AMD K7
AMD K7 is the code name of a microarchitecture from AMD . Unlike its predecessors, the AMD K6 and AMD K5 , AMD used a full name - Athlon and related models - as a product name for the K7, similar to Intel for the Pentium . The term K7 therefore primarily stands for the microarchitecture of these processor families, but is also used in part for the processors themselves.
Technical details
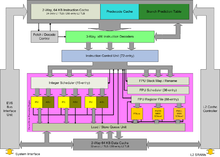
The K7 architecture is AMD's first completely redesigned CPU design, both in terms of the core itself and its infrastructure. The bus protocol of the Alpha EV6 was licensed, which enabled a significantly higher data throughput for the front side bus .
In addition, similar to the AMD K6-III , the L2 cache was integrated in the processor. In the first models for slot A , this was realized with external chips on a processor board together with the actual processor; later it was integrated directly into the processor die.
The FPU was also greatly improved by using the pipeline more efficiently (“fully pipelined”).
Processors of the K7 generation
successor
The K7 architecture laid the foundation for the successful K8 generation , the best-known representative of which is the AMD Athlon 64 .