Zen (micro architecture)
| << AMD Zen >> | |
|---|---|
 Zen micro-architecture scheme |
|
| Production: | since March 2, 2017 |
| Producer: | Globalfoundries |
| Instruction set : | AMD64 (x86-64) |
| Microarchitecture : | x86 processor |
| Base: | |
Names of the processor cores:
|
|
Zen is a processor - micro-architecture ( x86 - 64 ) of the company AMD . The market launch of the first Zen-based processors under the brand name Ryzen [ 'raɪzən: ] (code name "Summit Ridge") was on March 2nd, 2017. In June 2017, the Epyc server series followed as a multi-chip module made up of 4 Zen / Zeppelin single chips with eight cores each (code name “Naples”) and in October 2017 the processors with integrated graphics ( Accelerated Processing Unit - APU ) for mobile devices (code name “Raven Ridge”). The processors with graphics for desktop computers were added in February 2018.
In April 2018, an optimized edition of Zen called Zen + was introduced. In contrast to Zen, Zen + is manufactured in a 12 nm LP process at Globalfoundries. Together with cache optimizations, higher base and turbo clock frequencies and faster DDR4 memory, an increase in performance of approx. 10% is achieved.
On July 7, 2019, the first processors of the successor architecture Zen 2 came onto the market.
architecture
According to AMD, the primary goal of the development was to improve single-core performance instead of multithreading performance or increasing the number of CPU cores. Statements from AMD during development indicated that the core multithreading architecture CMT was abandoned in favor of the simultaneous multithreading (SMT) technology . The competitor Intel has been using SMT in its current form since Core i . It was assumed that the conversion would result in a great improvement in efficiency, possibly at the expense of increasing the chip area.
The Zen processors are manufactured by Globalfoundries using the 14 nm FinFET process . The previous processor generation AMD Fusion was based on the structure sizes 32 nm and 28 nm. With the architecture "Zen", both pure CPUs ("Summit Ridge") and APUs with integrated graphics processing unit ("Raven Ridge") are available. Both use the new socket AM4, used for the first time for these processors . DDR4 memory is supported. In addition to the models for desktop computers, there are also models for mobile use.
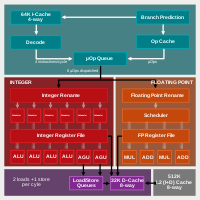
A Zen core contains four integer ALUs , two AGUs designed as load / storage units and a floating point unit divided into four pipelines . The floating point units are designed as 128-bit SIMD units and support AVX instructions and FMA operations. The two AVX units can be interconnected and then execute a 256-bit AVX-2 instruction. The L1 cache is 32 + 64 kB (data + instructions) and the L2 cache is 512 kB; the L3 cache is 8 or 16 MB for the quad-core and 16 MB for the six- and eight-core.
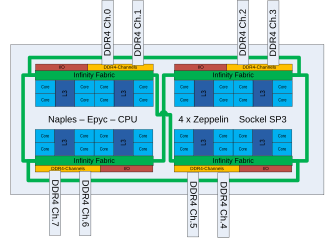
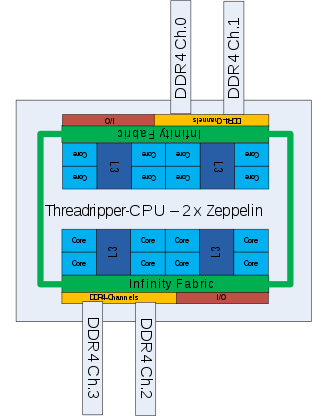
The basic building block for all “Summit Ridge” and “Naples” chips released by June 2017 is a complex (CCX: Core CompleX) of 4 cores with associated cache areas. Two of these complexes are referred to a "Zeppelin" " The integrated," the two complexes are interconnected with a bundle referred to "Infinity Fabric" from the serial links. With the same connection technology, several “dies” are interconnected on the multi-chip modules for the Threadripper and Naples / Epyc series as well as the two “SP3 socket” sockets in the server area. The two-chip module of the Threadripper series uses a modification of the server socket SP3 (called "TR4"), a land grid array with 4097 contacts, also called "Socket 4094" or "LGA 4094". The large number of contacts is required to be able to lead a total of 8 DDR4 memory channels , up to 128 PCIe 3.0 lanes per socket and the Infinity Fabric lines to the outside. With one chip and two sockets ( AM4 and SP3) systems from 4 to 32 cores can be implemented.
At Computex 2017, AMD presented a multi-chip module made up of two 8-core Zeppelin dies for high-performance desktops with the brand name Threadripper .
In the server area, four Zeppelin dies are combined into a 32-core Naples CPU (as a multi-chip module ). The code name Naples was replaced by the brand name Epyc , which is the successor to the Opteron server CPU series.
Ryzen particularly benefits from fast main memory because the clock rate of the “Infinity Fabric” depends directly on the memory clock. Faster working memory also means faster data exchange between two core complexes. Current AM4 mainboards support a maximum of DDR4-3200 in combination with Zen or Zen + CPUs. For higher clock rates, which are specified on modern Socket AM4 mainboards with x570 chipset, either operation outside of the specification (overclocking) or a CPU of the next generation with the Zen 2 microarchitecture is required.
Development history
The planning for Zen began shortly after the chief developer Jim Keller was hired again at AMD in 2012. He had already worked for AMD from 1998 to 1999, was involved in the development of the K7 architecture and was in charge of the development of the K8 architecture. Keller left AMD again in September 2015.
Originally, the K12 core, based on the ARM64 architecture, was supposed to appear before the processors with Zen architecture. However, on Financial Analysts Day in May 2015, it was announced that the K12 architecture would be postponed in favor of the Zen architecture in order for Zen to be ready for the market in the course of 2016.
In November 2015, a former AMD employee said the Zen technology had “met all expectations” in tests and “no significant bottlenecks were found”.
The market launch of the first Zen models with 8 cores under the name "Ryzen 7" took place on March 2, 2017. The smaller models with the name "Ryzen 5" (4 to 6 cores) followed in April 2017; the less powerful and cheaper models "Ryzen 3" (4 cores) then appeared in July 2017.
Market success
The market launch of the Ryzen models in spring 2017 helped AMD to significantly improve its competitive position compared to Intel, its only rival in the desktop processor segment: According to a report by Extremetech.com, AMD won the sales figures for the major German online from March 2017 -Händlers Mindfactory.de add 5 to 9 percentage points each month. In August 2017, AMD even surpassed its rival Intel in terms of sales and recorded a share of around 56 percent (Intel: around 44 percent).
Models
Socket AMD AM4 Model number Structure
Link to the picture
(Please note copyrights )
The model names of the Ryzen processors from AMD are heavily based on those of Intel. The Ryzen 7 models are to be seen as equivalent to the Intel Core i7 CPUs, the Ryzen 5 compete with the Core i5 and the Ryzen 3 models are the counterpart to Intel's Core i3.
Server without graphics unit
Epyc 7000
On June 20, 2017, AMD presented the server processor with the code name "Naples", which was given the trade name Epyc. It is a 4-chip module, which is made up of individual Zeppelin chips. Variants for one or two socket systems are available.
The large number of I / O connections or PCIe lanes and the high memory bandwidth through 8 memory channels surpass the competitor product Intel Xeon (Broadwell) at this point in time . Epyc is thus competitive in the server market, motherboards with PCI Express OcuLink connectors that each use 4 PCIe lanes to connect fast NVMe - Solid State Drive mass storage devices are offered.
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
TDP | Number of RAM channels |
Number of bases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epyc 7601 | 32/64 | 2.2 GHz (3.2 GHz) | 180 W | 8th | 2 |
| Epyc 7551 | 2.0 GHz (3.0 GHz) | 2 | |||
| Epyc 7551P | 2.0 GHz (3.0 GHz) | 1 | |||
| Epyc 7501 | 2.0 GHz (3.0 GHz) | 155/170 W | 2 | ||
| Epyc 7451 | 24/48 | 2.3 GHz (3.2 GHz) | 180 W | 2 | |
| Epyc 7401 | 2.0 GHz (3.0 GHz) | 155/170 W | 2 | ||
| Epyc 7401P | 2.0 GHz (3.0 GHz) | 1 | |||
| Epyc 7351 | 16/32 | 2.4 GHz (2.9 GHz) | 155/170 W | 2 | |
| Epyc 7351P | 2.4 GHz (2.9 GHz) | 1 | |||
| Epyc 7301 | 2.2 GHz (2.7 GHz) | 2 | |||
| Epyc 7281 | 2.2 GHz (2.7 GHz) | 2 | |||
| Epyc 7251 | 8/16 | 2.1 GHz (2.9 GHz) | 120 W | 2 |
Epyc 3000
In February 2018, AMD released another series of server processors under the brand name Epyc, which compete with the Xeon-D processors from Intel. They consist of one or two (on a multi-chip module ) Zeppelin chips that are integrated in a new BGA solder socket. A long availability of 10 years is promised, up to eight 10 Gbit Ethernet channels should be integrated. The high input / output performance through the 64 or 32 PCIe 3.0 lanes is particularly advertised. These processors are intended for so-called edge servers or embedded servers , small single-socket systems for IoT applications.
| model | Cores / threads |
CPU speed (GHz) | L3 cache |
TDP | Number of RAM channels |
Max. RAM clock (MHz) |
PCIe 3.0 lanes |
T j | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | AllCore Boost |
Max. Boost |
||||||||
| Epyc 3451 | 16/32 | 2.15 | 2.45 | 3.00 | 32 MB | 100 W | 4th | 2666 | × 64 | 95 ° C |
| Epyc 3401 | 16/16 | 1.85 | 2.25 | 85 W | 105 ° C | |||||
| Epyc 3351 | 12/24 | 1.90 | 2.75 | 80 W | 95 ° C | |||||
| Epyc 3301 | 12/12 | 2.00 | 2.15 | 65 W | 95 ° C | |||||
| Epyc 3251 | 8/16 | 2.50 | 3.10 | 16 MB | 50 W | 2 | 2666 | × 32 | 105 ° C | |
| Epyc 3201 | 8/8 | 1.50 | 3.10 | 30 W | 2133 | 95 ° C | ||||
| Epyc 3151 | 4/8 | 2.70 | 2.90 | 45 W | 2666 | 95 ° C | ||||
| Epyc 3101 | 4/4 | 2.10 | 2.90 | 8 MB | 35 W | 95 ° C | ||||
Desktop without graphics unit
Ryzen Threadripper
On August 10, 2017, the high-end desktop model series Ryzen Threadripper appeared in the LGA package for the socket TR4. The pins are no longer found on the processor, as is usual with AMD processors, but on the corresponding socket. Four models hit the market in August 2017: The Ryzen Threadripper 1950X with 16 cores and 32 threads was priced at $ 999, while the smaller Ryzen Threadripper 1920X processor with 12 cores and 24 threads was pretax $ 799 each. The 1920X runs at 3.5 GHz base clock and 4.0 GHz turbo clock. The base clock frequency of the 1950X is 3.4 GHz, which is 0.1 GHz lower, but the turbo clock frequency is also 4.0 GHz. The 1900X and 1920 models also came onto the market. The 1900X model has 8 cores and 16 threads and 16 MB L3 cache. The 1920 model has 12 cores and 24 threads with 32 MB L3 cache in a non-X variant, as known from the Ryzen 5 and 7, with a lower base clock and limited XFR. The socket TR4 is closely related to the Epyc / Naples socket SP3r2. It has 64 PCIe lanes, 4 DDR4 main memory channels and supports up to 2 TB of RAM and uses the X399 chipset (related to the X370 chipset).
Previously, there had been speculation about eight different models under the assumed name Ryzen 9 from 16 to 14 and 12 to 10 core CPUs. However, these speculations were based on false reports and have not been substantiated. 10- or 14-core CPUs could therefore not be produced, since the cores on the four CPU complexes (CCX) used would always have to be switched off symmetrically.
On August 6, 2018, almost a year later, AMD introduced the 2nd generation of the Ryzen Threadripper CPUs. The new top model Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX has 32 cores and 64 threads. The Threadripper 2000 series is now also based on the Zen + architecture like the Ryzen 2000 series and can be operated in existing TR4 mainboards with the X399 chipset. The WX models, which, in contrast to the other variants, consist of an MCM with 4 chips (instead of 2 as before) and thus largely correspond to the Epyc server processor, require approval from the mainboard manufacturer whether the TDP has increased to 250 W.
| model | Cores / threads |
Number
crisps |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
XFR | L3 cache |
TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen Threadripper 1900X | 8/16 | 2 | 3.8 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 4.2 GHz | 16 MB | 180 W |
| Ryzen Threadripper 1920X | 12/24 | 3.5 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 32 MB | |||
| Ryzen Threadripper 1950X | 16/32 | 3.4 GHz (4.0 GHz) | ||||
| Ryzen Threadripper 2920X | 12/24 | 3.5 GHz (4.3 GHz) | ||||
| Ryzen Threadripper 2950X | 16/32 | 3.5 GHz (4.4 GHz) | ||||
| Ryzen Threadripper 2970WX | 24/48 | 4th | 3.0 GHz (4.2 GHz) | 64 MB | 250 W | |
| Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX | 32/64 | 3.0 GHz (4.2 GHz) |
Ryzen 7
The first processor models in the Ryzen series were the Ryzen 7 1800X, Ryzen 7 1700X and Ryzen 7 1700. As a pure CPU without an additional graphics unit, they each offer 16 threads with eight cores through Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT). AMD only gives a guaranteed basic clock rate for new models. The specified turbo clock is only applied to a maximum of two cores under load, the turbo clock for load on all cores is lower. Using XFR (Extended Frequency Range), the processor can increase the clock speed in 25 MHz steps even beyond the turbo clock with sufficient cooling and load on just two cores.
With the 2nd generation (Zen +) and production in the 12 nm process, clockability and power consumption have been improved. In conjunction with the XFR2, the turbo clock is no longer only applied to two cores, but to all cores depending on the temperature and power budget. There is no indication of how much multi-cycle is possible. However, there is an almost linear clock distribution depending on the number of busy cores over the base clock.
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
XFR | L3 cache |
TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 1700 | 8/16 | 3.0 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 3.75 GHz | 16 MB | 65 W |
| Ryzen 7 2700 | 3.2 GHz (4.1 GHz) | XFR2 | |||
| Ryzen 7 1700X | 3.4 GHz (3.8 GHz) | 3.90 GHz | 95 W | ||
| Ryzen 7 1800X | 3.6 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 4.10 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 7 2700X | 3.7 GHz (4.3 GHz) | XFR2 | 105 W |
Ryzen 5
The first four available Ryzen 5 models came on April 11, 2017 at prices between 189 and 279 euros. The Ryzen 5 1600X model has six cores and has the same clock frequencies as the Ryzen 7 1800X model; the Ryzen 5 1500X model has four cores. The Ryzen 2500X is only available to OEMs. The Ryzen 5 1600 is available in two versions: OPNB (Ordering Part Number Boxed) YD1600BBAEBOX is based on the Zen microarchitecture and a version YD1600BBAFBOX released in September 2019 uses the Zen + microarchitecture and is therefore faster.
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
XFR | L3 cache |
TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 1400 | 4/8 | 3.2 GHz (3.4 GHz) | 3.45 GHz | 8 MB | 65 W |
| Ryzen 5 1500X | 3.5 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 3.90 GHz | 16 MB | ||
| Ryzen 5 2500X | 3.6 GHz (3.7 GHz) | XFR2 | 8 MB | ||
| Ryzen 5 1600 | 6/12 | 3.2 GHz (3.6 GHz) | 3.70 GHz | 16 MB | 65 W |
| Ryzen 5 2600 | 3.4 GHz (3.9 GHz) | XFR2 | |||
| Ryzen 5 1600X | 3.6 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 4.10 GHz | 95 W | ||
| Ryzen 5 2600X | 3.6 GHz (4.2 GHz) | XFR2 |
Ryzen 3
The first two models of the Ryzen 3 series came onto the market on July 27, 2017. The Ryzen 3 1200 with a base clock of 3.1 GHz and a turbo clock of 3.4 GHz, as well as the Ryzen 3 1300X with a base clock of 3.5 GHz and a turbo clock of 3.7 GHz, both equipped with four cores and four threads. The only difference between the two is therefore their clock frequencies and the XFR capability. The Ryzen 3 2300X is only available to OEMs. In April 2020, a Zen + version of the Ryzen 3 1200 (Zen: YD1200BBAEBOX; Zen +: YD1200BBAFBOX) analogous to the Ryzen 5 1600 (see above) was released.
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
XFR | L3 cache |
TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 3 1200 | 4/4 | 3.1 GHz (3.4 GHz) | 3.45 GHz | 8 MB | 65 W |
| Ryzen 3 1300X | 3.5 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 3.90 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 3 2300X | 3.5 GHz (4.0 GHz) | XFR2 |
Desktop with graphics unit
Ryzen 5, 3 and Athlon
Ryzen processors with an integrated graphics unit for desktop use ( APU ; "Raven Ridge") were launched on February 12, 2018. A GE version with a reduced clock rate and a lower TDP of 35 W was released on February 10 for each of the two processors. May 2018. In May 2018, a "Pro" version of all desktop processors with a graphics unit came onto the market. Among other things, the Pro models have the option of encrypting the main memory using "Transparent Secure Memory Encryption" (similar to Intel's SGX ) and are therefore primarily aimed at manufacturers of PCs in the business environment.
In the US, the 2200G processors launched for $ 99 and 2400G for $ 149 in February 2018. In view of their good price / performance ratio, the US computer magazine ZDNET said that they would "mess up" the market for cheap personal computers, especially because of their good graphics performance ( "The price points at which AMD is selling these new chips makes them particularly disruptive" ).
In contrast to the CPUs, the APUs of the 3000 class are manufactured in 12nm ( Zen + ; "Picasso") and thus only bring evolutionary improvement. The market launch of the 65W models took place at the same time as the 7nm CPUs from July 7, 2019. On September 30, the Pro models of the 3000 class were announced. The Athlon 3000G announced on November 15, 2019, on the other hand, only belongs to Zen ("Raven Ridge", sometimes called "Raven2" in connection with this APU).
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
XFR | L3 cache |
TDP | GPU | Max. GPU clock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 3400G | 4/8 | 3.7 GHz (4.2 GHz) | XFR2 | 4 MB | 65 W | 11 Vega CUs | 1.4 GHz |
| Ryzen 5 PRO 3400GE | 3.3 GHz (4.0 GHz) | XFR2 | 35 W | 1.3 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 5 2400G | 3.6 GHz (3.9 GHz) | 4.10 GHz | 65 W | 1.25 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 5 2400GE | 3.2 GHz (3.8 GHz) | GHz | 35 W | ||||
| Ryzen 3 3200G | 4/4 | 3.6 GHz (4.0 GHz) | XFR2 | 65 W | 8 Vega CUs | ||
| Ryzen 3 PRO 3200GE | 3.3 GHz (3.8 GHz) | XFR2 | 35 W | 1.2 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 3 2200G | 3.5 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 3.90 GHz | 65 W | 1.1 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 3 2200GE | 3.2 GHz (3.6 GHz) | GHz | 35 W | ||||
| Athlon 240GE | 2/4 | 3.5 GHz | - | 35 W | 3 Vega CUs | 1.0 GHz | |
| Athlon 220GE | 3.4 GHz | ||||||
| Athlon 200GE | 3.2 GHz | ||||||
| Athlon 3000G | 3.5 GHz | ||||||
| Athlon PRO 300GE | 3.4 GHz | 1.1 GHz |
The Pro models in the table are only available as such, in lists of processors supported by ASRock mainboards they have also been or only as normal models since June 2019. With the exception of the Athlons 220GE, 240GE and 3000G, there is also a Pro version of all other APUs that is identical to the data given in the table (see description above). All Ryzen processors with GE suffix and all Pro models are OEM products and are generally not available to end customers.
Mobile desktop with graphics unit
In October 2017, the first variants of the Ryzen processors intended for mobile computers, code-named "Raven Ridge", came onto the market. It is the four-core "Core Complex" already known from the other Ryzen processors with a graphics unit from the Vega graphics cores series integrated via "Infinity Fabric" . Since these processors are only installed by notebook manufacturers, they were de facto not immediately available. The first notebooks with these processors were available in Germany from January 2018.
The processors are competitive with the new Intel generation "Coffee Lake", which was released at the same time, in terms of processor performance as well as graphics performance and energy consumption.
On January 8, 2018, two more processors from the Ryzen 3 series appeared for more affordable mobile devices: The Ryzen 3 models 2300U and 2200U. The first notebooks with the mobile Ryzen 3 model were available in Germany in March 2018. Both processors can process four threads at the same time. The 2300U is a quad core without SMT and the 2200U is a dual core with SMT. The integrated graphics units are also reduced in performance: the 2300U has six Compute Units (CU), the 2200U only three CUs. According to AMD, this is still sufficient to outperform the graphics performance of the comparable Intel processor Core i3-7100U.
At CES 2019, AMD presented the Ryzen Mobile 3000 series (code name "Picasso"). These new models are now based on Zen +, models with a TDP of 35W are now also available, and there is also an entry-level model under the Athlon brand.
At CES 2020, AMD presented two more entry-level models "Athlon Gold" and "Athlon Silver". Zen processors with only 6W TDP also appeared for the first time in January 2020. The 3020e debuted in Lenovo Education school laptops this summer and is unbranded. An Athlon Silver with this TDP was also presented, as well as a Ryzen 3 3250U, whose technical data are identical to the 3200U. In the summer, the model 3015e appeared with a trimmed memory controller (single channel, max. DDR4-1600) and a low graphics clock.
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
L3 cache |
TDP | GPU | Max. GPU clock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 3750H | 4/8 | 2.3 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 4 MB | 35 W | 10 Vega CUs | 1.4 GHz |
| Ryzen 7 2800H | 3.3 GHz (3.8 GHz) | 45 W | 11 Vega CUs | 1.3 GHz | ||
| Ryzen 7 3780U | 2.3 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 15 W | 1.4 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 7 3700U | 2.3 GHz (4.0 GHz) | 10 Vega CUs | 1.4 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 7 2700U | 2.2 GHz (3.8 GHz) | 1.3 GHz | ||||
| Ryzen 5 3550H | 2.1 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 35 W | 8 Vega CUs | 1.2 GHz | ||
| Ryzen 5 2600H | 3.2 GHz (3.6 GHz) | 45 W | 1.1 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 5 3580U | 2.1 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 15 W | 9 Vega CUs | 1.3 GHz | ||
| Ryzen 5 3500U | 2.1 GHz (3.7 GHz) | 8 Vega CUs | 1.2 GHz | |||
| Ryzen 5 2500U | 2.0 GHz (3.6 GHz) | 1.1 GHz | ||||
| Ryzen 3 3300U | 4/4 | 2.1 GHz (3.5 GHz) | 6 Vega CUs | 1.2 GHz | ||
| Ryzen 3 2300U | 2.0 GHz (3.4 GHz) | 1.2 GHz | ||||
| Ryzen 3 3200U / 3250U | 2/4 | 2.6 GHz (3.5 GHz) | 3 Vega CUs | 1.2 GHz | ||
| Ryzen 3 2200U | 2.5 GHz (3.4 GHz) | 1.1 GHz | ||||
| Athlon Gold 3150U | 2.6 GHz (3.3 GHz) | 1.0 GHz | ||||
| Athlon 300U | 2.4 GHz (3.3 GHz) | 1.0 GHz | ||||
| Athlon Silver 3050U | 2/2 | 2.3 GHz (3.2 GHz) | 2 Vega CUs | 1.1 GHz | ||
| Athlon Silver 3050e | 2/4 | unknown (2.8 GHz) | 6 W | 3 Vega CUs | 1.0 GHz | |
| 3020e | 2/2 | 1.2 GHz (2.6 GHz) | ||||
| 3015e | 2/4 | 1.2 GHz (2.3 GHz) | 0.6 GHz |
Embedded with graphics unit
Ryzen V1000
In February 2018, AMD will be releasing another series of embedded processors, the Ryzen V1000 variants, in addition to the Epyc 3000 embedded server processors. They essentially correspond (except for the BGA solder base) to the Raven Ridge APUs. They are intended for embedded systems that include graphics applications, such as gaming machines or medical visualization applications. Long availability is promised, there will also be motherboards for the processors on the release date , the CPU package comes with a solder base called FP4 BGA package (37 mm × 29 mm, 0.8 mm pitch).
| model | Cores / threads |
Basic / (turbo clock) |
L2 cache |
L3 cache |
TDP (CPU) |
GPU | Sha of |
Max. GPU clock |
Working memory |
TDP (GPU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen V1807B | 4/8 | 3.35 GHz (3.8 GHz) | 2 MB | 4 MB | 35-54 W. | 11 Vega CUs | 704 | 1.3 GHz | 2 × DDR4- 3200 |
45 W |
| Ryzen V1756B | 4/8 | 3.25 GHz (3.6 GHz) | 2 MB | 8 Vega CUs | 512 | 1.3 GHz | ||||
| Ryzen V1605B | 4/8 | 2.00 GHz (3.6 GHz) | 2 MB | 15 W | 8 Vega CUs | 512 | 1.1 GHz | 2 × DDR4- 2400 |
12-25 W. | |
| Ryzen V1202B | 2/4 | 2.30 GHz (3.2 GHz) | 1 MB | 3 Vega CUs | 192 | 1.0 GHz |
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ Jeff Kampman: AMD gives us our first real moment of Zen. Tech Report, August 18, 2016, accessed August 18, 2016 .
- ↑ Christian Hirsch: AMD Ryzen 7 1800X: High-end processor for half the money. In: heise online. March 2, 2017. Retrieved March 3, 2017 .
- ↑ AMD Ryzen 3 2200G and Ryzen 5 2400G: Combination processors with Vega graphics. heise online, accessed on February 19, 2018 (German).
- ↑ Christof Windeck: AMD Ryzen 2000: Even better processors. heise online, April 19, 2018, accessed on June 18, 2018 .
- ↑ Weekend tech reading: AMD 'Zen' and their return to high-end CPUs, tracking Windows pirates . TechSpot. Retrieved May 12, 2015.
- ↑ AMD: Zen chips headed to desktops, servers in 2016 . The Tech Report. Retrieved May 12, 2015.
- ↑ a b Anton Shilov: AMD: 'Bulldozer' was not a game-changer, but next-gen 'Zen' will be . In: KitGuru , September 11, 2014. Retrieved February 1, 2015.
- ↑ AMD 2015 comeback attempt: reforming high-performance processor, abandon modular architecture. . Extreme performance review. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ↑ Peter Bright: AMD's moment of Zen: Finally, an architecture that can compete. In: Ars Technica . March 2, 2017. Retrieved December 9, 2017 .
- ↑ Sebastian Pop: 14nm AMD Zen CPU Will Have DDR4 and Simultaneous Multithreading. In: Softpedia News. January 8, 2015, accessed December 9, 2017 .
- ↑ AMD's next-gen Zen CPU due in 2016 . PC gamer. Retrieved May 12, 2015.
- ↑ First benchmarks for AMD Ryzen Threadripper. Retrieved May 31, 2017 .
- ↑ First motherboard for AMD Ryzen Threadripper. Retrieved May 31, 2017 .
- ↑ Marc Sauter: RAM overclocking tested: Ryzen benefits from DDR4-3200 and dual rank. In: Golem. Retrieved December 9, 2017 .
- ↑ Mark Mantel: AMD Ryzen 2000: Maximum RAM clock rates hardly seem to increase. In: pcgameshardware. Retrieved October 7, 2019 .
- ↑ Jim Keller Talks About AMD's Upcoming Zen And K12 Cores on YouTube
- ↑ Jim Keller Leaves AMD . anandtech.com. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
- ↑ Ryan Smith: AMD's 2016–2017 x86 Roadmap: Zen Is In, Skybridge Is Out. In: AnandTech. May 6, 2015, accessed December 11, 2017 .
- ↑ Mark Campbell: AMD Tests Zen CPUs, "Met All Expectation" with no "Significant Bottlenecks" found. In: Overclock3D. Time To Live Media, November 6, 2015, accessed December 9, 2017 .
- ↑ Joel Hruska: Global Foundries announces 14 nm validation with AMD Zen silicon. In: ExtremeTech. November 6, 2015, accessed December 9, 2017 .
- ^ Joel Hruska: Report: AMD Stealing Significant Market Share, Revenue from Intel. In: ExtremeTech. September 6, 2017. Retrieved November 6, 2017 .
- ↑ AMD Epyc The first server motherboards from Supermicro and Tyan. In: heise.de. Retrieved June 27, 2017 .
- ↑ http://www.amd.com/Documents/3000-Family-Product-Brief.pdf
- ↑ https://www.golem.de/news/ryzen-v1000-und-epyc-3000-amd-bringt-zen-architektur-fuer-den-embedded-markt-1802-132876.html
- ↑ https://www.computerbase.de/2018-02/amd-epyc-embedded-3000-ryzen-v1000/
- ↑ AMD Corporate: Ryzen Onslaught Continues with R ... | Community. Retrieved July 16, 2017 .
- ↑ Christof Windeck: AMD: Is Ryzen 9 just around the corner ?. In: Heise online . May 16, 2017 . Retrieved May 31, 2017.
- ↑ Christof Windeck: AMD promises Ryzen Threadripper with 16 cores. In: Heise online . 17th May 2017 . Retrieved May 31, 2017.
- ↑ AMD Ryzen Threadripper official: 16 cores with up to 4.0 GHz come for 999 US dollars. Retrieved July 19, 2017 .
- ↑ What you should know about AMD Zen. In: Hardwareschotte.de. Retrieved March 2, 2017 .
- ↑ Volker Rißka: AMD Ryzen 7 1800X, 1700X, 1700 in the test: king in applications, prince in games. ComputerBase, March 3, 2017, accessed April 12, 2017 .
- ↑ Volker Rißka: AMD Ryzen 2000 in the test: Ryzen 5 2600 in games faster than Ryzen 7 1800X. ComputerBase, April 19, 2018, accessed May 5, 2018 .
- ↑ The-Khoa Nguyen: Ryzen 5 Release: Sales start - prices from 189 to 279 euros. In: pc magazine. April 11, 2017. Retrieved December 9, 2017 .
- ↑ heise online: AMD Ryzen disappoints the stock market; 4- and 6-core types announced. March 3, 2017, accessed March 3, 2017 .
- ↑ Zen +: AMD sells Ryzen 5 1600 with faster CPU cores - Golem.de. Accessed January 2, 2020 (German).
- ↑ AMD Ryzen with Radeon Vega graphics will redefine desktop PCs , article on zdnet.com from February 12, 2018, accessed on February 13, 2018.
- ↑ 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen ™ 3 2200GE Desktop Processor | AMD. Retrieved May 20, 2018 .
- ↑ AMD Ryzen ™ 3 PRO 2200GE Processor with Radeon ™ Vega 8 Graphics | AMD. Retrieved May 20, 2018 .
- ↑ https://www.golem.de/news/ryzen-pro-amd-bringt-core-i-vpro-konkurrenten-mit-vielen-kernen-1706-128638.html
- ^ Adrian Kingsley-Hughes: AMD Ryzen with Radeon Vega graphics will redefine desktop PCs | ZDNet . In: ZDNet . ( zdnet.com [accessed February 19, 2018]).
- ↑ AMD's power-saving APUs “Picasso” Ryzen 3 3200GE and Ryzen 5 3400GE. In: Planet 3DNow! Retrieved November 12, 2019 .
- ↑ Ryzen Mobile AMD's big step back into the notebook market. Retrieved October 30, 2017 .
- ↑ Heise online: Acer Swift 3 SF315-41-R4W1 (NX.GV7EV.001) | heise online price comparison / Germany. Retrieved January 8, 2018 .
- ↑ Heise online: HP Envy x360 15-bq102ng (3DL75EA # ABD) | heise online price comparison / Germany. Retrieved January 22, 2018 .
- ↑ heise online: AMD brings new Ryzen processors for notebooks and desktop PCs. Retrieved January 27, 2018 (German).
- ↑ heise online: Acer Aspire 3 A315-41-R3AZ (NX.GY9EV.004) | heise online price comparison / Germany. Retrieved February 19, 2018 .
- ↑ heise online: AMD brings new Ryzen processors for notebooks and desktop PCs. Retrieved January 27, 2018 (German).
- ↑ anandtech: AMD at CES 2019: Ryzen Mobile 3000-Series Launched, 2nd Gen Mobile at 15W and 35W, and Chromebooks. Retrieved March 1, 2019 (American English).
- ↑ heise online: AMD launches Athlon Gold and Silver. Retrieved January 8, 2020 .
- ↑ Benjamin Gründken: AMD 3015e and 3020e: Zen APUs with only 6 watts TDP. In: PCGH. August 5, 2020, accessed August 6, 2020 .
- ↑ Volker Rißka: Epyc 3000 / Ryzen V1000: AMD brings Zen with 16 cores and Vega for embedded. ComputerBase, February 21, 2018, accessed May 11, 2018 .
- ↑ http://www.amd.com/Documents/V1000-Family-Product-Brief.pdf