Kiel-Wik
|
Wik
City of Kiel
Coordinates: 54 ° 21 ′ 20 ″ N , 10 ° 8 ′ 6 ″ E
|
|
|---|---|
| Area : | 7.73 km² |
| Residents : | 18,813 (Dec. 31, 2014) |
| Population density : | 2,435 inhabitants / km² |
| Incorporation : | April 1, 1893 |
| Postal code : | 24106 |
| Area code : | 0431 |
|
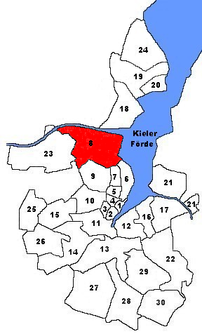
Location of Wik in Kiel
|
|

The Wik district is located in the north of the Schleswig-Holstein state capital, Kiel . In terms of area and with a total population of 18,813 inhabitants, the Wik is the second largest district of Kiel (as of December 31, 2014). Kiel-Wik has a maritime character and is home to the Kiel naval base (Tirpitzhafen) and is the berth for the training ship Gorch Fock .
history
The village of Wik is documented as Kotelwik in 1286. The name indicates semi-Slavic origin and means something like Kesselbucht. But the village was named Wyck as early as 1317. In 1886 negotiations about the incorporation were conducted on the initiative of the rural community Wik. The community was unable to bear the costs of building the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal on its own. Due to the objection of the royal government, the incorporation was delayed and could only take place on April 1, 1893. The Kiel city area increased by 514.43 hectares.
In the years 2007–2009, a bunker built in the Second World War was demolished on the site of the former Technical Marine School (TMS) on Prinz-Heinrich- Strasse.
The district within its limits
The following are the boundaries are starting given the district to the north in a clockwise direction continuously: in the north of the district is by running in east-west direction Kiel Canal limited the east by the Kiel Fjord on the south by Park Street, Niemannsweg, Koesterallee, Düvelsbeker Weg, Belvedere intersection, Paul-Fuß-Straße, Westring, Bundesstraße 76 , Bremerskamp, the green area between Johann-Fleck-Straße and Klausbrooker Weg. In the west, the freight railway line and a zigzag line east of the sports facilities through the Projensdorfer Gehölz form the border of the district.
The neighboring districts in the north, starting in a clockwise direction: to the north is the district of Holtenau , which also includes the canal; to the south, the districts of Düsternbrook , Blücherplatz and Ravensberg, as well as the municipality of Kronshagen . In the west, Wik borders the Suchsdorf district.
The Steenbek-Projensdorf district is part of the Wik district. The border forms from the Holtenauer Hochbrücken to the south running federal road 503 to the tunnel intersection with the Steenbeker Weg and from there on to Projensdorfer Straße and Westring.
The Klausbrook settlement is located between Projensdorf and Suchsdorf, a residential area that was created in the late 1980s. The streets there are named after professors from Kiel. The Martinsgemeinde merged in 2008 with the Oster- und Petrus-Nord-Gemeinde to form the Emmausgemeinde and maintained a second community center here until 2009.
Canal crossing
Four high bridges lead over the canal in Kiel. Two in the Wik and two in Suchsdorf . For a crossing by bike or on foot, a ferry connection was already used in the days of the canal construction. The crossing has always been free of charge, a corresponding law for free crossing was already passed by the builder of the canal, Kaiser Wilhelm I (completion and inauguration by Kaiser Wilhelm II ), as it is an unnatural landscape obstacle. The Wik – Holtenau ferry is operated by the Adler I , which is 14 meters long and 5 meters wide . The vehicle, which can accommodate up to 49 people and around 24 bicycles, transports 3000–4000 passengers daily on the 3-5 minute journey from one bank to the other during the summer months; in winter it is only up to 1000.
education
The following educational institutions are located in the district:
- Hebbelschule (grammar school) - The school was founded in 1902 as the “Städtische Realschule Kiel” (exclusively for boys) and at that time used premises in Waitzstrasse. In 1903 it was renamed "Oberrealschule I" and in 1922 renamed Hebbelschule after the poet Friedrich Hebbel . In 1944 the buildings were badly damaged, so that lessons from 1945 to 1958 took place in the rooms of the Ricarda Huch School . In 1958 the current location on Feldstrasse was moved. Boys and girls have been attending this school since 1971. The premises are under monument protection.
- Timm-Kröger Regional School - The school was created in 2010 from the merger of the Timm-Kröger Realschule and the elementary and secondary school Peter Petersen School.
- School on Sonderburger Platz (primary school)
- Ernst-Barlach -Gymnasium ( Steenbek-Projensdorf )
Sports facilities
- Holstein Stadium , home stadium of the Kiel football club Holstein Kiel
- Timmerberg sports complex. Home of Wiker SV
Buildings
In Kiel-Wik there was a thermal power station with two 110 meter high chimneys until 1994/1995. To the south of the locks at 54.363846 ° N 10.143865 ° E there is a steel truss mast braced in three levels. In 2012 the lock park was inaugurated, in which the Wiker balcony is located, a 2.30 meter high viewing platform that allows a view of the Kiel Canal, locks and fjord.
traffic
Kiel-Wik is on the in rail freight traffic railway Suchsdorf-Wik .
See also
Web links
- Kiel district Wik in Stadtwiki Kiel
Individual evidence
- ↑ The population in the Kiel districts in 2014 . (PDF) State capital Kiel
- ↑ Vera Stoy: Kiel on the way to the big city, Kiel 2003
- ↑ kiel.de
- ↑ a b Statistical report of the Kiel districts 2008 by the city of Kiel ( Memento of the original from November 25, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b City map of the city of Kiel published by the city of Kiel with detailed district boundaries
- ↑ Kiel Street Lexicon. Retrieved May 5, 2020 .
- ↑ Peter Kleinort: With the shoe box across the canal . In: Daily port report from October 6, 2016, p. 14