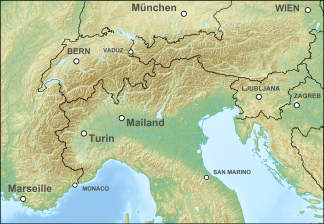
Julian Alps
| Julian Alps | ||
|---|---|---|
| Highest peak | Triglav ( 2864 m. I. J. ) | |
| location |
Friuli-Venezia Giulia ( Italy ) / Upper Carniola ( Slovenia ) |
|
| part of | Southern Limestone Alps | |
| Classification according to | AVE 58 | |
|
|
||
| Coordinates | 46 ° 22 ' N , 13 ° 49' E | |
The Julian Alps (colloquially also Julier ; Slov. Julijske Alpe ; Italian. Alpi Giulie ) are a mountain group of the Southern Limestone Alps , which are divided into the Slovene regions of Upper and Inner Carniola and the Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia .
The name refers to Gaius Julius Caesar , who set up the Municipium Forum Iulii in the Friuli and Western Carniola area . In ancient times , the term "Julian Alps" also included mountains further south; the low mountain ranges of the Ternowaner and the Birnbaumer forest in today's Slovenia were part of it, while today they form independent regions.
nature
The Julian Alps are a very rugged mountain range. The highest mountain is the Triglav (Dreikopf), 2864 m, also the highest mountain in Slovenia and the former Yugoslavia . Kargletscher can be found here and there . The Julian Alps are divided into an eastern and a western group by the Raibler Valley, the Predil Pass and the Koritnica and Soča valleys .
Transitions and traffic
Population and history
The Julian Alps were and are the border between the Slovenian and Friulian language areas. Since they were entirely part of the Habsburg Empire , at least for a time , for the most part for centuries, German gained a foothold in isolated cases, namely in the language island of Zarz and in the Canal Valley .
Italy received a share of the Julian Alps from Austria in 1866 with Friuli .
The tourist development was done by Belshazzar Hacquet , who first ascented Triglav (1778), and above all by Julius Kugy .
In the First World War in the Julian Alps ran a front on which a very grueling trench warfare was conducted, the consequences of which are currently being positions, barbed wire scraps and even dud today. (see Mountain War 1915–1918 )
After the First World War , Italy received most of the Julier, but after the Second World War had to retreat to the watershed between the Tagliamento and Gailitz on this side and the Save and Isonzo on the other. The rest went to Yugoslavia and the Free State of Trieste .
As a result, Italian also gained a foothold in this area, so that it is four languages today.
economy
Today the Julian Alps are showing themselves to be structurally weak. Lead mining in Raibl came to a standstill in the late 20th century, and the decline of agriculture hit such a difficult-to-manage area particularly hard.
Municipalities such as Tarvisio , Ratschach and Kronau live well from small border traffic at the border triangle of Slovenia, Italy and Austria .
Most important peaks of the Julian Alps
- Triglav 2864 m
- Montasch 2754 m
- Škrlatica 2740 m
- Mangart 2677 m
- Jof Fuart 2666 m
- Jalovec 2645 m
- Razor 2602 m
- Kanin 2585 m
- Kanjavec 2568 m
- Prisojnik 2547 m
- Little Mojstrovka 2332 m
- Strug 2265 m
Tourist centers
- Bled ( Veldes ) (summer; casino, lake)
- Bohinj ( week one ) (summer and winter; ski areas )
- Kranjska Gora ( Kronau ) (summer and winter; ski area, casino )
- Rateče ( Ratschach ) ( World Cup hill in Planica )
- Tarvisio (summer and winter)
- Neveasattel (ski area)
literature
- Helmut Lang, Roswitha Ortner: Julian Alps: The most beautiful hikes and mountain tours. (= Rother hiking guide). 5th, revised edition. Bergverlag Rother, Munich 2018, ISBN 978-3-7633-4051-4 .
- Teddy Inthal, Karl Pallasmann: Julian Alps . Verlag Johannes Heyn, Klagenfurt 2007, ISBN 978-3-7084-0246-8 .
- Helmut Teissl: Julian Alps . 2nd, expanded edition. Verlag Mohorjeva-Hermagoras, Klagenfurt 2013, ISBN 978-3-7086-0757-3 .