, which is also a locality and cadastral municipality .
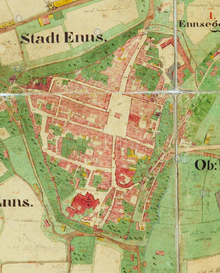
The place Enns is located on the northeastern hill spur of the pre-alpine Traun-Enns-Riedelland , slightly elevated above the Linzer Feld and Lower Ennstal to around 280 m above sea level. A. This location includes the old town on the Stadtberg (Ennsberg) , the upstream Georgenberg (today Schloßpark), and the surrounding old suburbs in the river valley, these at around 250 m above sea level. A. These suburbs are Reintal (Ober-, Unter-Reintal) east on the Enns, Lerchental Enns upstream, and Schmidberg west on Moosbachl (Bleicherbach). The old town is located within the limits of the old city walls, which are still partially preserved today. Today Enns is only part of the municipality. Ennsdorf , the old bridgehead of the city on the right bank of the Enns, has belonged to Lower Austria from ancient times.
In addition to the Maria Anger area (after a church that has now been abandoned), the Forstberg and the Neugablonz settlement in the south, and the locations on the Eichberg in the southwest, the Severinusstrasse residential complex near the Lorch basilica also belongs to the village of Enns - the latter, however, is in the cadastral community Lorch (the Papstwiese but in the Enns KG).
The cadastral municipality of Enns is even more extensive with a good 970 hectares , and represents the urban area before 1938. It extends in the northwest to the north bank of the Danube at the Spielberg ruins (which today belongs to Langenstein), in the northeast to the middle of the Danube , in the east along the Enns (partly in the middle, partly on one of the banks), and in the south to the western motorway (A1) and the Enns Ost junction . This also includes the town of Enghagen at the mouth of the Kristeinerbach , the old overpass Enghagen at Tabor and the Enns-left bank part of the Ennshafen .
The city in the broader sense today also includes the districts Kristein , Einsiedl and Lorch , which are largely grown together with the Enns in the area between the motorway and the route of the New West Railway - the other places in the community are still independent localities.
|
Lorch (O and KG)
|
Enghagen (O) |
Enghagen am Tabor (O) Ennshafen (Enns and Ennsdorf) |

|
||
|
Moss (KG)
|
Forstberg
Hiesendorf (O and KG)
|
Economy and Infrastructure
Industry
After 1980 the chemical industry and the Enns port were built at the corner of the confluence of the Danube and Enns.
education
- Enns is the seat of the Army NCOs Academy (HUAk).
- In Enns there is a primary school , two new middle schools , a polytechnic school and a ( secondary ) grammar school .
Culture and sights
Cityscape
The townscape of Enns is characterized by buildings from the Renaissance and Baroque periods , with parts of a medieval town fortification.
- City fortifications from 1193
- Town square with the town tower (1568)
- Ennsegg Castle : first mentioned around 900, heavily renovated after 1565
- Alte Ennsburg , first castle on the Georgenberg (Enns)
- Neue Ennsburg , princely castle built in 1475
- Parish Church Enns-St. Marien : from around 1270, former Minorite Church of the Franciscan Monastery of Enns , with the Wallseerkapelle around 1340, one of the most important Gothic buildings in Upper Austria in terms of art history
- Museum Lauriacum (Roman museum on the main square of Enns), which has taken care of the artistic estate of around 400 works by the medalist and sculptor Arnold Hartig since 1965 .
Other buildings in the community:
- Enns-Lorch basilica : with the only visible excavations from the Roman Lauriacum
Cultural offer
- Club Time cult-great-room-Enns , Location Kulturzentrum'd'Zuckerfabrik
- Theater im Hof , Enns: Since 2006 in the k. u. k. Indoor summer stage. Has dedicated himself to the classics of theater literature. Showed u. a. Romeo and Juliet , Faust 1 , Hamlet and stories from the Vienna Woods .
- Sellawie Theater , Enns: amateur theater, cellar vault of Ennsegg Castle
- Medieval and cultural association Civium Anasi - Enns Citizenship - Every two years in August there is a three-day medieval festival on the Georgenberg (Enns Castle Park). In addition, Walpurgis Night takes place every year on the night of May 1st .
- Trachtenverein Enns:
sport and freetime
Enns has several sports clubs (basketball club, soccer club, volleyball club, two tennis clubs, fistball club, gymnastics club, endurance sports club ). As leisure activities, Enns offers a climbing wall and an outdoor pool with sauna.
Personalities
Honorary citizen
- Carl Adam Kaltenbrunner (1804–1867), Austrian poet, writer and dialect researcher
- Herbert Kneifel (1908–2010), doctor, local researcher, archivist and local politician
- Friedrich Mayr (1929–2019), steel cutting artist
sons and daughters of the town
- Ulrich von Pottenstein (died 1416/17), dean and pastor in Enns 1412-1416 / 17 and theological writer
- Josef Hafner (1799–1891), color lithographer
- Osvald Polívka (1859–1931), architect
- Vilma Eckl (1892–1982), painter
- Johannes Krejci (1912–1997), painter
- Hanna Hager (1916–1997), politician ( SPÖ ) and economic manager
- Josef "Beppo" Mauhart (1933–2017), manager, president of the Austrian Football Association
- Wilhelm Neuwirth (* 1941), Roman Catholic clergyman
- Gottfried Kneifel (* 1948), journalist and politician
- Heidi Baratta (* 1952), actress and painter
- Markus Binder (* 1963), musician and author
- Viktor Gernot (* 1965), singer, cabaret artist, actor, musical performer, presenter
People related to the city
- Christine Haberlander (* 1981), politician ( ÖVP )
- Philipp Kroiss (* 1988), national volleyball player
Web links
- City website (www.enns.at) . The website was redesigned in June 2018.
- 41005 - Enns. Community data, Statistics Austria .
- Further information about the municipality of Enns can be found on the geographic information system of the federal state of Upper Austria .
- Map in the Digital Upper Austrian Room Information System ( DORIS )
Historical:
- Enns. In: Austrian City Atlas (Vienna City and State Archives, Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Urban History Research; online mapire.eu; with map )
- Museum Lauriacum Enns
Individual evidence
- ↑ Statistics Austria: Population on January 1st, 2020 by locality (area status on January 1st, 2020) , ( CSV )
- ^ Franz Hutter: History of Schladming and the Styrian-Salzburg Ennstal. onA
- ^ Karl Oettinger, Renate Wagner-Rieger, Franz Fuhrmann, Alfred Schmeller : Reclams Art Guide Austria , Volume I (Vienna, Lower Austria, Upper Austria, Burgenland), 4th edition, Philipp Reclam jun., Stuttgart 1974, ISBN 3-15-008605- 1 , p. 81 f.
- ↑ Entry about Ennsegg on Burgen-Austria
- ^ Ernst Theodor Gaupp : German city rights of the Middle Ages, with legal historical explanations . Second volume, Breslau 1852, pp. 206-224, online
- ↑ Entry on city law in the Austria Forum (in the AEIOU Austria Lexicon ) cf. also list of cities in Austria
- ^ Norbert Haslhofer: Politics with Enns History 1419-1421. Church policy in Passau and Jewish policy in Vienna. Backgrounds of the Vienna Geserah (= research on the history of the city of Enns in the Middle Ages . Volume 2 ). Norderstedt 2019, ISBN 978-3-7528-6701-5 .
- ↑ Michael Hochedlinger, Petr Mata, Thomas Winkelbauer: Administrative history of the Habsburg monarchy in the early modern period. Volume 1: Court and dynasty, emperor and empire, central administrations, warfare and sovereign finance. Böhlau, Vienna 2019, ISBN 978-3-205-20766-5 , p. 399 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Franz Stundner: The office of the regiment of n.-ö. Land at the time of Ferdinand I (1521-1564) . In: Yearbook for regional studies of Lower Austria . tape 31 , 1954, pp. 95–112 ( PDF on ZOBODAT ).
- ↑ Willibald Katzinger : Remarkable details on the construction of the Danube bridge in Mauthausen in 1502 . In: Yearbook of the Upper Austrian Museum Association . tape 159 . Linz 2013, p. 113–179 ( PDF on ZOBODAT ).
- ^ Norbert Haslhofer: Sources on the life and work of the Renaissance architect Hans von Matz. Architecture in the city of Enns 1550 - 1580 (= research on the history of the city of Enns in the Middle Ages . Volume 1 ). Norderstedt 2018, ISBN 978-3-7460-6061-3 .
- ↑ Election report. (pdf, on wahl.land-oberoesterreich.gv.at; ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ).
- ^ Cittaslow list ( Memento from July 11, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 350 kB).
- ↑ Statistics Austria, register census from October 31, 2011 . (PDF, statistik.at).
- ↑ Kulturzentrum'd'Zuckerfabrik (d-zuckerfabrik) .
- ↑ Sellawie Theater (sellawie.a) .
- ↑ Civium Anasi - Ennser Bürgerschaft (civium-anasi.at) ( Memento of the original from February 15, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Trachten Brochure: Tracht. Tradition. Enns. (download from enns.at)











