Caribbean community
| Caribbean Community CARICOM |
|
|---|---|
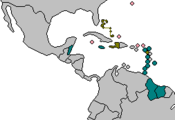
 Member States of CARICOM |
|
| English name | Caribbean Community and Common Market |
| Organization type | Regional cooperation |
| Seat of the organs |
Georgetown , Guyana |
| Chair | changing irregularly |
| Secretary General |
|
| Member States |
15th |
| Associate members |
5 |
| Official and working languages | |
| surface | 462,902 km² excluding mainland: 61,146 km² |
| population | approx. 16.8 million (2010) excluding mainland: 15.2 million |
| Population density | 36.3 inhabitants per km² (2010) excluding mainland: 248.6 inhabitants per km² |
| gross domestic product | US $ 76,620 million (estimate, 2013) |
| Gross domestic product per inhabitant | 4,560 US $ (estimate, 2013) |
| founding |
1st August 1973 |
| Currencies |
East Caribbean Dollar (XCD) and 8 more
|
| Time zone | UTC − 5 to UTC − 3 |
| www.caricom.org | |
The Caribbean Community (English Caribbean Community and Common Market , CARICOM) is an international organization in the Caribbean area, based in Guyana's capital, Georgetown .
history
CARICOM was founded on July 4th 1973 as a result of 15 years of negotiations by the Treaty of Chaguaramas , which came into force on August 1st of the same year. The first four signatory states were Barbados , Jamaica , Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago . Was predecessor of the Caribbean Free Trade Association CARIFTA (Caribbean Free Trade Area) between 1968 and 1974. With the establishment of the CARICOM began at the EC -oriented transformation of a free trade area to a more intense structured community that not only economic cooperation aims. A year later, seven more states and Montserrat joined the organization. The Bahamas joined in 1984, Suriname in 1999 and Haiti followed in 2002 , the last member for the time being. In 2001 the heads of government signed a new treaty of Chaguaramas (Trinidad) , with which a Caribbean community was established. Since February 23, 2010, this has again been part of the much larger Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC).
General Secretaries
The Caribbean Community has had the following General Secretaries since its inception:
| Term of office | General Secretaries | Member State |
|---|---|---|
| 1973-1974 | William Demas |
|
| 1974-1977 | Sir Alister McIntyre |
|
| 1977-1988 | Joseph Tyndall (acting) |
|
| 1978-1983 | Kurleigh King |
|
| 1983-1992 | Roderick Rainford |
|
| 1992-2010 | Edwin W. Carrington |
|
| 2010-2011 | Lolita Applewhaite (acting) |
|
| since 2011 | Irwin LaRocque |
|
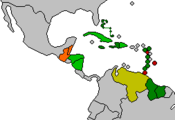
Members
Full members
Full members are the following 14 states and 1 British overseas territory :
| location | Country | accession | GDP in million US $ (2007) |
GDP in million US $ (2013) |
Economic growth (2013) |
Government debt ratio (2011) |
Corruption (2013) |
Petrocaribe | CSME | CARICOM passport | CARIPASS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
1973 | 3,739 | 4,262 | −0.75% | 68 | 75 | - | 2006 | Yes | Yes |

|
|
1973 | 1,039 | 3,020 | 5.33% | - | 27 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |
|
|
1973 | 11.206 | 14,389 | 0.42% | 140 | 38 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |

|
|
1973 | 20,700 | 27,130 | 1.62% | 32 | 38 | - | 2006 | Yes | Yes |
|
|
1974 | 1,089 | 1,220 | 1.65% | 93 | - | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |

|
|
1974 | 1,274 | 1,637 | 2.50% | 83 | - | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | No |

|
|
1974 | 311 | 495 | 1.14% | 70 | 58 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |

|
|
1974 | 590 | 811 | 0.80% | 104 | - | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |
|
|
1974 | 43.8 PPP- $ (2006 estimate) | - (see GB ) | - (see GB ) | - (see GB ) | - (see GB ) | - | - (applied for in 2006) | No | No |
|
|
1974 | 527 | 767 | 1.92% | 154 | - | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |

|
|
1974 | 958 | 1,377 | 0.21% | 70 | 71 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |
|
|
1974 | 559 | 742 | 1.26% | 68 | 62 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | Yes |
|
|
1983 | 6,586 | 8,373 | 1.90% | 50 | 71 | 2005 | - | No | No |

|
|
1995 | 1,345 (2005) |
5,009 | 4.68% | 19th | 36 | 2005 | 2006 | Yes | No |

|
|
2002 | 5,435 | 7,388 | 8.98% | 12 | 19th | 2007 | - | No | No |
Associate members
Associate members are the following 5 UK overseas territories:
| location | area | accession |
|---|---|---|

|
|
1991 |

|
|
1991 |

|
|
1999 |
|
|
2002 |

|
|
2003 |
observer
The following 5 countries have observer status:
| location | area |
|---|---|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
aims
- Common Caribbean Market (CSME) members
- CARICOM members who do not participate in the Common Caribbean Market
- Associated States
- Members with a CARICOM passport
- Members without a CARICOM passport
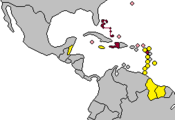
- Associated States
- Venezuela
- Member countries of Petrocaribe and CARICOM
- Members of Petrocaribe, not part of CARICOM
- Members of CARICOM, not part of Petrocaribe
The aim of CARICOM is the coordination of foreign policy and cooperation in the areas of health and social affairs, education, culture and sport, science and technology. The Common Caribbean Market (English Caribbean Single Market and Economy , CSME ) was created for economic integration . It forms a customs union with a uniform external tariff. In addition, there are double taxation agreements and cooperations in the field of development planning and the promotion of industrialization between the countries . The CSME has been in force since January 1, 2006. In 2013, 13 out of 15 CARICOM member states participated in the Community market .
In addition, CARICOM has introduced a uniform passport, which was issued by 12 of the 15 CARICOM countries in 2009, i. H. not in the Bahamas, Haiti and Montserrat. In 2010 this was expanded to include the CARIPASS , a kind of identity card that ten full members have so far been using.
This was preceded by the Petrocaribe Agreement , which was signed in 2005 by 11 CARICOM countries under the leadership of Venezuela . It allows only 40% of oil deliveries from Venezuela to be paid for within 90 days at a market price of over 100 US dollars. The rest can be owed over 25 years at an interest rate of 1%. The aim of this contract is to jointly develop, promote and process crude oil and natural gas, as well as to create a network of petroleum industrial plants, through which the supply of the region is to be guaranteed in the long term.
Characteristic and meaning
With an area of almost 0.5 million km² and almost 17 million inhabitants, the dimensions of CARICOM are roughly comparable to those of Cameroon . In contrast to “market giants” such as the EU or ASEAN, it is relatively manageable in terms of population, territorial expansion and economic power , but its member states are sometimes heterogeneously structured and thus by no means protected from difficulties in development and progress. With around 58% of the total population, Haiti is a heavyweight in this regard, followed by Jamaica with around 17% and Trinidad and Tobago with around 8%. Whereas most of the land mass of CARICOM falls on the South American mainland , on the one hand through Guyana with around 46% and on the other hand through Suriname with around 35%. The latter two states are parallel members of the Union of South American Nations (UNASUR). In addition, all CARICOM states except Montserrat belong to the Association of Caribbean States (ACS).
In half of the members, the East Caribbean dollar is the official currency, the exchange rate of which has been linked to the US $ at a rate of 2.7 to 1 for decades. The other half uses other forms of the dollar. Most states are considered to be low-income developing countries . Some, on the other hand, have more of the characteristics of an emerging market . With a human development index of 0.456, Haiti is the poorest country on the entire American continent , while Barbados has the clearly highest CARICOM value and the lowest corruption with 0.825 . In addition, Trinidad and Tobago accounts for a good 32% of the gross regional product (total GDP ), followed by Jamaica with just under 16%. While Jamaica and St. Kitts and Nevis have one of the highest national debt ratios in the world with well over 100% , Suriname with 19% and Haiti with 12% have one of the lowest.
The whole region has in common its colonial past through European conquerors, above all Great Britain and France , but also through the Netherlands . A cultural peculiarity is Creole , which emerged from the mixing of Western European and native languages , which is still used sporadically in Haiti with Haitian and in other island states.
Dark side of the Caribbean "civilization" was for a one-sided orientation of the export structure in favor of European and North American consumers to the need for groceries to cover such as cocoa or sugar. This is still evident today, for example, in the cultivation and sale of so-called " cash crops ", which are usually only processed in the importing country. On the other hand, there is the drastic decline in the population of the indigenous people under Spanish rule . For example, on the central Caribbean island of Hispaniola , on whose west side Haiti lies, the originally resident Indians and their culture u. a. almost completely destroyed due to imported diseases.
Today almost all member states are in direct or indirect British influence, with most of them organized as a Commonwealth Realm . In addition, natural disasters such as hurricanes or earthquakes are currently one of the most significant challenges. Occasional volcanic eruptions can devastate large parts of an island state.
See also
- CARIFORUM , CELAC , ALBA
- List of member states of American organizations
- Permanent representative of Austria to the Caribbean Community
literature
- RA Abdullah Khan: The Caribbean Court of Justice and Referrals from National Courts: Unavoidable Supremacy? In: Griffin's View on International and Comparative Law. 5, 1, 2004, pp. 26–31, http://www.rechte.vu.nl/nl/organisatie/bureau/transnational-legal-studies/abdullah-khan/publications.asp
Web links
- Official website of CARICOM (English)
- Official website of the CSME (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ List of countries according to gross domestic product
- ↑ List of countries by government debt ratio
- ↑ Amnesty International - Corruption Perceptions Index
- ↑ CIA World Factbook Montserrat (English)